* Annotate your protein result page
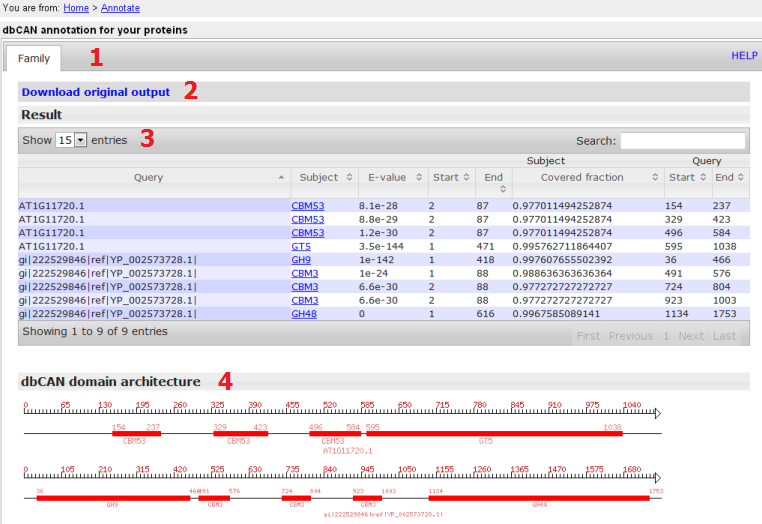
- The tabular output of dbCAN annotation;
- The raw hmmscan output; right click to download;
- The parsed hmmscan result: if alignment length > 80aa, use E-value < 1e-5, otherwise use E-value < 1e-3; specific information is shown such as, what CAZyme domains are found and where they are located; "subject" is the matched CAZyme domain; ""Covered fraction" is calculated as (End-Start)/length of HMM; only rows with "Covered fraction" > 0.3 are shown; to download, choose show "all" entries and copy & paste to excel
- Graphical display of the CAZyme domain architecture; right click to download the diagram;
* Family browse page
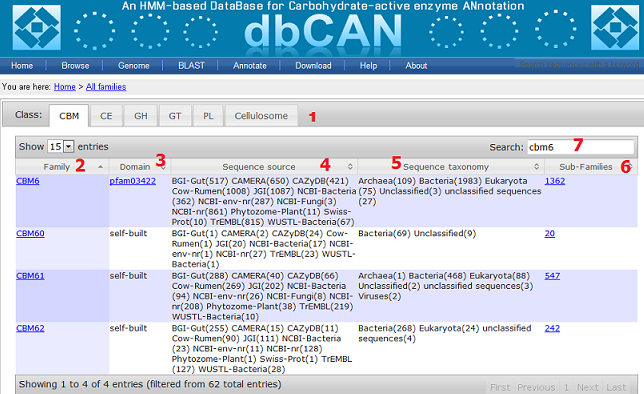
- Class: shows the five CAZy classes and the cellulosome class, each corresponding to one panel; all columns in the table can be sorted;
- Family: CAZy family ID, clicking on one will bring you to a new page for that particular family;
- Domain: CDD signature domain model if any, otherwise the self-built model;
- Sequence source: within the parenthesis are the number of full length sequences found in that source; we have in total 13 sources:
(1) CAZyDB,
(2) NCBI-nr,
(3) Swiss-Prot,
(4) TrEMBL,
(5) CAMERA,
(6) NCBI-env-nr,
(7) JGI,
(8) BGI-Gut,
(9) Cow-Rumen,
(10) WUSTL-bacteria,
(11) Phytozome-plants,
(12) NCBI-bacteria,
(13) NCBI-fungi.
Note that:
(3) Swiss-Prot and (4) TrEMBL together are called UniProt,
(1) to (4) have lots of redundancy,
(5) to (9) are metagenome data sources,
(10) includes 84 gut bacterial genomes sequenced by WUSTL which are not available in GenBank,
(11) includes 30 different plant genomes available at Phytozome, most of which are not available in GenBank,
(12) and (13) are supposed to be completely included in (2) NCBI-nr; - Sequence taxonomy: within the parenthesis are the number of full length sequences found under that taxonomy rank. Note that the five metagenome sources are not considered in this statistics;
- Subfamilies: the number of subfamilies found in that family;
- Search: typing in any letters/words can search any columns of the table.
