You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003650_00243
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003650_00243
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | UBA1786 sp900771425 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; UBA1786; UBA1786 sp900771425 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003650_00243 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CE6 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Carbohydrate acetyl esterase/feruloyl esterase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 1249; End: 2538 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE6 | 103 | 213 | 2.7e-32 | 0.9797979797979798 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam03629 | SASA | 1.51e-33 | 24 | 288 | 1 | 226 | Carbohydrate esterase, sialic acid-specific acetylesterase. The catalytic triad of this esterase enzyme comprises residues Ser127, His403 and Asp391 in UniProtKB:P70665. |
| cd11294 | E_set_Esterase_like_N | 3.54e-15 | 318 | 393 | 4 | 83 | N-terminal Early set domain associated with the catalytic domain of putative esterases. E or "early" set domains are associated with the catalytic domain of esterase at the N-terminal end. Esterases catalyze the hydrolysis of organic esters to release an alcohol or thiol and acid. The term esterase can be applied to enzymes that hydrolyze carboxylate, phosphate and sulphate esters, but is more often restricted to the first class of substrate. The N-terminal domain of esterase may be related to the immunoglobulin and/or fibronectin type III superfamilies. These domains are associated with different types of catalytic domains at either the N-terminal or C-terminal end and may be involved in homodimeric/tetrameric/dodecameric interactions. Members of this family include members of the alpha amylase family, sialidase, galactose oxidase, cellulase, cellulose, hyaluronate lyase, chitobiase, and chitinase, among others. |
| cd02858 | E_set_Esterase_N | 1.99e-07 | 319 | 376 | 5 | 60 | N-terminal Early set domain associated with the catalytic domain of esterase. E or "early" set domains are associated with the catalytic domain of esterase at the N-terminal end. Esterases catalyze the hydrolysis of organic esters to release an alcohol or thiol and acid. The term esterase can be applied to enzymes that hydrolyze carboxylate, phosphate and sulphate esters, but is more often restricted to the first class of substrate. The N-terminal domain of esterase may be related to the immunoglobulin and/or fibronectin type III superfamilies. These domains are associated with different types of catalytic domains at either the N-terminal or C-terminal end and may be involved in homodimeric/tetrameric/dodecameric interactions. Members of this family include members of the alpha amylase family, sialidase, galactose oxidase, cellulase, cellulose, hyaluronate lyase, chitobiase, and chitinase, among others. |
| cd02859 | E_set_AMPKbeta_like_N | 2.66e-05 | 316 | 376 | 1 | 62 | N-terminal Early set domain, a glycogen binding domain, associated with the catalytic domain of AMP-activated protein kinase beta subunit. E or "early" set domains are associated with the catalytic domain of AMP-activated protein kinase beta subunit glycogen binding domain at the N-terminal end. AMPK is a metabolic stress sensing protein that senses AMP/ATP and has recently been found to act as a glycogen sensor as well. The protein functions as an alpha-beta-gamma heterotrimer. This N-terminal domain is the glycogen binding domain of the beta subunit. This domain is also a member of the CBM48 (Carbohydrate Binding Module 48) family whose members include pullulanase, maltooligosyl trehalose synthase, starch branching enzyme, glycogen branching enzyme, glycogen debranching enzyme, and isoamylase. |
