You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000096_01067
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000096_01067
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Lactobacillales; Lactobacillaceae; Leuconostoc; Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000096_01067 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM50 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 363550; End: 364701 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRK10783 | mltD | 4.35e-12 | 27 | 132 | 342 | 446 | membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase D; Provisional |
| pfam01476 | LysM | 9.43e-11 | 90 | 133 | 1 | 43 | LysM domain. The LysM (lysin motif) domain is about 40 residues long. It is found in a variety of enzymes involved in bacterial cell wall degradation. This domain may have a general peptidoglycan binding function. The structure of this domain is known. |
| cd00118 | LysM | 1.41e-10 | 89 | 132 | 2 | 45 | Lysin Motif is a small domain involved in binding peptidoglycan. LysM, a small globular domain with approximately 40 amino acids, is a widespread protein module involved in binding peptidoglycan in bacteria and chitin in eukaryotes. The domain was originally identified in enzymes that degrade bacterial cell walls, but proteins involved in many other biological functions also contain this domain. It has been reported that the LysM domain functions as a signal for specific plant-bacteria recognition in bacterial pathogenesis. Many of these enzymes are modular and are composed of catalytic units linked to one or several repeats of LysM domains. LysM domains are found in bacteria and eukaryotes. |
| pfam00188 | CAP | 1.90e-10 | 285 | 376 | 5 | 105 | Cysteine-rich secretory protein family. This is a large family of cysteine-rich secretory proteins, antigen 5, and pathogenesis-related 1 proteins (CAP) that are found in a wide range of organisms, including prokaryotes and non-vertebrate eukaryotes, The nine subfamilies of the mammalian CAP 'super'family include: the human glioma pathogenesis-related 1 (GLIPR1), Golgi associated pathogenesis related-1 (GAPR1) proteins, peptidase inhibitor 15 (PI15), peptidase inhibitor 16 (PI16), cysteine-rich secretory proteins (CRISPs), CRISP LCCL domain containing 1 (CRISPLD1), CRISP LCCL domain containing 2 (CRISPLD2), mannose receptor like and the R3H domain containing like proteins. Members are most often secreted and have an extracellular endocrine or paracrine function and are involved in processes including the regulation of extracellular matrix and branching morphogenesis, potentially as either proteases or protease inhibitors; in ion channel regulation in fertility; as tumor suppressor or pro-oncogenic genes in tissues including the prostate; and in cell-cell adhesion during fertilisation. The overall protein structural conservation within the CAP 'super'family results in fundamentally similar functions for the CAP domain in all members, yet the diversity outside of this core region dramatically alters the target specificity and, thus, the biological consequences. The Ca++-chelating function would fit with the various signalling processes (e.g. the CRISP proteins) that members of this family are involved in, and also the sequence and structural evidence of a conserved pocket containing two histidines and a glutamate. It also may explain how the cysteine-rich venom protein helothermine blocks the Ca++ transporting ryanodine receptors. |
| cd00118 | LysM | 4.71e-10 | 30 | 73 | 2 | 45 | Lysin Motif is a small domain involved in binding peptidoglycan. LysM, a small globular domain with approximately 40 amino acids, is a widespread protein module involved in binding peptidoglycan in bacteria and chitin in eukaryotes. The domain was originally identified in enzymes that degrade bacterial cell walls, but proteins involved in many other biological functions also contain this domain. It has been reported that the LysM domain functions as a signal for specific plant-bacteria recognition in bacterial pathogenesis. Many of these enzymes are modular and are composed of catalytic units linked to one or several repeats of LysM domains. LysM domains are found in bacteria and eukaryotes. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QQB27187.1 | 3.59e-172 | 1 | 383 | 1 | 381 |
| QEA41112.1 | 3.59e-172 | 1 | 383 | 1 | 381 |
| QSB51658.1 | 1.56e-171 | 1 | 383 | 1 | 383 |
| QQB01765.1 | 5.60e-163 | 1 | 383 | 1 | 386 |
| API71422.1 | 9.55e-124 | 1 | 383 | 1 | 436 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2MKX_A | 7.62e-06 | 90 | 133 | 7 | 49 | Solutionstructure of LysM the peptidoglycan binding domain of autolysin AtlA from Enterococcus faecalis [Enterococcus faecalis V583] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q49UX4 | 4.08e-12 | 27 | 141 | 25 | 138 | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase sle1 OS=Staphylococcus saprophyticus subsp. saprophyticus (strain ATCC 15305 / DSM 20229 / NCIMB 8711 / NCTC 7292 / S-41) OX=342451 GN=sle1 PE=3 SV=1 |
| P37710 | 1.65e-08 | 33 | 144 | 569 | 686 | Autolysin OS=Enterococcus faecalis (strain ATCC 700802 / V583) OX=226185 GN=EF_0799 PE=1 SV=2 |
| O34669 | 9.02e-08 | 5 | 142 | 1 | 131 | Cell wall-binding protein YocH OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=yocH PE=1 SV=1 |
| P11187 | 1.75e-07 | 32 | 132 | 164 | 257 | Endolysin OS=Bacillus phage phi29 OX=10756 GN=15 PE=1 SV=1 |
| P07540 | 1.75e-07 | 32 | 132 | 164 | 257 | Endolysin OS=Bacillus phage PZA OX=10757 GN=15 PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
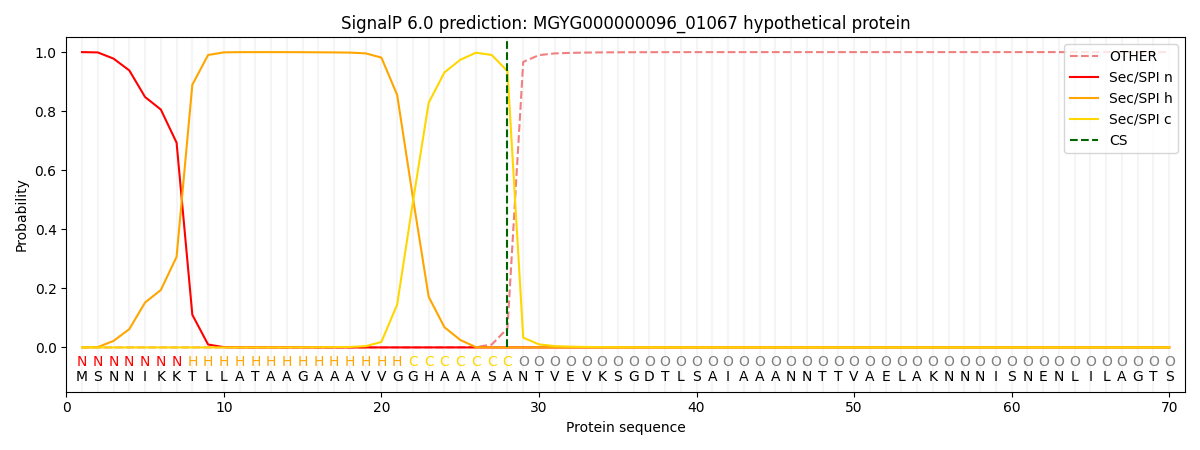
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000362 | 0.998929 | 0.000177 | 0.000177 | 0.000166 | 0.000146 |