* Browse each CAZy Family: basic information
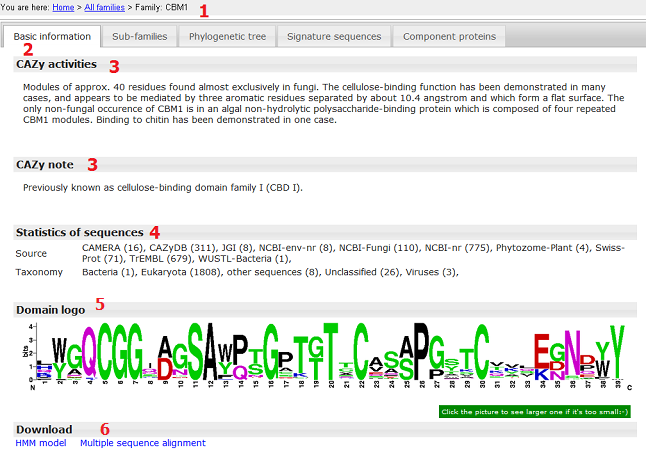
- The browse page for each family has five tabular panels (member sequences are NOT full length proteins, but signature domain regions);
- Basic information panel;
- CAZy activies and CAZy note were taken from the CAZyDB;
- Within the parenthesis are the number of full length sequences found in that source;
- Domain logo was generated based on the multiple sequence alignment of signature domains of proteins from the CAZyDB;
- HMM and alignment for this particular family can be downloaded.
* Browse each CAZy Family: Subfamilies
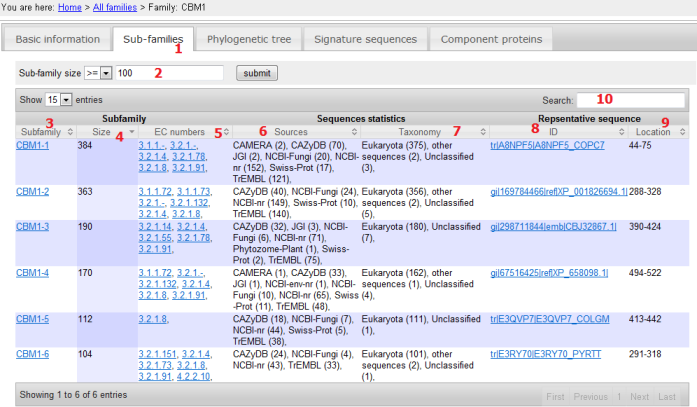
- The Subfamilies panel shows all the subfamilies clustered using UCLUST at 40% sequence identity level, i.e. all sequences within each subfamily have >= 40% identity, between different subfamilies < 40% identity;
- Subfamily size filter, e.g. only show subfamilies with size > 100;
- Subfamily ID: named with family ID followed by '-' and a number; the smaller the number, the more sequences the subfamily has;
- Subfamily size: the number of signature domain sequences found in that subfamily; can be sorted;
- EC numbers: if any protein has any signature domain classified into the subfamily, retrieve the EC numbers associated with that protein;
- Sources: within the parenthesis are the number of signature domain sequences found in that source;
- Taxonomy: within the parenthesis are the number of signature domain sequences found under that taxonomy rank. Note that the five metagenome sources are not considered in this statistics;
- Representative sequence ID: the representative sequence of that subfamily selected by UCLUST when doing clustering, ususally is the longest one in that subfamily;
- Location: the signature domain sequence region in the full length protein.
