You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000019_00850
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000019_00850
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Enterobacter cloacae_O | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Enterobacterales; Enterobacteriaceae; Enterobacter; Enterobacter cloacae_O | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000019_00850 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH23 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 85620; End: 86072 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH23 | 25 | 141 | 1.8e-22 | 0.8518518518518519 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRK15328 | PRK15328 | 2.61e-92 | 12 | 150 | 14 | 152 | type III secretion system invasion protein IagB. |
| cd13400 | LT_IagB-like | 9.46e-53 | 27 | 139 | 1 | 109 | Escherichia coli invasion protein IagB and similar proteins. Lytic transglycosylase-like protein, similar to Escherichia coli invasion protein IagB. IagB is encoded within a pathogenicity island in Salmonella enterica and has been shown to degrade polymeric peptidoglycan. IagB-like invasion proteins are implicated in the invasion of eukaryotic host cells by bacteria. Lytic transglycosylase (LT) catalyzes the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc), as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. Members of this family resemble the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria and the LTs in bacteriophage lambda. |
| pfam01464 | SLT | 1.75e-30 | 20 | 118 | 1 | 96 | Transglycosylase SLT domain. This family is distantly related to pfam00062. Members are found in phages, type II, type III and type IV secretion systems. |
| PRK13722 | PRK13722 | 2.90e-26 | 18 | 141 | 21 | 146 | lytic transglycosylase; Provisional |
| cd00254 | LT-like | 8.44e-15 | 31 | 138 | 1 | 111 | lytic transglycosylase(LT)-like domain. Members include the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria and LTs in bacteriophage lambda. LTs catalyze the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc), as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QLA67095.1 | 1.31e-108 | 1 | 150 | 1 | 150 |
| QKZ99780.1 | 1.86e-108 | 1 | 150 | 1 | 150 |
| QLA60923.1 | 2.34e-102 | 1 | 150 | 1 | 150 |
| ADF62327.1 | 2.34e-102 | 1 | 150 | 1 | 150 |
| QCZ37936.1 | 6.72e-102 | 1 | 150 | 1 | 150 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4XP8_A | 7.61e-12 | 18 | 102 | 2 | 87 | Structureof EtgA D60N mutant [Escherichia coli] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1WAC2 | 1.14e-45 | 9 | 149 | 11 | 151 | Invasion protein IagB OS=Salmonella typhimurium (strain SL1344) OX=216597 GN=iagB PE=3 SV=1 |
| P0CL15 | 1.14e-45 | 9 | 149 | 11 | 151 | Invasion protein IagB OS=Salmonella typhimurium (strain LT2 / SGSC1412 / ATCC 700720) OX=99287 GN=iagB PE=3 SV=1 |
| P43018 | 3.26e-45 | 9 | 149 | 11 | 151 | Invasion protein IagB OS=Salmonella typhi OX=90370 GN=iagB PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q07568 | 1.28e-35 | 1 | 149 | 1 | 148 | Protein IpgF OS=Shigella flexneri OX=623 GN=ipgF PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q55287 | 2.07e-34 | 1 | 149 | 1 | 148 | Protein IpgF OS=Shigella sonnei OX=624 GN=ipgF PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
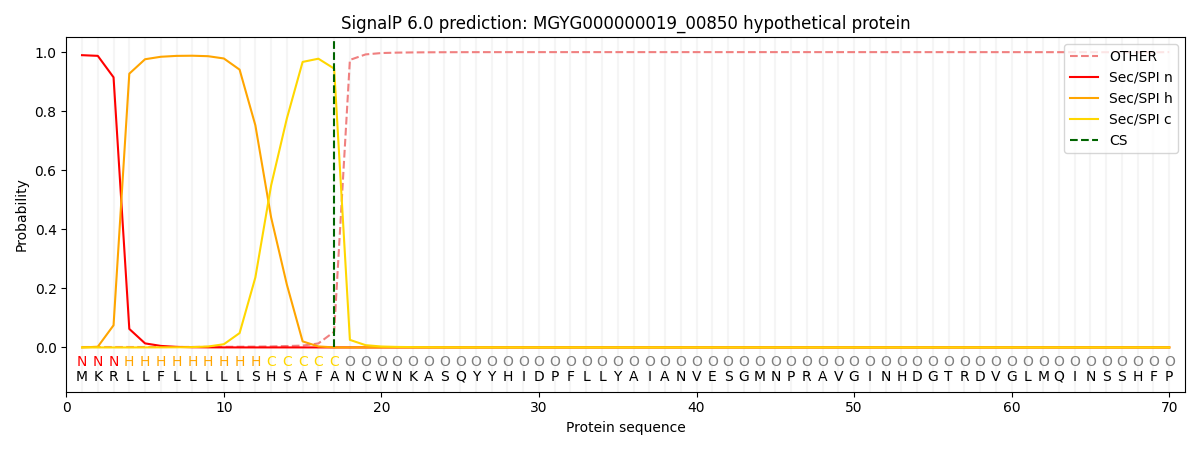
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.003533 | 0.984417 | 0.011234 | 0.000274 | 0.000254 | 0.000265 |
