You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003138_00040
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003138_00040
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
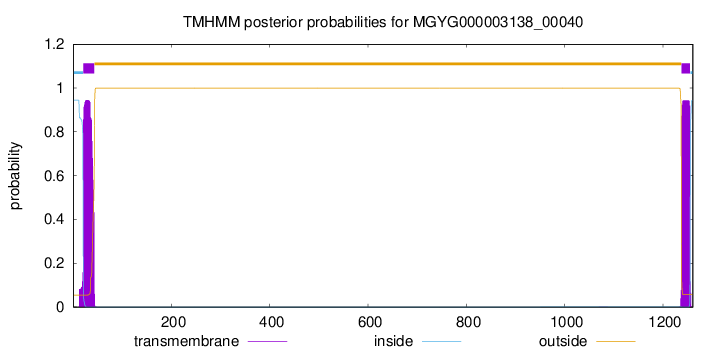
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Streptococcus pseudopneumoniae_O | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Lactobacillales; Streptococcaceae; Streptococcus; Streptococcus pseudopneumoniae_O | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003138_00040 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM41 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Glycogen debranching enzyme | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 44002; End: 47787 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH13 | 620 | 956 | 5.2e-130 | 0.9964788732394366 |
| CBM41 | 252 | 356 | 1.9e-26 | 0.9803921568627451 |
| CBM41 | 143 | 246 | 6.1e-24 | 0.9803921568627451 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIGR02102 | pullulan_Gpos | 0.0 | 140 | 1243 | 1 | 1095 | pullulanase, extracellular, Gram-positive. Pullulan is an unusual, industrially important polysaccharide in which short alpha-1,4 chains (maltotriose) are connected in alpha-1,6 linkages. Enzymes that cleave alpha-1,6 linkages in pullulan and release maltotriose are called pullulanases although pullulan itself may not be the natural substrate. In contrast, a glycogen debranching enzyme such GlgX, homologous to this family, can release glucose at alpha,1-6 linkages from glycogen first subjected to limit degradation by phosphorylase. Characterized members of this family include a surface-located pullulanase from Streptococcus pneumoniae () and an extracellular bifunctional amylase/pullulanase with C-terminal pullulanase activity (. |
| COG1523 | PulA | 0.0 | 386 | 1147 | 1 | 696 | Pullulanase/glycogen debranching enzyme [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| cd11341 | AmyAc_Pullulanase_LD-like | 1.08e-165 | 593 | 1035 | 1 | 406 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in Pullulanase (also called dextrinase; alpha-dextrin endo-1,6-alpha glucosidase), limit dextrinase, and related proteins. Pullulanase is an enzyme with action similar to that of isoamylase; it cleaves 1,6-alpha-glucosidic linkages in pullulan, amylopectin, and glycogen, and in alpha-and beta-amylase limit-dextrins of amylopectin and glycogen. Pullulanases are very similar to limit dextrinases, although they differ in their action on glycogen and the rate of hydrolysis of limit dextrins. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| TIGR02104 | pulA_typeI | 3.10e-128 | 449 | 1118 | 3 | 602 | pullulanase, type I. Pullulan is an unusual, industrially important polysaccharide in which short alpha-1,4 chains (maltotriose) are connected in alpha-1,6 linkages. Enzymes that cleave alpha-1,6 linkages in pullulan and release maltotriose are called pullulanases although pullulan itself may not be the natural substrate. This family consists of pullulanases related to the subfamilies described in TIGR02102 and TIGR02103 but having a different domain architecture with shorter sequences. Members are called type I pullulanases. |
