You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004468_01392
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004468_01392
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Alistipes_A sp900539755 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Rikenellaceae; Alistipes_A; Alistipes_A sp900539755 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004468_01392 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM67 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 74806; End: 77547 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH78 | 357 | 875 | 2.1e-156 | 0.998015873015873 |
| CBM67 | 166 | 336 | 4.8e-34 | 0.9147727272727273 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam17389 | Bac_rhamnosid6H | 1.82e-119 | 463 | 809 | 1 | 340 | Bacterial alpha-L-rhamnosidase 6 hairpin glycosidase domain. This family consists of bacterial rhamnosidase A and B enzymes. L-Rhamnose is abundant in biomass as a common constituent of glycolipids and glycosides, such as plant pigments, pectic polysaccharides, gums or biosurfactants. Some rhamnosides are important bioactive compounds. For example, terpenyl glycosides, the glycosidic precursor of aromatic terpenoids, act as important flavouring substances in grapes. Other rhamnosides act as cytotoxic rhamnosylated terpenoids, as signal substances in plants or play a role in the antigenicity of pathogenic bacteria. |
| pfam08531 | Bac_rhamnosid_N | 2.69e-48 | 182 | 350 | 2 | 172 | Alpha-L-rhamnosidase N-terminal domain. This family consists of bacterial rhamnosidase A and B enzymes. This domain is probably involved in substrate recognition. |
| pfam05592 | Bac_rhamnosid | 1.84e-32 | 358 | 459 | 1 | 102 | Bacterial alpha-L-rhamnosidase concanavalin-like domain. This family consists of bacterial rhamnosidase A and B enzymes. L-Rhamnose is abundant in biomass as a common constituent of glycolipids and glycosides, such as plant pigments, pectic polysaccharides, gums or biosurfactants. Some rhamnosides are important bioactive compounds. For example, terpenyl glycosides, the glycosidic precursor of aromatic terpenoids, act as important flavouring substances in grapes. Other rhamnosides act as cytotoxic rhamnosylated terpenoids, as signal substances in plants or play a role in the antigenicity of pathogenic bacteria. |
| pfam17390 | Bac_rhamnosid_C | 5.51e-21 | 811 | 887 | 1 | 75 | Bacterial alpha-L-rhamnosidase C-terminal domain. This family consists of bacterial rhamnosidase A and B enzymes. L-Rhamnose is abundant in biomass as a common constituent of glycolipids and glycosides, such as plant pigments, pectic polysaccharides, gums or biosurfactants. Some rhamnosides are important bioactive compounds. For example, terpenyl glycosides, the glycosidic precursor of aromatic terpenoids, act as important flavouring substances in grapes. Other rhamnosides act as cytotoxic rhamnosylated terpenoids, as signal substances in plants or play a role in the antigenicity of pathogenic bacteria. |
