You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003835_00212
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003835_00212
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | UBA7173 sp001915385 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Muribaculaceae; UBA7173; UBA7173 sp001915385 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003835_00212 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH13 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 13080; End: 16031 Strand: + | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MNIRNISHKV SAAVAMMLLG TAFTATGAAV NSGDATLSAL EIKVDGQNLV NFDRNTTSYS | 60 |
| IELDDTSLMT LSAAPTASDA TVTITVNGRE YDNHSLASLD GGENTIVYNI VSGTASQAYT | 120 |
| IKIKTPQVLR GRHFSWKNAT IYFVLTDRFY NGDTANDMSY HRQRSQGNMP DYATFHGGDI | 180 |
| KGLTEKLDYL NRLGVDAIWI SAPYEQMHGW TGGKGDAFPH YAFHGYYALD WTYMDRNMGT | 240 |
| VEEFRSFVTE AHKRGIRVVM DIVLNHTGYC TLDDCVDYDF GNFNGTATAG WMPSNGNYTM | 300 |
| WSDDNEVSFN ADTQGKWGNW WSGWVRAFGD RSWSSSAGFA PGGGDNFTMS LAGLPDVVTE | 360 |
| KTSAVNIPPF LKLKWEQENS GDYLDYRLPN LDAWRTDGKG APADYLIAWL AGWVEEFGID | 420 |
| GFRCDTAKHV ELSRWNQLKQ ACKTALANWR ASSRADEYAK SWTEDFWMTG EAFGWDHGDT | 480 |
| GYFTSGGFDS MINFAFNSSE GSQGRTPSTS DWEYYANYCN GSNGRQVLNY VSSHDTGLHR | 540 |
| PGDQKKVATM FLLCPGGAQI YYGDETSRGY MSGCPDQSMA TRSDFNWDAV DNADNKHWQL | 600 |
| IGQFRRRNPA VGAGTQSNLG PDTYGRSFTD GAYANAVVIR LNTSAGQTYT VNVNGFFADG | 660 |
| TKVMDGYNTA TTATVDGGKV TMQASGPVLL VEAYGQITDD EIDTPTPPVP PVPQKPVVTA | 720 |
| TPGSSTFSES VTVTLSVNPA GTPIRYSVAG AANASSTVYT SPLTFTETTT LSTYVENEAG | 780 |
| SNVQSFTYTK SDTPGPGPDP DPDPNKQYVY FNNTQNWTPY VWAWNETENC TAAGAWPGDA | 840 |
| MTQKDGKYYW EAPAGKVPTL IIISDKGGTR AGNGNLEYVN GATYNPDGST GDGPTPPTGD | 900 |
| NVVYFDNGAT NWSTVKVHYW GGESASSWPG VNMIVHSGNI YKYTVPSGTT GLVFNNGSGD | 960 |
| QSGNLTFAKG HLYDKNGDKG EYK | 983 |
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH13 | 178 | 566 | 9.2e-121 | 0.9972222222222222 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRK09505 | malS | 1.88e-168 | 134 | 616 | 185 | 655 | alpha-amylase; Reviewed |
| cd11339 | AmyAc_bac_CMD_like_2 | 7.94e-47 | 140 | 608 | 4 | 344 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in bacterial cyclomaltodextrinases and related proteins. Cyclomaltodextrinase (CDase; EC3.2.1.54), neopullulanase (NPase; EC 3.2.1.135), and maltogenic amylase (MA; EC 3.2.1.133) catalyze the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages on a number of substrates including cyclomaltodextrins (CDs), pullulan, and starch. These enzymes hydrolyze CDs and starch to maltose and pullulan to panose by cleavage of alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds whereas alpha-amylases essentially lack activity on CDs and pullulan. They also catalyze transglycosylation of oligosaccharides to the C3-, C4- or C6-hydroxyl groups of various acceptor sugar molecules. Since these proteins are nearly indistinguishable from each other, they are referred to as cyclomaltodextrinases (CMDs). This group of CMDs is bacterial. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| cd00551 | AmyAc_family | 4.60e-36 | 140 | 562 | 1 | 253 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain family. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; and C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost this catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| COG0366 | AmyA | 5.67e-34 | 139 | 565 | 1 | 355 | Glycosidase [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| cd11320 | AmyAc_AmyMalt_CGTase_like | 6.24e-34 | 137 | 307 | 3 | 173 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in maltogenic amylases, cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase, and related proteins. Enzymes such as amylases, cyclomaltodextrinase (CDase), and cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase (CGTase) degrade starch to smaller oligosaccharides by hydrolyzing the alpha-D-(1,4) linkages between glucose residues. In the case of CGTases, an additional cyclization reaction is catalyzed yielding mixtures of cyclic oligosaccharides which are referred to as alpha-, beta-, or gamma-cyclodextrins (CDs), consisting of six, seven, or eight glucose residues, respectively. CGTases are characterized depending on the major product of the cyclization reaction. Besides having similar catalytic site residues, amylases and CGTases contain carbohydrate binding domains that are distant from the active site and are implicated in attaching the enzyme to raw starch granules and in guiding the amylose chain into the active site. The maltogenic alpha-amylase from Bacillus is a five-domain structure, unlike most alpha-amylases, but similar to that of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase. In addition to the A, B, and C domains, they have a domain D and a starch-binding domain E. Maltogenic amylase is an endo-acting amylase that has activity on cyclodextrins, terminally modified linear maltodextrins, and amylose. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QSI03195.1 | 5.76e-159 | 37 | 692 | 378 | 1096 |
| CQR56565.1 | 1.46e-158 | 95 | 849 | 21 | 749 |
| QQZ60411.1 | 8.56e-153 | 95 | 849 | 21 | 748 |
| ADZ82879.1 | 1.28e-152 | 133 | 869 | 49 | 762 |
| CAA37453.1 | 7.41e-152 | 129 | 822 | 46 | 712 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5A2A_A | 1.51e-26 | 135 | 496 | 5 | 244 | CrystalStructure of Anoxybacillus Alpha-amylase Provides Insights into a New Glycosyl Hydrolase Subclass [Anoxybacillus ayderensis] |
| 5A2B_A | 2.42e-26 | 135 | 496 | 39 | 278 | CrystalStructure of Anoxybacillus Alpha-amylase Provides Insights into a New Glycosyl Hydrolase Subclass [Anoxybacillus ayderensis],5A2C_A Crystal Structure of Anoxybacillus Alpha-amylase Provides Insights into a New Glycosyl Hydrolase Subclass [Anoxybacillus ayderensis] |
| 4E2O_A | 2.71e-26 | 135 | 614 | 6 | 371 | Crystalstructure of alpha-amylase from Geobacillus thermoleovorans, GTA, complexed with acarbose [Geobacillus thermoleovorans CCB_US3_UF5] |
| 6SAO_A | 6.35e-21 | 136 | 681 | 6 | 424 | Structuraland functional characterisation of three novel fungal amylases with enhanced stability and pH tolerance [Thamnidium elegans] |
| 6WNI_A | 1.28e-20 | 137 | 307 | 32 | 210 | ChainA, Cyclomaltodextrin glucanotransferase [Caldanaerobacter subterraneus],6WNI_B Chain B, Cyclomaltodextrin glucanotransferase [Caldanaerobacter subterraneus],6WNU_A Chain A, Cyclomaltodextrin glucanotransferase [Caldanaerobacter subterraneus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P25718 | 3.42e-121 | 134 | 619 | 184 | 651 | Periplasmic alpha-amylase OS=Escherichia coli (strain K12) OX=83333 GN=malS PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q05884 | 1.17e-29 | 171 | 686 | 91 | 614 | Alpha-amylase OS=Streptomyces lividans OX=1916 GN=amy PE=1 SV=1 |
| P21543 | 4.51e-26 | 136 | 663 | 744 | 1166 | Beta/alpha-amylase OS=Paenibacillus polymyxa OX=1406 PE=1 SV=1 |
| P36905 | 7.29e-25 | 137 | 696 | 387 | 926 | Amylopullulanase OS=Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum OX=28896 GN=apu PE=3 SV=2 |
| P38536 | 1.57e-20 | 137 | 696 | 387 | 925 | Amylopullulanase OS=Thermoanaerobacterium thermosulfurigenes OX=33950 GN=amyB PE=3 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
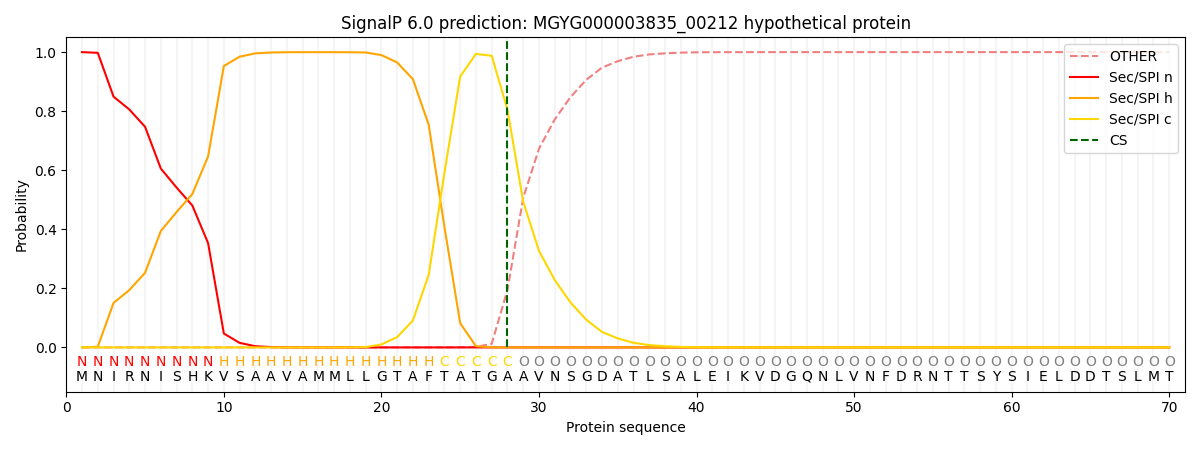
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000538 | 0.998658 | 0.000200 | 0.000210 | 0.000185 | 0.000165 |