| cd02853 | E_set_MTHase_like_N | 0.001 | 324 | 377 | 17 | 69 | N-terminal Early set domain associated with the catalytic domain of Maltooligosyl trehalose trehalohydrolase (also called Glycosyltrehalose trehalohydrolase) and similar proteins. E or "early" set domains are associated with the catalytic domain of Maltooligosyl trehalose trehalohydrolase (MTHase) and similar proteins at the N-terminal end. This subfamily also includes bacterial alpha amylases and 1,4-alpha-glucan branching enzymes which are highly similar to MTHase. Maltooligosyl trehalose synthase (MTSase) and MTHase work together to produce trehalose. MTSase is responsible for converting the alpha-1,4-glucosidic linkage to an alpha,alpha-1,1-glucosidic linkage at the reducing end of the maltooligosaccharide through an intramolecular transglucosylation reaction, while MTHase hydrolyzes the penultimate alpha-1,4 linkage of the reducing end, resulting in the release of trehalose. The N-terminal domain of MTHase may be related to the immunoglobulin and/or fibronectin type III superfamilies. These domains are associated with different types of catalytic domains at either the N-terminal or C-terminal end and may be involved in homodimeric/tetrameric/dodecameric interactions. Members of this family include members of the alpha amylase family, sialidase, galactose oxidase, cellulase, cellulose, hyaluronate lyase, chitobiase, and chitinase, among others. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCS85270.1 | 1.10e-113 | 2 | 376 | 9 | 374 |
| QDO71517.1 | 3.11e-107 | 22 | 394 | 18 | 380 |
| AVM57872.1 | 3.64e-107 | 17 | 376 | 21 | 368 |
| QUT32423.1 | 4.74e-107 | 22 | 376 | 21 | 364 |
| AVM52697.1 | 7.23e-107 | 17 | 376 | 21 | 368 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1ZMB_A | 1.57e-07 | 85 | 285 | 36 | 223 | CrystalStructure of the Putative Acetylxylan Esterase from Clostridium acetobutylicum, Northeast Structural Genomics Target CaR6 [Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824],1ZMB_B Crystal Structure of the Putative Acetylxylan Esterase from Clostridium acetobutylicum, Northeast Structural Genomics Target CaR6 [Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824],1ZMB_C Crystal Structure of the Putative Acetylxylan Esterase from Clostridium acetobutylicum, Northeast Structural Genomics Target CaR6 [Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824],1ZMB_D Crystal Structure of the Putative Acetylxylan Esterase from Clostridium acetobutylicum, Northeast Structural Genomics Target CaR6 [Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824],1ZMB_E Crystal Structure of the Putative Acetylxylan Esterase from Clostridium acetobutylicum, Northeast Structural Genomics Target CaR6 [Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824],1ZMB_F Crystal Structure of the Putative Acetylxylan Esterase from Clostridium acetobutylicum, Northeast Structural Genomics Target CaR6 [Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D5EXZ4 | 9.05e-90 | 14 | 376 | 35 | 394 | Carbohydrate acetyl esterase/feruloyl esterase OS=Prevotella ruminicola (strain ATCC 19189 / JCM 8958 / 23) OX=264731 GN=axe1-6A PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
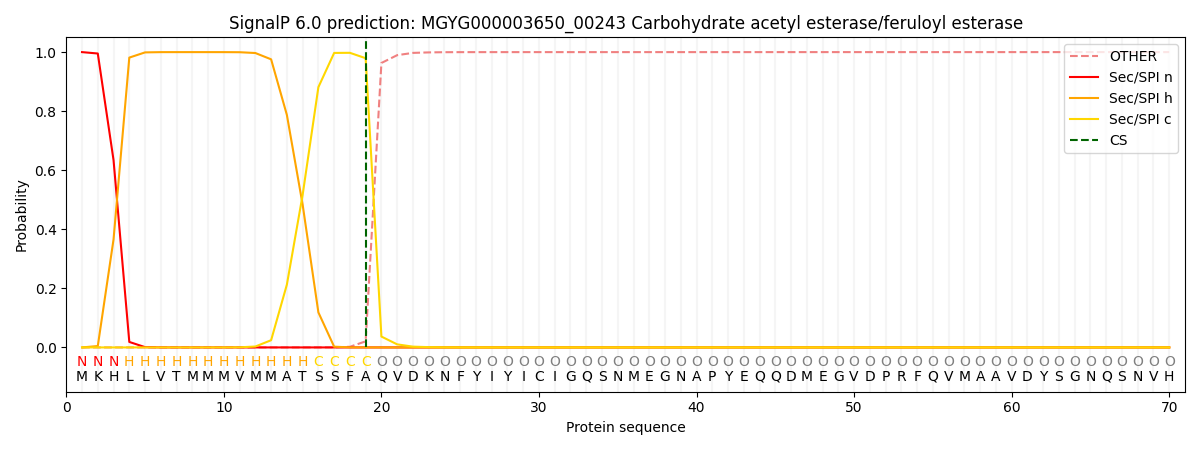
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000398 | 0.998806 | 0.000229 | 0.000191 | 0.000176 | 0.000175 |
