You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002736_02059
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002736_02059
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
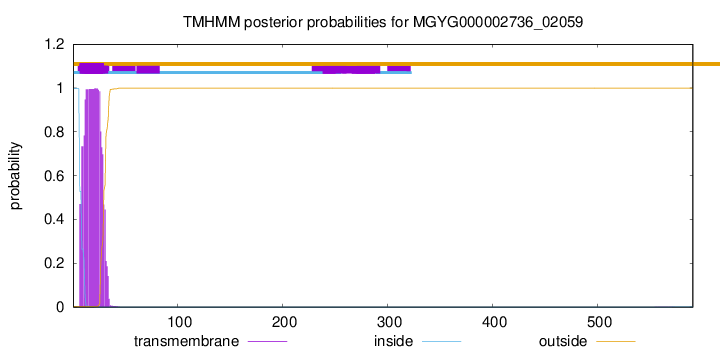
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | UMGS403 sp900541565 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes_A; Clostridia; Oscillospirales; Acutalibacteraceae; UMGS403; UMGS403 sp900541565 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002736_02059 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH13 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Alpha-amylase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 3558; End: 5333 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH13 | 65 | 347 | 2.7e-76 | 0.9924812030075187 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd11315 | AmyAc_bac1_AmyA | 7.55e-100 | 56 | 410 | 1 | 347 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in bacterial Alpha-amylases (also called 1,4-alpha-D-glucan-4-glucanohydrolase). AmyA (EC 3.2.1.1) catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages of glycogen, starch, related polysaccharides, and some oligosaccharides. This group includes Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Cyanobacteria. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| cd11317 | AmyAc_bac_euk_AmyA | 1.87e-29 | 57 | 300 | 2 | 194 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in bacterial and eukaryotic Alpha amylases (also called 1,4-alpha-D-glucan-4-glucanohydrolase). AmyA (EC 3.2.1.1) catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages of glycogen, starch, related polysaccharides, and some oligosaccharides. This group includes AmyA proteins from bacteria, fungi, mammals, insects, mollusks, and nematodes. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| pfam00128 | Alpha-amylase | 1.90e-15 | 126 | 294 | 49 | 228 | Alpha amylase, catalytic domain. Alpha amylase is classified as family 13 of the glycosyl hydrolases. The structure is an 8 stranded alpha/beta barrel containing the active site, interrupted by a ~70 a.a. calcium-binding domain protruding between beta strand 3 and alpha helix 3, and a carboxyl-terminal Greek key beta-barrel domain. |
| pfam16738 | CBM26 | 6.31e-13 | 495 | 563 | 1 | 67 | Starch-binding module 26. CBM26 is a carbohydrate-binding module that binds starch. |
| cd11319 | AmyAc_euk_AmyA | 1.61e-12 | 126 | 296 | 95 | 246 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in eukaryotic Alpha-amylases (also called 1,4-alpha-D-glucan-4-glucanohydrolase). AmyA (EC 3.2.1.1) catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages of glycogen, starch, related polysaccharides, and some oligosaccharides. This group includes eukaryotic alpha-amylases including proteins from fungi, sponges, and protozoans. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QCT06294.1 | 7.14e-110 | 5 | 488 | 4 | 497 |
| SDT05525.1 | 4.24e-95 | 30 | 486 | 30 | 476 |
| AWM46637.1 | 1.03e-93 | 35 | 499 | 27 | 478 |
| AMQ72789.1 | 1.03e-93 | 35 | 499 | 27 | 478 |
| AFC90847.1 | 1.07e-93 | 53 | 487 | 3 | 424 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1UA7_A | 8.82e-93 | 53 | 486 | 2 | 422 | ChainA, Alpha-amylase [Bacillus subtilis] |
| 1BAG_A | 1.36e-92 | 51 | 486 | 3 | 425 | ChainA, ALPHA-1,4-GLUCAN-4-GLUCANOHYDROLASE [Bacillus subtilis] |
| 3DC0_A | 4.88e-92 | 53 | 486 | 2 | 422 | Crystalstructure of native alpha-amylase from Bacillus sp. KR-8104 [Bacillus sp. KR-8104] |
| 1VIW_A | 4.36e-17 | 59 | 242 | 13 | 190 | TENEBRIOMOLITOR ALPHA-AMYLASE-INHIBITOR COMPLEX [Tenebrio molitor] |
| 1CLV_A | 7.71e-17 | 59 | 242 | 13 | 190 | YELLOWMEAL WORM ALPHA-AMYLASE IN COMPLEX WITH THE AMARANTH ALPHA-AMYLASE INHIBITOR [Tenebrio molitor],1JAE_A STRUCTURE OF TENEBRIO MOLITOR LARVAL ALPHA-AMYLASE [Tenebrio molitor],1TMQ_A STRUCTURE OF TENEBRIO MOLITOR LARVAL ALPHA-AMYLASE IN COMPLEX WITH RAGI BIFUNCTIONAL INHIBITOR [Tenebrio molitor] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P00691 | 9.58e-91 | 35 | 499 | 27 | 478 | Alpha-amylase OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=amyE PE=1 SV=2 |
| P23671 | 4.71e-77 | 37 | 485 | 33 | 462 | Alpha-amylase OS=Clostridium acetobutylicum (strain ATCC 824 / DSM 792 / JCM 1419 / LMG 5710 / VKM B-1787) OX=272562 GN=amyA PE=3 SV=2 |
| P30269 | 3.53e-57 | 53 | 526 | 144 | 653 | Alpha-amylase OS=Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens OX=831 GN=amyA PE=3 SV=1 |
| P29750 | 7.75e-20 | 33 | 484 | 16 | 481 | Alpha-amylase OS=Thermomonospora curvata OX=2020 GN=tam PE=1 SV=1 |
| O18345 | 2.09e-19 | 59 | 377 | 31 | 338 | Alpha-amylase 2 OS=Drosophila ananassae OX=7217 GN=Amy58 PE=3 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.094035 | 0.233714 | 0.668922 | 0.002128 | 0.000712 | 0.000477 |