| cd17643 | A_NRPS_Cytc1-like | 0.004 | 188 | 236 | 299 | 347 | similar to adenylation domain of cytotrienin synthetase CytC1. This family of the adenylation (A) domain of nonribosomal peptide synthases (NRPS) includes Streptomyces sp. cytotrienin synthetase (CytC1), a relatively promiscuous adenylation enzyme that installs the aminoacyl moieties on the phosphopantetheinyl arm of the holo carrier protein CytC2. Also included are Streptomyces sp Thr1, involved in the biosynthesis of 4-chlorothreonine, Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyoverdine synthetase D (PvdD), involved in the biosynthesis of the siderophore pyoverdine and Pseudomonas syringae syringopeptin synthetase, where syringpeptin is a necrosis-inducing phytotoxin that functions as a virulence determinant in the plant-pathogen interaction. The adenylation (A) domain of NRPS recognizes a specific amino acid or hydroxy acid and activates it as an (amino) acyl adenylate by hydrolysis of ATP. The activated acyl moiety then forms a thioester bond to the enzyme-bound cofactor phosphopantetheine of a peptidyl carrier protein domain. NRPSs are large multifunctional enzymes which synthesize many therapeutically useful peptides in bacteria and fungi via a template-directed, nucleic acid independent nonribosomal mechanism. These natural products include antibiotics, immunosuppressants, plant and animal toxins, and enzyme inhibitors. NRPS has a distinct modular structure in which each module is responsible for the recognition, activation, and in some cases, modification of a single amino acid residue of the final peptide product. The modules can be subdivided into domains that catalyze specific biochemical reactions. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCG54613.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 912 | 1 | 933 |
| QUT49169.1 | 0.0 | 4 | 907 | 7 | 907 |
| SCD21045.1 | 0.0 | 4 | 909 | 13 | 904 |
| CEA16358.1 | 0.0 | 18 | 909 | 24 | 909 |
| SCM59085.1 | 0.0 | 4 | 912 | 5 | 908 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6I60_A | 3.31e-163 | 27 | 912 | 34 | 942 | Structureof alpha-L-rhamnosidase from Dictyoglumus thermophilum [Dictyoglomus thermophilum H-6-12],6I60_B Structure of alpha-L-rhamnosidase from Dictyoglumus thermophilum [Dictyoglomus thermophilum H-6-12] |
| 3W5M_A | 1.45e-124 | 21 | 913 | 2 | 1032 | CrystalStructure of Streptomyces avermitilis alpha-L-rhamnosidase [Streptomyces avermitilis MA-4680 = NBRC 14893],3W5N_A Crystal Structure of Streptomyces avermitilis alpha-L-rhamnosidase complexed with L-rhamnose [Streptomyces avermitilis MA-4680 = NBRC 14893] |
| 6GSZ_A | 1.43e-102 | 23 | 886 | 2 | 859 | Crystalstructure of native alfa-L-rhamnosidase from Aspergillus terreus [Aspergillus terreus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2KNB2 | 7.18e-141 | 17 | 899 | 25 | 894 | Alpha-L-rhamnosidase OS=Formosa agariphila (strain DSM 15362 / KCTC 12365 / LMG 23005 / KMM 3901 / M-2Alg 35-1) OX=1347342 GN=BN863_22090 PE=1 SV=2 |
| Q82PP4 | 6.18e-123 | 21 | 911 | 2 | 1030 | Alpha-L-rhamnosidase OS=Streptomyces avermitilis (strain ATCC 31267 / DSM 46492 / JCM 5070 / NBRC 14893 / NCIMB 12804 / NRRL 8165 / MA-4680) OX=227882 GN=SAVERM_828 PE=1 SV=1 |
| P9WF03 | 4.16e-122 | 3 | 908 | 5 | 907 | Alpha-L-rhamnosidase OS=Alteromonas sp. (strain LOR) OX=1537994 GN=LOR_34 PE=1 SV=1 |
| T2KPL4 | 3.37e-120 | 3 | 910 | 5 | 948 | Alpha-L-rhamnosidase OS=Formosa agariphila (strain DSM 15362 / KCTC 12365 / LMG 23005 / KMM 3901 / M-2Alg 35-1) OX=1347342 GN=BN863_22170 PE=2 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
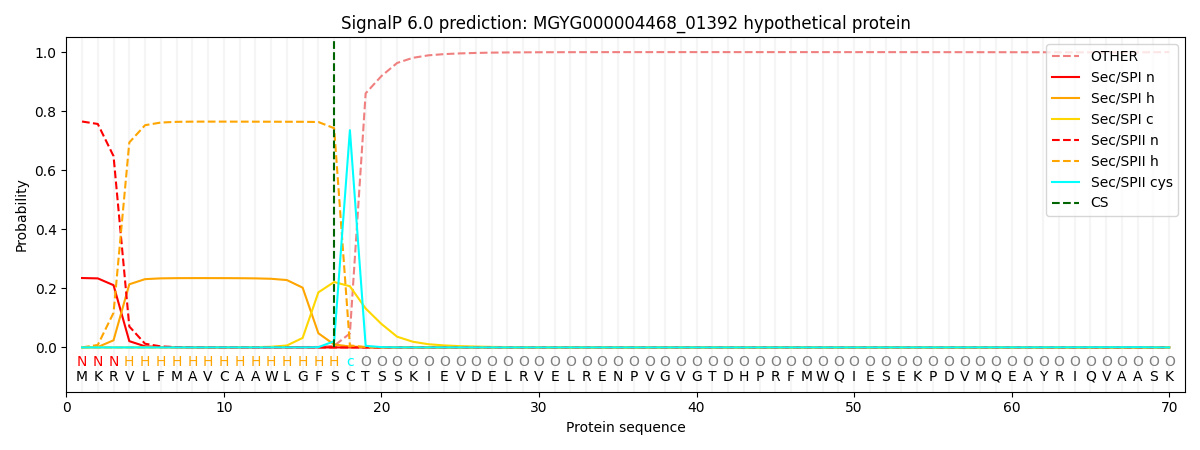
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000482 | 0.230097 | 0.769113 | 0.000090 | 0.000112 | 0.000099 |