* Browse each CAZy Family: Phylogenetic tree
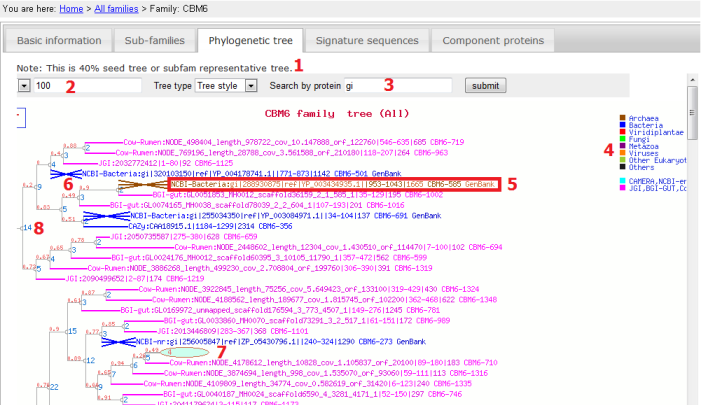
- The Phylogenetic tree panel shows the phylogeny of representative sequences of all subfamilies, i.e. each leaf node in the tree is the representative sequence of each subfamily;
- Tree depth: from the root node to the leaf node, there may be too many steps which makes the phylogram too wide; this parameter set up to what step you want to show the tree, e.g. if using 100, the depths > 100 will not be shown, instead shown as an oval (see 7 for an example);
- Search: typing in any letters/words can search for particular proteins in the tree; after the search the matched proteins will be highlighted by crosses in the phylogram (see 6 for example);
- Legend: tree branches and leaf names are color-coded based on taxnomy and sources (if metagenomes);
- Leaf name: named as [Sequence source]:[ID]|[signature domain location]|[protein full length] [link to subfamily] [link to GenBank/UniProt]; clicking on each field will link out to other pages, e.g. to Subfamily browse page;
- Crosses: see 3;
- Ovals: see 2; clicking on these ovals will open a new page to show all sequences included;
- Numbers on the node: red is bootstrap value and blue is the number of sequences under that node.
* Browse each CAZy Family: Signature domains
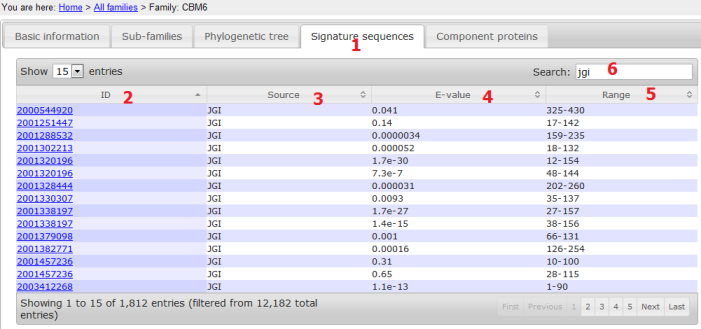
- The Signature domain panel shows all the member sequences (signature domain regions) in the subfamily;
- ID: the full length protein ID;
- Source: we have in total 13 sources;
- E-value: reflects how similar it is to the domain HMM (built based on signature domain regions from CAZyDB proteins);
- Range: signature domain location in the full length;
- Search: typing in any letters/words can search any columns of the table; the example just shows sequences from JGI.
* Browse each CAZy Family: Component proteins
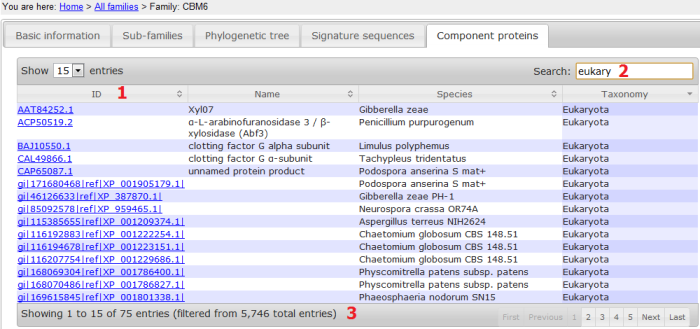
- ID: the full length protein ID;
- Search: typing in any letters/words can search any columns of the table;
- The total number of full length proteins in the family and the number of proteins after the search (see 2).
