You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000639_00438
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000639_00438
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Treponema_D sp900541945 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Spirochaetota; Spirochaetia; Treponematales; Treponemataceae; Treponema_D; Treponema_D sp900541945 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000639_00438 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH13 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 10281; End: 13874 Strand: - | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MKKVLCAIGA IVLFAFCSCS NELEENSRDV VSSGGYGSLV VSKSDSERAL DIQSLKFASA | 60 |
| SVSGAGISSG REPSAKDISV TDGTGTLTID NIPAGKNRII TVQALDSSKN EIFGVTMRAV | 120 |
| CDVEAGKTVN VSVNWKTTAL GNVFYELNKS GYGVSNISKD DVKIIDSLID KSVSSFLIDT | 180 |
| ESLASDFKNK ILKDKPSFYV LEPASLAFTC NDNGNFKIQV CDPASSVFSG SGTGGTVKNI | 240 |
| APGKWKVLLL DNEGTKVAEK TAVFTSGKES SVSFASVTDK IIVHVEKSAG WTHVYAWVSK | 300 |
| SEKLFGVWPG ELMVDSDGDG WFDVVIEKTA CSLIFNNGGN KQTDDLSCTA GEWWFKDNVW | 360 |
| NEENPTDSEP PVINSLVMNV ASPVSGTVTF TLTASDNKKL KNAELFVDDV KFSEKSFSSL | 420 |
| NDSLVFEWNS SSAKNGEHKI SAVVYDAAGN KSEPKTISVV TENENVRPVA SITGSIKVSK | 480 |
| GSEKVYSASN SSDKNGTVAG YKWKVVGATI ITGSETSENI TVKAPDSEGS FTISLVVTDD | 540 |
| EGLDSEETVI TVTVKDKVSN DFREETIYFL MTARFYDGDS SNNRWCRSDD SSGNRDNGDY | 600 |
| PWRGDFKGLI EKLDYIKALG FSAIWITPPV LNRSDYDFHG YHAWDMTKID PRLESAGATY | 660 |
| QDLINAAHAK GIKIIQDIVL NHSCRFGLKN FFVPKYWGDR DNQYWGTSNE INYYDEYNPN | 720 |
| FEYNGLDVEP KSGKAWYNGD LWQKEKPSLS WNPNLSDWGV QKGFNKEGRA YYGCQWPDLR | 780 |
| LFDPEKFHTE WLGNWEDETC QSGTIHEDCI DLNTEAAAVQ KYLIDAYTKY IDMGVDAFRI | 840 |
| DTVKHVSRVM FNRHFIPAFK EAGGENFYMF GEVCTRVNET WNHGVAPLST PFYTWKERTT | 900 |
| FSADDSVAVH EGYEYENRQG VNNQPTSDNH ALIGNAYHTP DYSQKSGLDV IDFPMHWNFS | 960 |
| DASSAYNQRQ NDKYYNDATW NVVYVDSHDY GPNMDNRYEG GTEAWAENMT YMWTFRGIPC | 1020 |
| LYYGSEIEFM AGAPCDKGSS APLSTTGRAY YGDNIEGSVQ VSGFGEWSNA TGSMKATLES | 1080 |
| PLSKHLSHLN KIRREIPALQ KGQYSNEGCS GGMSFKRRFT DDSTDSFVLV SISGDATFSG | 1140 |
| LPGGTYTDVV TGDSKTISEG GSITASCSGK GNARIYVLST AKTPAPGKIT GSSPYLK | 1197 |
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH13 | 603 | 1032 | 5.4e-180 | 0.997624703087886 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd11339 | AmyAc_bac_CMD_like_2 | 2.80e-124 | 563 | 1096 | 1 | 344 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in bacterial cyclomaltodextrinases and related proteins. Cyclomaltodextrinase (CDase; EC3.2.1.54), neopullulanase (NPase; EC 3.2.1.135), and maltogenic amylase (MA; EC 3.2.1.133) catalyze the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages on a number of substrates including cyclomaltodextrins (CDs), pullulan, and starch. These enzymes hydrolyze CDs and starch to maltose and pullulan to panose by cleavage of alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds whereas alpha-amylases essentially lack activity on CDs and pullulan. They also catalyze transglycosylation of oligosaccharides to the C3-, C4- or C6-hydroxyl groups of various acceptor sugar molecules. Since these proteins are nearly indistinguishable from each other, they are referred to as cyclomaltodextrinases (CMDs). This group of CMDs is bacterial. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| cd11320 | AmyAc_AmyMalt_CGTase_like | 3.84e-47 | 561 | 1026 | 1 | 348 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in maltogenic amylases, cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase, and related proteins. Enzymes such as amylases, cyclomaltodextrinase (CDase), and cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase (CGTase) degrade starch to smaller oligosaccharides by hydrolyzing the alpha-D-(1,4) linkages between glucose residues. In the case of CGTases, an additional cyclization reaction is catalyzed yielding mixtures of cyclic oligosaccharides which are referred to as alpha-, beta-, or gamma-cyclodextrins (CDs), consisting of six, seven, or eight glucose residues, respectively. CGTases are characterized depending on the major product of the cyclization reaction. Besides having similar catalytic site residues, amylases and CGTases contain carbohydrate binding domains that are distant from the active site and are implicated in attaching the enzyme to raw starch granules and in guiding the amylose chain into the active site. The maltogenic alpha-amylase from Bacillus is a five-domain structure, unlike most alpha-amylases, but similar to that of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase. In addition to the A, B, and C domains, they have a domain D and a starch-binding domain E. Maltogenic amylase is an endo-acting amylase that has activity on cyclodextrins, terminally modified linear maltodextrins, and amylose. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| cd11340 | AmyAc_bac_CMD_like_3 | 7.12e-44 | 566 | 1027 | 5 | 353 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in bacterial cyclomaltodextrinases and related proteins. Cyclomaltodextrinase (CDase; EC3.2.1.54), neopullulanase (NPase; EC 3.2.1.135), and maltogenic amylase (MA; EC 3.2.1.133) catalyze the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages on a number of substrates including cyclomaltodextrins (CDs), pullulan, and starch. These enzymes hydrolyze CDs and starch to maltose and pullulan to panose by cleavage of alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds whereas alpha-amylases essentially lack activity on CDs and pullulan. They also catalyze transglycosylation of oligosaccharides to the C3-, C4- or C6-hydroxyl groups of various acceptor sugar molecules. Since these proteins are nearly indistinguishable from each other, they are referred to as cyclomaltodextrinases (CMDs). This group of CMDs is bacterial. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| cd11352 | AmyAc_5 | 6.20e-40 | 567 | 873 | 2 | 280 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in an uncharacterized protein family. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| pfam00128 | Alpha-amylase | 2.82e-38 | 604 | 1027 | 1 | 326 | Alpha amylase, catalytic domain. Alpha amylase is classified as family 13 of the glycosyl hydrolases. The structure is an 8 stranded alpha/beta barrel containing the active site, interrupted by a ~70 a.a. calcium-binding domain protruding between beta strand 3 and alpha helix 3, and a carboxyl-terminal Greek key beta-barrel domain. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QSI03197.1 | 0.0 | 4 | 1196 | 20 | 1204 |
| ATB40107.1 | 3.46e-257 | 558 | 1197 | 334 | 977 |
| AAW03335.1 | 1.37e-256 | 558 | 1197 | 334 | 977 |
| ADO70697.1 | 1.20e-255 | 558 | 1197 | 424 | 1067 |
| ATB33730.1 | 4.61e-255 | 490 | 1197 | 257 | 980 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1CYG_A | 2.18e-23 | 562 | 1189 | 9 | 500 | CyclodextrinGlucanotransferase (E.C.2.4.1.19) (Cgtase) [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
| 1QHO_A | 1.55e-22 | 565 | 1152 | 9 | 463 | FIVE-DOMAINALPHA-AMYLASE FROM BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS, MALTOSE/ACARBOSE COMPLEX [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],1QHP_A Five-Domain Alpha-Amylase From Bacillus Stearothermophilus, Maltose Complex [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
| 3WMS_A | 5.64e-20 | 540 | 1189 | 24 | 536 | Thecrystal structure of Y195I mutant alpha-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from Paenibacillus macerans [Paenibacillus macerans] |
| 6AIJ_A | 9.45e-20 | 553 | 1189 | 26 | 526 | Cyclodextringlycosyltransferase from Paenibacillus macerans mutant N603D [Paenibacillus macerans] |
| 4E2O_A | 1.28e-19 | 556 | 1124 | 1 | 394 | Crystalstructure of alpha-amylase from Geobacillus thermoleovorans, GTA, complexed with acarbose [Geobacillus thermoleovorans CCB_US3_UF5] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P21543 | 1.14e-25 | 551 | 1032 | 733 | 1079 | Beta/alpha-amylase OS=Paenibacillus polymyxa OX=1406 PE=1 SV=1 |
| P08704 | 3.84e-24 | 561 | 1159 | 39 | 532 | Cyclomaltodextrin glucanotransferase OS=Klebsiella oxytoca OX=571 GN=cgt PE=3 SV=1 |
| P31797 | 1.31e-22 | 562 | 1189 | 40 | 531 | Cyclomaltodextrin glucanotransferase OS=Geobacillus stearothermophilus OX=1422 GN=cgt PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q05884 | 5.62e-22 | 604 | 1137 | 98 | 565 | Alpha-amylase OS=Streptomyces lividans OX=1916 GN=amy PE=1 SV=1 |
| P19531 | 9.26e-22 | 565 | 1152 | 42 | 496 | Maltogenic alpha-amylase OS=Geobacillus stearothermophilus OX=1422 GN=amyM PE=1 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
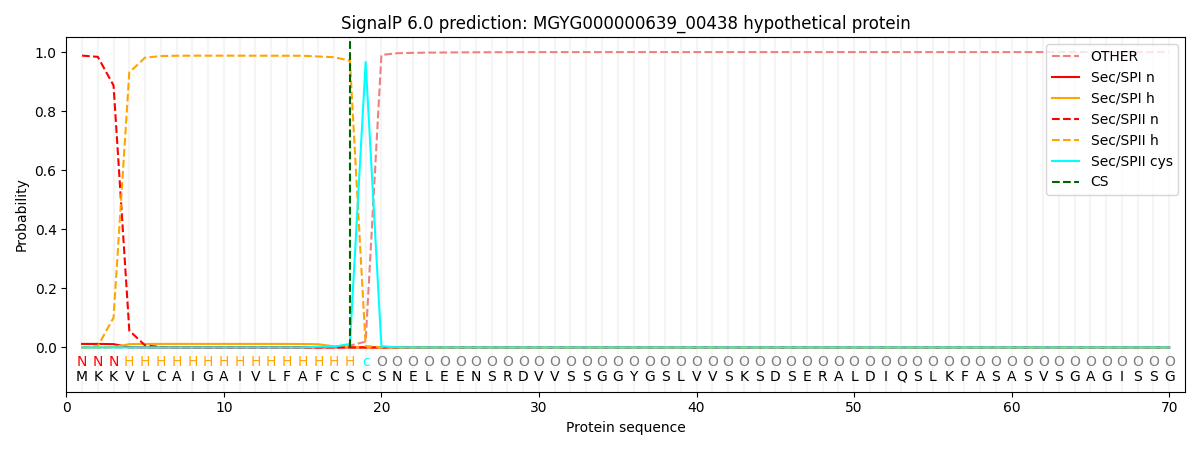
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000022 | 0.011436 | 0.988561 | 0.000005 | 0.000007 | 0.000005 |