| TIGR02103 | pullul_strch | 2.57e-78 | 442 | 1053 | 110 | 800 | alpha-1,6-glucosidases, pullulanase-type. Members of this protein family include secreted (or membrane-anchored) pullulanases of Gram-negative bacteria and pullulanase-type starch debranching enzymes of plants. Both enzymes hydrolyze alpha-1,6 glycosidic linkages. Pullulan is an unusual, industrially important polysaccharide in which short alpha-1,4 chains (maltotriose) are connected in alpha-1,6 linkages. Enzymes that cleave alpha-1,6 linkages in pullulan and release maltotriose are called pullulanases although pullulan itself may not be the natural substrate. This family is closely homologous to, but architecturally different from, the Gram-positive pullulanases of Gram-positive bacteria (TIGR02102). [Energy metabolism, Biosynthesis and degradation of polysaccharides] |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AYF94996.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 1261 | 1 | 1261 |
| QQQ35148.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 1261 | 1 | 1261 |
| QKL33807.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 1261 | 1 | 1261 |
| CBJ23088.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 1261 | 1 | 1298 |
| BBP10455.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 1261 | 3 | 1304 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3FAW_A | 0.0 | 324 | 1202 | 1 | 862 | CrystalStructure of the Group B Streptococcus Pullulanase SAP [Streptococcus agalactiae COH1],3FAX_A The crystal structure of GBS pullulanase SAP in complex with maltotetraose [Streptococcus agalactiae COH1] |
| 2YA0_A | 0.0 | 444 | 1151 | 1 | 708 | CatalyticModule of the Multi-modular glycogen-degrading pneumococcal virulence factor SpuA [Streptococcus pneumoniae TIGR4] |
| 2YA1_A | 0.0 | 141 | 1149 | 5 | 1013 | Productcomplex of a multi-modular glycogen-degrading pneumococcal virulence factor SpuA [Streptococcus pneumoniae TIGR4] |
| 2YA2_A | 0.0 | 443 | 1149 | 1 | 707 | CatalyticModule of the Multi-modular glycogen-degrading pneumococcal virulence factor SpuA in complex with an inhibitor. [Streptococcus pneumoniae TIGR4] |
| 2J44_A | 1.68e-140 | 142 | 360 | 1 | 217 | Alpha-glucanbinding by a streptococcal virulence factor [Streptococcus pneumoniae] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0A0H2ZL64 | 0.0 | 1 | 1261 | 1 | 1256 | Pullulanase A OS=Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 2 (strain D39 / NCTC 7466) OX=373153 GN=spuA PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q9F930 | 0.0 | 1 | 1261 | 1 | 1287 | Pullulanase A OS=Streptococcus pneumoniae OX=1313 GN=spuA PE=1 SV=1 |
| A0A0H2UNG0 | 0.0 | 1 | 1261 | 1 | 1280 | Pullulanase A OS=Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 4 (strain ATCC BAA-334 / TIGR4) OX=170187 GN=spuA PE=1 SV=1 |
| O33840 | 2.43e-76 | 252 | 1056 | 22 | 766 | Pullulanase OS=Thermotoga maritima (strain ATCC 43589 / DSM 3109 / JCM 10099 / NBRC 100826 / MSB8) OX=243274 GN=pulA PE=1 SV=2 |
| C0SPA0 | 1.48e-58 | 449 | 1058 | 97 | 636 | Pullulanase OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=amyX PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
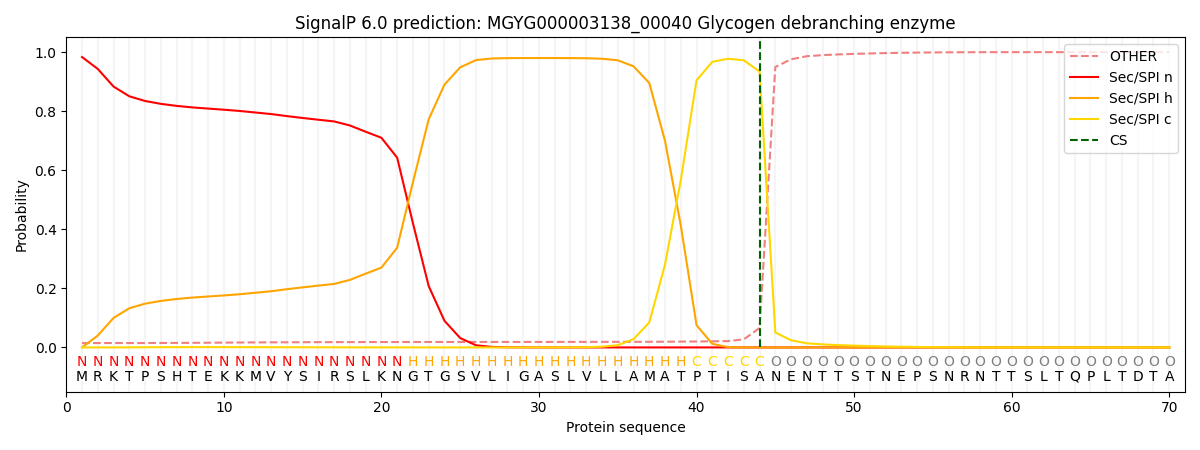
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.016941 | 0.979514 | 0.002730 | 0.000328 | 0.000251 | 0.000228 |