You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004621_02120
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004621_02120
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
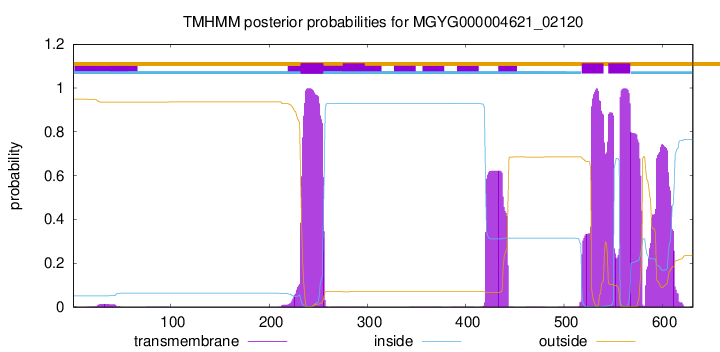
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; Prevotella; | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004621_02120 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CE4 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Undecaprenyl-phosphate 4-deoxy-4-formamido-L-arabinose transferase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 1994; End: 3889 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT2 | 274 | 499 | 9.6e-34 | 0.991304347826087 |
| CE4 | 2 | 99 | 1.3e-23 | 0.7384615384615385 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd10962 | CE4_GT2-like | 3.31e-89 | 2 | 197 | 4 | 196 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of uncharacterized bacterial glycosyl transferase, group 2-like family proteins. This family includes many uncharacterized bacterial proteins containing an N-terminal GH18 (glycosyl hydrolase, family 18) domain, a middle NodB-like homology domain, and a C-terminal GT2-like (glycosyl transferase group 2) domain. Although their biological function is unknown, members in this family contain a middle NodB homology domain that is similar to the catalytic domain of Streptococcus pneumoniae polysaccharide deacetylase PgdA (SpPgdA), an extracellular metal-dependent polysaccharide deacetylase with de-N-acetylase activity toward a hexamer of chitooligosaccharide N-acetylglucosamine, but not shorter chitooligosaccharides or a synthetic peptidoglycan tetrasaccharide. Like SpPgdA, this family is a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. The presence of three domains suggests that members of this family may be multifunctional. |
| cd06423 | CESA_like | 9.18e-66 | 278 | 456 | 1 | 180 | CESA_like is the cellulose synthase superfamily. The cellulose synthase (CESA) superfamily includes a wide variety of glycosyltransferase family 2 enzymes that share the common characteristic of catalyzing the elongation of polysaccharide chains. The members include cellulose synthase catalytic subunit, chitin synthase, glucan biosynthesis protein and other families of CESA-like proteins. Cellulose synthase catalyzes the polymerization reaction of cellulose, an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues in plants, most algae, some bacteria and fungi, and even some animals. In bacteria, algae and lower eukaryotes, there is a second unrelated type of cellulose synthase (Type II), which produces acylated cellulose, a derivative of cellulose. Chitin synthase catalyzes the incorporation of GlcNAc from substrate UDP-GlcNAc into chitin, which is a linear homopolymer of beta-(1,4)-linked GlcNAc residues and Glucan Biosynthesis protein catalyzes the elongation of beta-1,2 polyglucose chains of Glucan. |
| PRK11204 | PRK11204 | 1.16e-60 | 220 | 619 | 1 | 411 | N-glycosyltransferase; Provisional |
| COG1215 | BcsA | 1.69e-59 | 220 | 609 | 2 | 397 | Glycosyltransferase, catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase and poly-beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine synthase [Cell motility]. |
| cd10917 | CE4_NodB_like_6s_7s | 1.57e-51 | 3 | 183 | 5 | 171 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of rhizobial NodB-like proteins. This family belongs to the large and functionally diverse carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily, whose members show strong sequence similarity with some variability due to their distinct carbohydrate substrates. It includes many rhizobial NodB chitooligosaccharide N-deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.-)-like proteins, mainly from bacteria and eukaryotes, such as chitin deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.41), bacterial peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.