You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002453_01055
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002453_01055
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
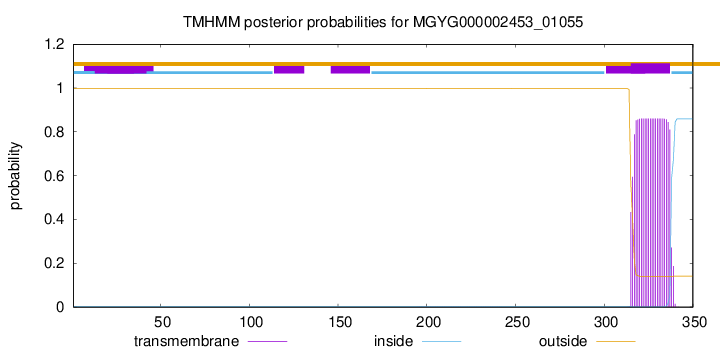
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Akkermansia muciniphila_B | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Verrucomicrobiota; Verrucomicrobiae; Verrucomicrobiales; Akkermansiaceae; Akkermansia; Akkermansia muciniphila_B | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002453_01055 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT2 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 185640; End: 186692 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT2 | 10 | 134 | 7.2e-18 | 0.711764705882353 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd00761 | Glyco_tranf_GTA_type | 1.71e-19 | 11 | 162 | 2 | 152 | Glycosyltransferase family A (GT-A) includes diverse families of glycosyl transferases with a common GT-A type structural fold. Glycosyltransferases (GTs) are enzymes that synthesize oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and glycoconjugates by transferring the sugar moiety from an activated nucleotide-sugar donor to an acceptor molecule, which may be a growing oligosaccharide, a lipid, or a protein. Based on the stereochemistry of the donor and acceptor molecules, GTs are classified as either retaining or inverting enzymes. To date, all GT structures adopt one of two possible folds, termed GT-A fold and GT-B fold. This hierarchy includes diverse families of glycosyl transferases with a common GT-A type structural fold, which has two tightly associated beta/alpha/beta domains that tend to form a continuous central sheet of at least eight beta-strands. The majority of the proteins in this superfamily are Glycosyltransferase family 2 (GT-2) proteins. But it also includes families GT-43, GT-6, GT-8, GT13 and GT-7; which are evolutionarily related to GT-2 and share structure similarities. |
| pfam00535 | Glycos_transf_2 | 3.32e-17 | 10 | 178 | 1 | 163 | Glycosyl transferase family 2. Diverse family, transferring sugar from UDP-glucose, UDP-N-acetyl- galactosamine, GDP-mannose or CDP-abequose, to a range of substrates including cellulose, dolichol phosphate and teichoic acids. |
| cd04196 | GT_2_like_d | 3.64e-15 | 10 | 216 | 1 | 202 | Subfamily of Glycosyltransferase Family GT2 of unknown function. GT-2 includes diverse families of glycosyltransferases with a common GT-A type structural fold, which has two tightly associated beta/alpha/beta domains that tend to form a continuous central sheet of at least eight beta-strands. These are enzymes that catalyze the transfer of sugar moieties from activated donor molecules to specific acceptor molecules, forming glycosidic bonds. Glycosyltransferases have been classified into more than 90 distinct sequence based families. |
