You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000029_03135
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000029_03135
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Bacteroides finegoldii | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; Bacteroides; Bacteroides finegoldii | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000029_03135 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH18 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 9398; End: 10543 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd06542 | GH18_EndoS-like | 8.72e-53 | 63 | 356 | 1 | 255 | Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases are bacterial chitinases that hydrolyze the chitin core of various asparagine (N)-linked glycans and glycoproteins. The endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases have a glycosyl hydrolase family 18 (GH18) catalytic domain. Some members also have an additional C-terminal glycosyl hydrolase family 20 (GH20) domain while others have an N-terminal domain of unknown function (pfam08522). Members of this family include endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase S (EndoS) from Streptococcus pyogenes, EndoF1, EndoF2, EndoF3, and EndoH from Flavobacterium meningosepticum, and EndoE from Enterococcus faecalis. EndoS is a secreted endoglycosidase from Streptococcus pyogenes that specifically hydrolyzes the glycan on human IgG between two core N-acetylglucosamine residues. EndoE is a secreted endoglycosidase, encoded by the ndoE gene in Enterococcus faecalis, that hydrolyzes the glycan on human RNase B. |
| pfam16141 | DUF4849 | 7.47e-32 | 22 | 361 | 1 | 318 | Putative glycoside hydrolase Family 18, chitinase_18. This DUF is likely to be a form of glycosyl hydrolase from CAZy family 18, possibly chitinase 18. This would have the EC number of EC:3.2.1.14. |
| COG3325 | ChiA | 0.006 | 172 | 300 | 136 | 281 | Chitinase, GH18 family [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| cd06548 | GH18_chitinase | 0.007 | 172 | 286 | 94 | 209 | The GH18 (glycosyl hydrolases, family 18) type II chitinases hydrolyze chitin, an abundant polymer of N-acetylglucosamine and have been identified in bacteria, fungi, insects, plants, viruses, and protozoan parasites. The structure of this domain is an eight-stranded alpha/beta barrel with a pronounced active-site cleft at the C-terminal end of the beta-barrel. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QPH59426.1 | 2.02e-196 | 1 | 370 | 1 | 362 |
| QMI80610.1 | 1.17e-195 | 1 | 370 | 1 | 362 |
| QBJ19126.1 | 1.17e-195 | 1 | 370 | 1 | 362 |
| ALJ48449.1 | 8.43e-178 | 1 | 374 | 1 | 365 |
| QRQ55290.1 | 8.43e-178 | 1 | 374 | 1 | 365 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6Q64_A | 1.85e-39 | 46 | 366 | 58 | 359 | BT1044SeMetE190Q [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
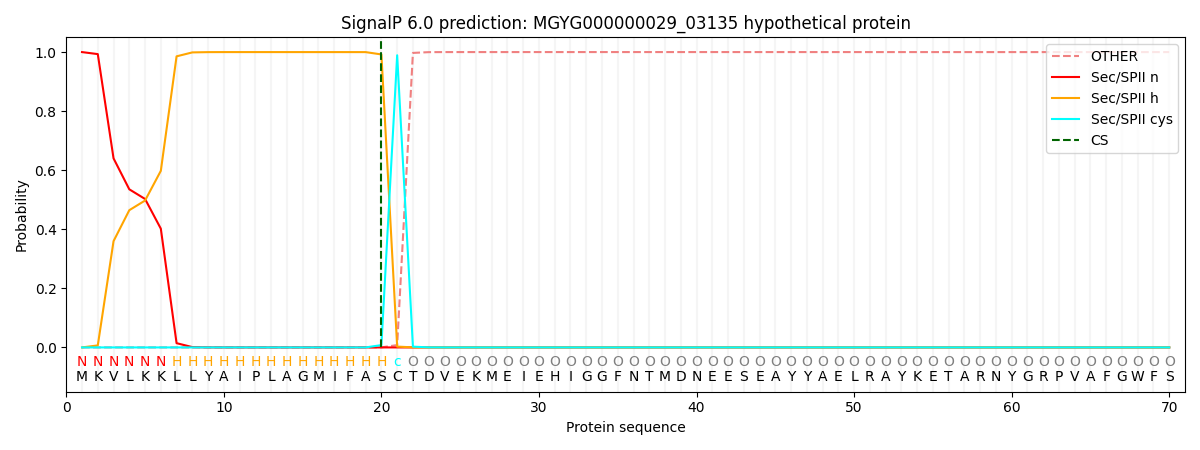
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000000 | 0.000003 | 1.000054 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
