You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003099_00174
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003099_00174
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
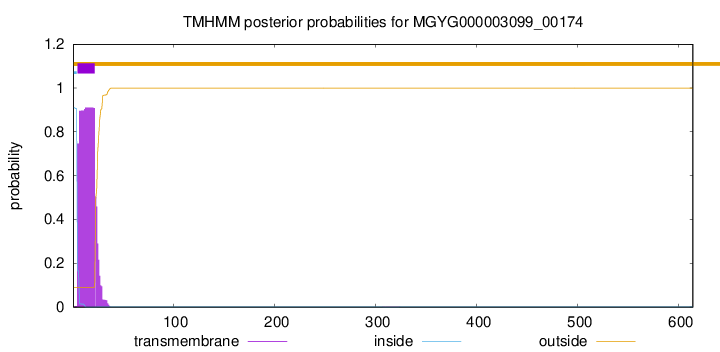
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Barnesiella sp900538555 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Barnesiellaceae; Barnesiella; Barnesiella sp900538555 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003099_00174 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH13 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | 1,4-alpha-glucan branching enzyme GlgB | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 249745; End: 251589 Strand: - | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MKTKFLFVCL LSVLGFCPIY AANTVHKVAP VFWWSGMKNP ELQILLYGDR IATADVTLTS | 60 |
| ADVVLKEVVV QENPNYLILY VDIANAAPQQ FDIILKQGKK RTVVPYELRQ RREGASDVTG | 120 |
| FHADDVLYLI MPDRFSNGNP DNDIIPGMRE GRVDRSDSFA RHGGDLKGIE NHLDYLSDLG | 180 |
| VTAIWLNPIQ ENDMADGSYH GYAITDYYQV DRRLGSNEEF CELVDRAHEK GIKVVMDMIF | 240 |
| NHCGSENYLF RDMPSKEWFN YRGDYVQTNF RTATQIDPYA SGIETELAVD GWFTRTMPDF | 300 |
| NQRNRHVAAY LIQSSIWWIE YAGINGIRQD THPYADFDCM ARWCKAVKDE YPDFNIVGET | 360 |
| WLGSNVLVSY WQKDSRLASP KNSFLPVVMD FPLMEEMNRA FDEETADGGR GLNRLYEYLT | 420 |
| QDIVYADPMS LLTFLDNHDT SRFYRTEAEN IDRFKQALTF LLTTRGIPQI YYGTEILMAA | 480 |
| DKANGDGMLR CDFPGGWSGD AVNAFDPAQR TDLQNEAFAF ARRLLQWRKG NETIAKGSLK | 540 |
| HFTPDNGIYL YERRYEGRSV VVMLNGSDSE RSIETSFYRE IVPAGSAIDW LTGETVDLRT | 600 |
| KVTLQPRGIY IFNL | 614 |
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH13 | 164 | 480 | 1.3e-63 | 0.9833333333333333 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd11340 | AmyAc_bac_CMD_like_3 | 0.0 | 123 | 530 | 2 | 407 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in bacterial cyclomaltodextrinases and related proteins. Cyclomaltodextrinase (CDase; EC3.2.1.54), neopullulanase (NPase; EC 3.2.1.135), and maltogenic amylase (MA; EC 3.2.1.133) catalyze the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages on a number of substrates including cyclomaltodextrins (CDs), pullulan, and starch. These enzymes hydrolyze CDs and starch to maltose and pullulan to panose by cleavage of alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds whereas alpha-amylases essentially lack activity on CDs and pullulan. They also catalyze transglycosylation of oligosaccharides to the C3-, C4- or C6-hydroxyl groups of various acceptor sugar molecules. Since these proteins are nearly indistinguishable from each other, they are referred to as cyclomaltodextrinases (CMDs). This group of CMDs is bacterial. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| cd11339 | AmyAc_bac_CMD_like_2 | 9.33e-77 | 123 | 507 | 1 | 326 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in bacterial cyclomaltodextrinases and related proteins. Cyclomaltodextrinase (CDase; EC3.2.1.54), neopullulanase (NPase; EC 3.2.1.135), and maltogenic amylase (MA; EC 3.2.1.133) catalyze the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages on a number of substrates including cyclomaltodextrins (CDs), pullulan, and starch. These enzymes hydrolyze CDs and starch to maltose and pullulan to panose by cleavage of alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds whereas alpha-amylases essentially lack activity on CDs and pullulan. They also catalyze transglycosylation of oligosaccharides to the C3-, C4- or C6-hydroxyl groups of various acceptor sugar molecules. Since these proteins are nearly indistinguishable from each other, they are referred to as cyclomaltodextrinases (CMDs). This group of CMDs is bacterial. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| cd11338 | AmyAc_CMD | 6.80e-75 | 126 | 539 | 3 | 389 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in cyclomaltodextrinases and related proteins. Cyclomaltodextrinase (CDase; EC3.2.1.54), neopullulanase (NPase; EC 3.2.1.135), and maltogenic amylase (MA; EC 3.2.1.133) catalyze the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages on a number of substrates including cyclomaltodextrins (CDs), pullulan, and starch. These enzymes hydrolyze CDs and starch to maltose and pullulan to panose by cleavage of alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds whereas alpha-amylases essentially lack activity on CDs and pullulan. They also catalyze transglycosylation of oligosaccharides to the C3-, C4- or C6-hydroxyl groups of various acceptor sugar molecules. Since these proteins are nearly indistinguishable from each other, they are referred to as cyclomaltodextrinases (CMDs). The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| cd11320 | AmyAc_AmyMalt_CGTase_like | 1.25e-64 | 125 | 485 | 5 | 358 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in maltogenic amylases, cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase, and related proteins. Enzymes such as amylases, cyclomaltodextrinase (CDase), and cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase (CGTase) degrade starch to smaller oligosaccharides by hydrolyzing the alpha-D-(1,4) linkages between glucose residues. In the case of CGTases, an additional cyclization reaction is catalyzed yielding mixtures of cyclic oligosaccharides which are referred to as alpha-, beta-, or gamma-cyclodextrins (CDs), consisting of six, seven, or eight glucose residues, respectively. CGTases are characterized depending on the major product of the cyclization reaction. Besides having similar catalytic site residues, amylases and CGTases contain carbohydrate binding domains that are distant from the active site and are implicated in attaching the enzyme to raw starch granules and in guiding the amylose chain into the active site. The maltogenic alpha-amylase from Bacillus is a five-domain structure, unlike most alpha-amylases, but similar to that of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase. In addition to the A, B, and C domains, they have a domain D and a starch-binding domain E. Maltogenic amylase is an endo-acting amylase that has activity on cyclodextrins, terminally modified linear maltodextrins, and amylose. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| pfam00128 | Alpha-amylase | 3.21e-58 | 164 | 479 | 1 | 329 | Alpha amylase, catalytic domain. Alpha amylase is classified as family 13 of the glycosyl hydrolases. The structure is an 8 stranded alpha/beta barrel containing the active site, interrupted by a ~70 a.a. calcium-binding domain protruding between beta strand 3 and alpha helix 3, and a carboxyl-terminal Greek key beta-barrel domain. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QQA08180.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 613 | 1 | 616 |
| QUT41579.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 613 | 1 | 616 |
| QUT69421.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 613 | 1 | 617 |
| CAZ78747.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 613 | 1 | 616 |
| ALJ44108.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 613 | 1 | 616 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3EDE_A | 8.08e-157 | 21 | 614 | 2 | 595 | ChainA, Cyclomaltodextrinase [Flavobacterium sp. 92],3EDE_B Chain B, Cyclomaltodextrinase [Flavobacterium sp. 92] |
| 3EDD_A | 1.14e-156 | 21 | 614 | 2 | 595 | ChainA, Cyclomaltodextrinase [Flavobacterium sp. 92],3EDD_B Chain B, Cyclomaltodextrinase [Flavobacterium sp. 92] |
| 3EDF_A | 2.28e-156 | 21 | 614 | 2 | 595 | ChainA, Cyclomaltodextrinase [Flavobacterium sp. 92],3EDF_B Chain B, Cyclomaltodextrinase [Flavobacterium sp. 92],3EDJ_A Chain A, Cyclomaltodextrinase [Flavobacterium sp. 92],3EDJ_B Chain B, Cyclomaltodextrinase [Flavobacterium sp. 92],3EDK_A Chain A, Cyclomaltodextrinase [Flavobacterium sp. 92],3EDK_B Chain B, Cyclomaltodextrinase [Flavobacterium sp. 92] |
| 1H3G_A | 1.68e-147 | 21 | 614 | 2 | 595 | Cyclomaltodextrinasefrom Flavobacterium sp. No. 92: from DNA sequence to protein structure [Flavobacterium sp. 92],1H3G_B Cyclomaltodextrinase from Flavobacterium sp. No. 92: from DNA sequence to protein structure [Flavobacterium sp. 92] |
| 5A2A_A | 1.08e-64 | 124 | 573 | 8 | 406 | CrystalStructure of Anoxybacillus Alpha-amylase Provides Insights into a New Glycosyl Hydrolase Subclass [Anoxybacillus ayderensis] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q8A1G0 | 0.0 | 1 | 613 | 1 | 616 | Neopullulanase SusA OS=Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron (strain ATCC 29148 / DSM 2079 / JCM 5827 / CCUG 10774 / NCTC 10582 / VPI-5482 / E50) OX=226186 GN=susA PE=3 SV=1 |
| P29964 | 6.79e-52 | 123 | 611 | 130 | 572 | Cyclomaltodextrinase OS=Thermoanaerobacter pseudethanolicus (strain ATCC 33223 / 39E) OX=340099 GN=Teth39_0676 PE=1 SV=2 |
| Q08751 | 9.94e-50 | 126 | 613 | 132 | 583 | Neopullulanase 2 OS=Thermoactinomyces vulgaris OX=2026 GN=tvaII PE=1 SV=1 |
| P38940 | 1.83e-48 | 124 | 612 | 134 | 583 | Neopullulanase OS=Geobacillus stearothermophilus OX=1422 GN=nplT PE=1 SV=1 |
| P21543 | 9.23e-48 | 127 | 612 | 749 | 1194 | Beta/alpha-amylase OS=Paenibacillus polymyxa OX=1406 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
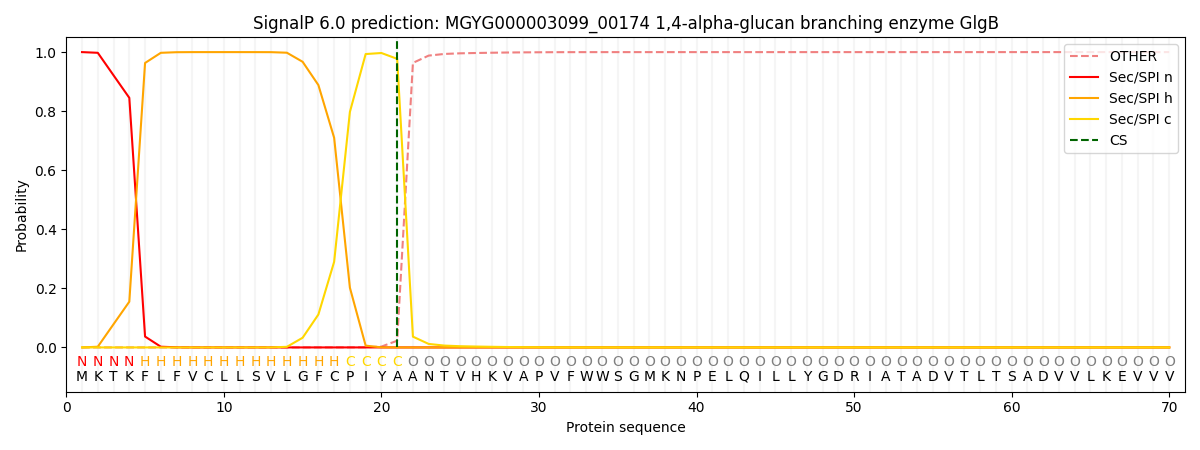
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000335 | 0.998924 | 0.000228 | 0.000166 | 0.000162 | 0.000141 |