* Browse each CAZy Subfamily: Phylogenetic tree
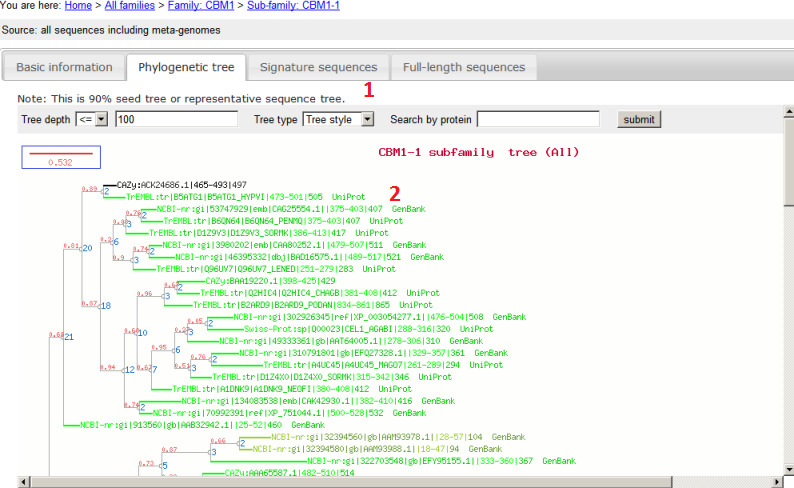
- In this phylogeny, not all component signature domains of this subfamily are included. Because there is much redundancy among different sources, we removed very similar sequences first using UCLUST at 90% sequence identity, meaning that if two sequences are > 90% identical we only keep the longer one;
- Leaf name: named as [Sequence source]:[ID]|[signature domain location]|[protein full length] [link to GenBank/UniProt if any]; clicking on each field will link out to other pages, e.g. to sequence browse page.
* Browse each CAZy Subfamily: Basic information
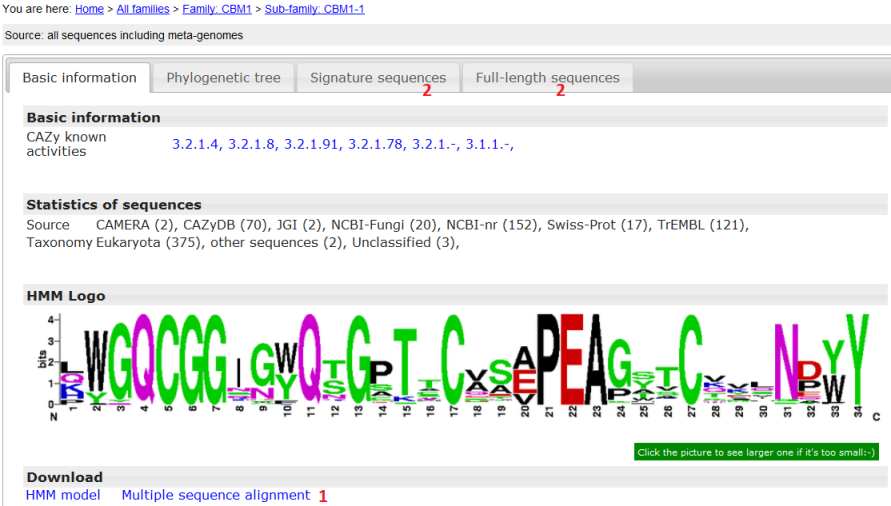
- Same as the phylogeny, the HMM and alignment are for 90% representative sequences;
- The Signature sequences panel and Full-length sequences panel show all the sequences.
Cite us
Yin Y*, Mao X*, Yang JC, Chen X, Mao F and Xu Y, dbCAN: a web resource for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation, Nucleic Acids Res. web server issue 2012, DOI:10.1093/nar/GKS479