| cd06423 | CESA_like | 3.99e-15 | 11 | 133 | 1 | 119 | CESA_like is the cellulose synthase superfamily. The cellulose synthase (CESA) superfamily includes a wide variety of glycosyltransferase family 2 enzymes that share the common characteristic of catalyzing the elongation of polysaccharide chains. The members include cellulose synthase catalytic subunit, chitin synthase, glucan biosynthesis protein and other families of CESA-like proteins. Cellulose synthase catalyzes the polymerization reaction of cellulose, an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues in plants, most algae, some bacteria and fungi, and even some animals. In bacteria, algae and lower eukaryotes, there is a second unrelated type of cellulose synthase (Type II), which produces acylated cellulose, a derivative of cellulose. Chitin synthase catalyzes the incorporation of GlcNAc from substrate UDP-GlcNAc into chitin, which is a linear homopolymer of beta-(1,4)-linked GlcNAc residues and Glucan Biosynthesis protein catalyzes the elongation of beta-1,2 polyglucose chains of Glucan. |
| COG0463 | WcaA | 8.66e-15 | 5 | 107 | 1 | 99 | Glycosyltransferase involved in cell wall bisynthesis [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QWP03674.1 | 4.33e-261 | 1 | 350 | 1 | 350 |
| QWP61548.1 | 4.33e-261 | 1 | 350 | 1 | 350 |
| QWP22345.1 | 4.33e-261 | 1 | 350 | 1 | 350 |
| QWP27465.1 | 4.33e-261 | 1 | 350 | 1 | 350 |
| QWP54369.1 | 4.33e-261 | 1 | 350 | 1 | 350 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P71054 | 8.38e-15 | 7 | 232 | 5 | 233 | Putative glycosyltransferase EpsE OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=epsE PE=2 SV=2 |
| P64864 | 4.15e-09 | 9 | 143 | 1 | 134 | Uncharacterized protein Mb1547 OS=Mycobacterium bovis (strain ATCC BAA-935 / AF2122/97) OX=233413 GN=BQ2027_MB1547 PE=4 SV=1 |
| P9WLV4 | 4.15e-09 | 9 | 143 | 1 | 134 | Uncharacterized protein MT1570 OS=Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain CDC 1551 / Oshkosh) OX=83331 GN=MT1570 PE=4 SV=1 |
| P9WLV5 | 4.15e-09 | 9 | 143 | 1 | 134 | Uncharacterized protein Rv1520 OS=Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv) OX=83332 GN=Rv1520 PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q67FW5 | 5.89e-09 | 9 | 123 | 20 | 137 | UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=B3GNTL1 PE=2 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
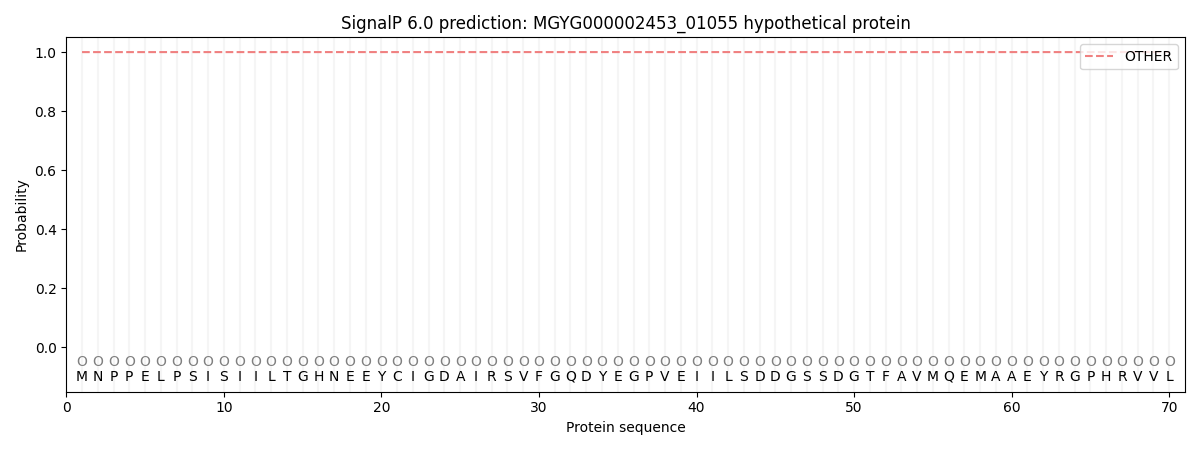
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.000055 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |