You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000044_01355
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000044_01355
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Parabacteroides merdae | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Tannerellaceae; Parabacteroides; Parabacteroides merdae | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000044_01355 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH20 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Beta-hexosaminidase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 527679; End: 529253 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH20 | 136 | 473 | 4.8e-113 | 0.973293768545994 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd06563 | GH20_chitobiase-like | 1.43e-170 | 141 | 486 | 1 | 357 | The chitobiase of Serratia marcescens is a beta-N-1,4-acetylhexosaminidase with a glycosyl hydrolase family 20 (GH20) domain that hydrolyzes the beta-1,4-glycosidic linkages in oligomers derived from chitin. Chitin is degraded by a two step process: i) a chitinase hydrolyzes the chitin to oligosaccharides and disaccharides such as di-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and chitobiose, ii) chitobiase then further degrades these oligomers into monomers. This GH20 domain family includes an N-acetylglucosamidase (GlcNAcase A) from Pseudoalteromonas piscicida and an N-acetylhexosaminidase (SpHex) from Streptomyces plicatus. SpHex lacks the C-terminal PKD (polycystic kidney disease I)-like domain found in the chitobiases. The GH20 hexosaminidases are thought to act via a catalytic mechanism in which the catalytic nucleophile is not provided by solvent or the enzyme, but by the substrate itself. |
| pfam00728 | Glyco_hydro_20 | 4.65e-149 | 141 | 473 | 1 | 345 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 20, catalytic domain. This domain has a TIM barrel fold. |
| cd06568 | GH20_SpHex_like | 7.27e-101 | 141 | 474 | 1 | 317 | A subgroup of the Glycosyl hydrolase family 20 (GH20) catalytic domain found in proteins similar to the N-acetylhexosaminidase from Streptomyces plicatus (SpHex). SpHex catalyzes the hydrolysis of N-acetyl-beta-hexosaminides. An Asp residue within the active site plays a critical role in substrate-assisted catalysis by orienting the 2-acetamido group and stabilizing the transition state. The GH20 hexosaminidases are thought to act via a catalytic mechanism in which the catalytic nucleophile is not provided by solvent or the enzyme, but by the substrate itself. Proteins belonging to this subgroup lack the C-terminal PKD (polycystic kidney disease I)-like domain found in the chitobiases. |
| COG3525 | Chb | 1.40e-93 | 20 | 487 | 132 | 629 | N-acetyl-beta-hexosaminidase [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| cd06562 | GH20_HexA_HexB-like | 3.04e-93 | 141 | 489 | 1 | 340 | Beta-N-acetylhexosaminidases catalyze the removal of beta-1,4-linked N-acetyl-D-hexosamine residues from the non-reducing ends of N-acetyl-beta-D-hexosaminides including N-acetylglucosides and N-acetylgalactosides. The hexA and hexB genes encode the alpha- and beta-subunits of the two major beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase isoenzymes, N-acetyl-beta-D-hexosaminidase A (HexA) and beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase B (HexB). Both the alpha and the beta catalytic subunits have a TIM-barrel fold and belong to the glycosyl hydrolase family 20 (GH20). The HexA enzyme is a heterodimer containing one alpha and one beta subunit while the HexB enzyme is a homodimer containing two beta-subunits. Hexosaminidase mutations cause an inability to properly hydrolyze certain sphingolipids which accumulate in lysosomes within the brain, resulting in the lipid storage disorders Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff. Mutations in the alpha subunit cause in a deficiency in the HexA enzyme and result in Tay-Sachs, mutations in the beta-subunit cause in a deficiency in both HexA and HexB enzymes and result in Sandhoff disease. In both disorders GM(2) gangliosides accumulate in lysosomes. The GH20 hexosaminidases are thought to act via a catalytic mechanism in which the catalytic nucleophile is not provided by solvent or the enzyme, but by the substrate itself. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QUT50216.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 524 | 1 | 524 |
| AUI48789.1 | 1.43e-256 | 10 | 524 | 22 | 511 |
| QLK81785.1 | 2.87e-256 | 10 | 524 | 22 | 511 |
| QCQ44390.1 | 2.87e-256 | 10 | 524 | 22 | 511 |
| QKH85477.1 | 4.08e-256 | 10 | 524 | 22 | 511 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7CBN_A | 7.98e-102 | 19 | 505 | 9 | 515 | Crystalstructure of beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase Am0868 from Akkermansia muciniphila [Akkermansia muciniphila ATCC BAA-835],7CBO_A Crystal structure of beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase Am0868 from Akkermansia muciniphila in complex with GlcNAc [Akkermansia muciniphila ATCC BAA-835] |
| 6EZR_A | 3.68e-84 | 22 | 504 | 140 | 641 | Crystalstructure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi [Vibrio harveyi],6EZR_B Crystal structure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi [Vibrio harveyi],6EZS_A Crystal structure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi in complex with N-acetylglucosamine [Vibrio harveyi],6EZS_B Crystal structure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi in complex with N-acetylglucosamine [Vibrio harveyi],6K35_A Crystal structure of GH20 exo beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi in complex with NAG-thiazoline [Vibrio harveyi],6K35_B Crystal structure of GH20 exo beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi in complex with NAG-thiazoline [Vibrio harveyi] |
| 6EZT_A | 5.10e-83 | 22 | 504 | 137 | 638 | Crystalstructure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase D437A inactive mutant from Vibrio harveyi [Vibrio harveyi],6EZT_B Crystal structure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase D437A inactive mutant from Vibrio harveyi [Vibrio harveyi] |
| 6Q63_A | 1.82e-80 | 91 | 513 | 106 | 552 | BT0459[Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron],6Q63_B BT0459 [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron],6Q63_C BT0459 [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron] |
| 3RCN_A | 5.34e-80 | 20 | 512 | 6 | 521 | CrystalStructure of Beta-N-Acetylhexosaminidase from Arthrobacter aurescens [Paenarthrobacter aurescens TC1] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B2UQG6 | 2.34e-100 | 17 | 505 | 25 | 534 | Beta-hexosaminidase Amuc_0868 OS=Akkermansia muciniphila (strain ATCC BAA-835 / DSM 22959 / JCM 33894 / BCRC 81048 / CCUG 64013 / CIP 107961 / Muc) OX=349741 GN=Amuc_0868 PE=1 SV=1 |
| P49008 | 8.11e-88 | 53 | 503 | 74 | 535 | Beta-hexosaminidase OS=Porphyromonas gingivalis (strain ATCC BAA-308 / W83) OX=242619 GN=nahA PE=3 SV=2 |
| P96155 | 1.55e-77 | 24 | 469 | 141 | 603 | Beta-hexosaminidase OS=Vibrio furnissii OX=29494 GN=exoI PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q7WUL4 | 5.93e-64 | 74 | 498 | 65 | 475 | Beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase OS=Cellulomonas fimi OX=1708 GN=hex20 PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q04786 | 2.43e-55 | 24 | 478 | 200 | 724 | Beta-hexosaminidase OS=Vibrio vulnificus OX=672 GN=hex PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
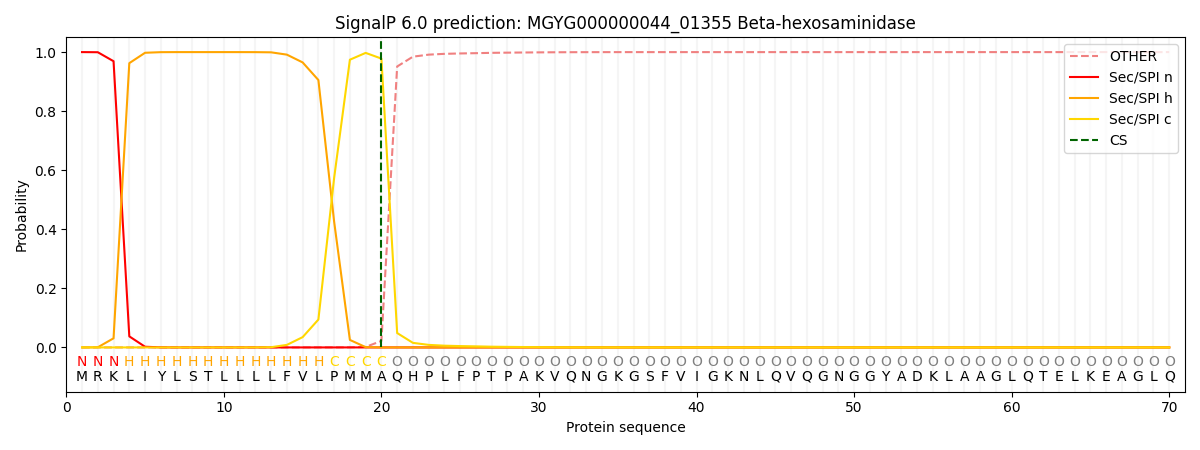
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000262 | 0.999094 | 0.000171 | 0.000153 | 0.000149 | 0.000141 |