-), and acetylxylan esterases (EC 3.1.1.72), which catalyze the N- or O-deacetylation of substrates such as acetylated chitin, peptidoglycan, and acetylated xylan. All members of this family contain a catalytic NodB homology domain with the same overall topology and a deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold with 6- or 7 strands. Their catalytic activity is dependent on the presence of a divalent cation, preferably cobalt or zinc, and they employ a conserved His-His-Asp zinc-binding triad closely associated with the conserved catalytic base (aspartic acid) and acid (histidine) to carry out acid/base catalysis. Several family members show diversity both in metal ion specificities and in the residues that coordinate the metal. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCS85120.1 | 1.64e-304 | 1 | 631 | 506 | 1138 |
| QUB71850.1 | 2.10e-300 | 1 | 628 | 503 | 1132 |
| QUI94514.1 | 4.80e-299 | 1 | 629 | 503 | 1133 |
| QUB88773.1 | 6.80e-299 | 1 | 629 | 503 | 1133 |
| AEA22230.1 | 6.80e-299 | 1 | 629 | 503 | 1133 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5O6Y_A | 8.94e-33 | 3 | 201 | 25 | 213 | Crystalstructure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase in complex with 4-naphthalen-1-yl-~{N}-oxidanyl-benzamide [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579] |
| 5O6Y_B | 1.11e-31 | 3 | 201 | 25 | 213 | Crystalstructure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase in complex with 4-naphthalen-1-yl-~{N}-oxidanyl-benzamide [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579],5O6Y_C Crystal structure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase in complex with 4-naphthalen-1-yl-~{N}-oxidanyl-benzamide [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579],5O6Y_D Crystal structure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase in complex with 4-naphthalen-1-yl-~{N}-oxidanyl-benzamide [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579] |
| 4L1G_A | 4.82e-31 | 3 | 201 | 77 | 265 | Crystalstructure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase from Bacillus cereus [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579],4L1G_B Crystal structure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase from Bacillus cereus [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579],4L1G_C Crystal structure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase from Bacillus cereus [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579],4L1G_D Crystal structure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase from Bacillus cereus [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579] |
| 2C1G_A | 2.31e-25 | 3 | 197 | 240 | 417 | Structureof Streptococcus pneumoniae peptidoglycan deacetylase (SpPgdA) [Streptococcus pneumoniae R6] |
| 2C1I_A | 1.01e-24 | 3 | 197 | 240 | 417 | Structureof Streptococcus pneumoniae peptidoglycan deacetylase (SpPgdA) D 275 N Mutant. [Streptococcus pneumoniae R6] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P75905 | 3.89e-32 | 274 | 524 | 75 | 322 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine synthase OS=Escherichia coli (strain K12) OX=83333 GN=pgaC PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q8XAR5 | 3.89e-32 | 274 | 524 | 75 | 322 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine synthase OS=Escherichia coli O157:H7 OX=83334 GN=pgaC PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q81EK9 | 2.28e-31 | 3 | 201 | 85 | 273 | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase BC_1960 OS=Bacillus cereus (strain ATCC 14579 / DSM 31 / CCUG 7414 / JCM 2152 / NBRC 15305 / NCIMB 9373 / NCTC 2599 / NRRL B-3711) OX=226900 GN=BC_1960 PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q5HKQ0 | 2.87e-31 | 257 | 505 | 31 | 280 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine synthase OS=Staphylococcus epidermidis (strain ATCC 35984 / RP62A) OX=176279 GN=icaA PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q8GLC5 | 5.28e-31 | 276 | 505 | 49 | 280 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine synthase OS=Staphylococcus epidermidis OX=1282 GN=icaA PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
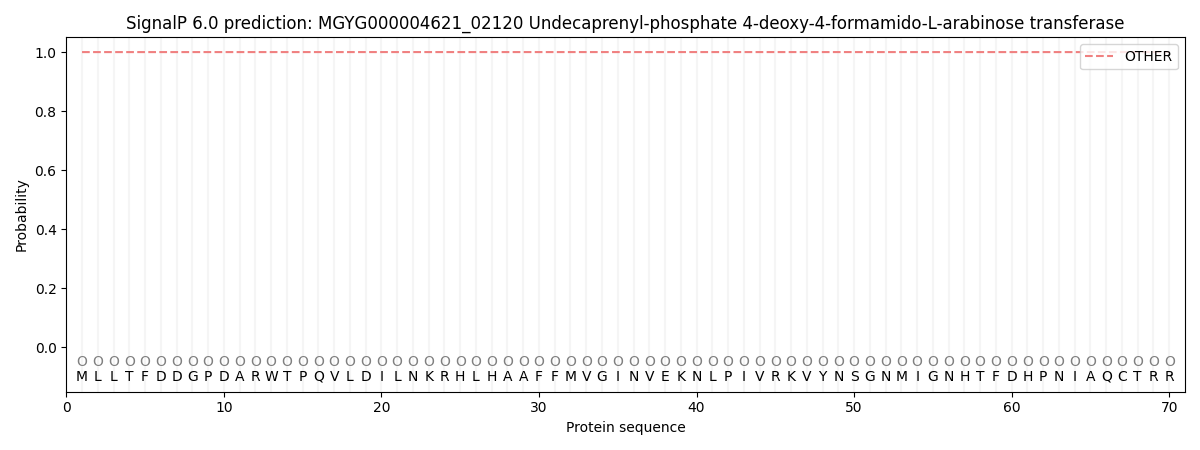
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.000066 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |