You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000096_01114
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000096_01114
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
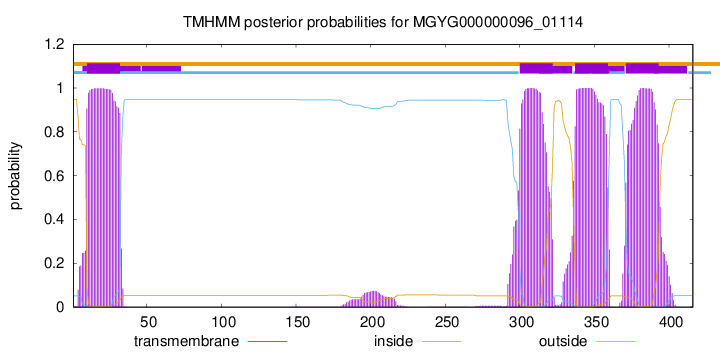
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Lactobacillales; Lactobacillaceae; Leuconostoc; Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000096_01114 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT2 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine synthase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 413911; End: 415161 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT2 | 50 | 272 | 1.5e-27 | 0.9739130434782609 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRK11204 | PRK11204 | 1.92e-70 | 15 | 415 | 17 | 418 | N-glycosyltransferase; Provisional |
| COG1215 | BcsA | 4.99e-41 | 15 | 413 | 18 | 432 | Glycosyltransferase, catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase and poly-beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine synthase [Cell motility]. |
| cd06423 | CESA_like | 5.67e-39 | 53 | 231 | 2 | 180 | CESA_like is the cellulose synthase superfamily. The cellulose synthase (CESA) superfamily includes a wide variety of glycosyltransferase family 2 enzymes that share the common characteristic of catalyzing the elongation of polysaccharide chains. The members include cellulose synthase catalytic subunit, chitin synthase, glucan biosynthesis protein and other families of CESA-like proteins. Cellulose synthase catalyzes the polymerization reaction of cellulose, an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues in plants, most algae, some bacteria and fungi, and even some animals. In bacteria, algae and lower eukaryotes, there is a second unrelated type of cellulose synthase (Type II), which produces acylated cellulose, a derivative of cellulose. Chitin synthase catalyzes the incorporation of GlcNAc from substrate UDP-GlcNAc into chitin, which is a linear homopolymer of beta-(1,4)-linked GlcNAc residues and Glucan Biosynthesis protein catalyzes the elongation of beta-1,2 polyglucose chains of Glucan. |
| PRK14583 | hmsR | 3.88e-38 | 53 | 416 | 80 | 440 | poly-beta-1,6 N-acetyl-D-glucosamine synthase. |
| pfam00535 | Glycos_transf_2 | 4.66e-25 | 53 | 217 | 3 | 164 | Glycosyl transferase family 2. Diverse family, transferring sugar from UDP-glucose, UDP-N-acetyl- galactosamine, GDP-mannose or CDP-abequose, to a range of substrates including cellulose, dolichol phosphate and teichoic acids. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QQB01722.1 | 1.14e-278 | 1 | 415 | 1 | 415 |
| QQB27140.1 | 1.14e-278 | 1 | 415 | 1 | 415 |
| QEA41065.1 | 4.65e-278 | 1 | 415 | 1 | 415 |
| AUS69134.1 | 7.91e-98 | 5 | 413 | 20 | 438 |
| AVH74897.1 | 8.12e-97 | 6 | 413 | 21 | 436 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q8GLC5 | 7.34e-45 | 15 | 413 | 10 | 407 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine synthase OS=Staphylococcus epidermidis OX=1282 GN=icaA PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q5HKQ0 | 1.43e-44 | 15 | 413 | 10 | 407 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine synthase OS=Staphylococcus epidermidis (strain ATCC 35984 / RP62A) OX=176279 GN=icaA PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q5HCN1 | 1.50e-40 | 15 | 413 | 10 | 407 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine synthase OS=Staphylococcus aureus (strain COL) OX=93062 GN=icaA PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q9RQP9 | 1.50e-40 | 15 | 413 | 10 | 407 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine synthase OS=Staphylococcus aureus (strain NCTC 8325 / PS 47) OX=93061 GN=icaA PE=3 SV=2 |
| Q7A351 | 1.50e-40 | 15 | 413 | 10 | 407 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine synthase OS=Staphylococcus aureus (strain N315) OX=158879 GN=icaA PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
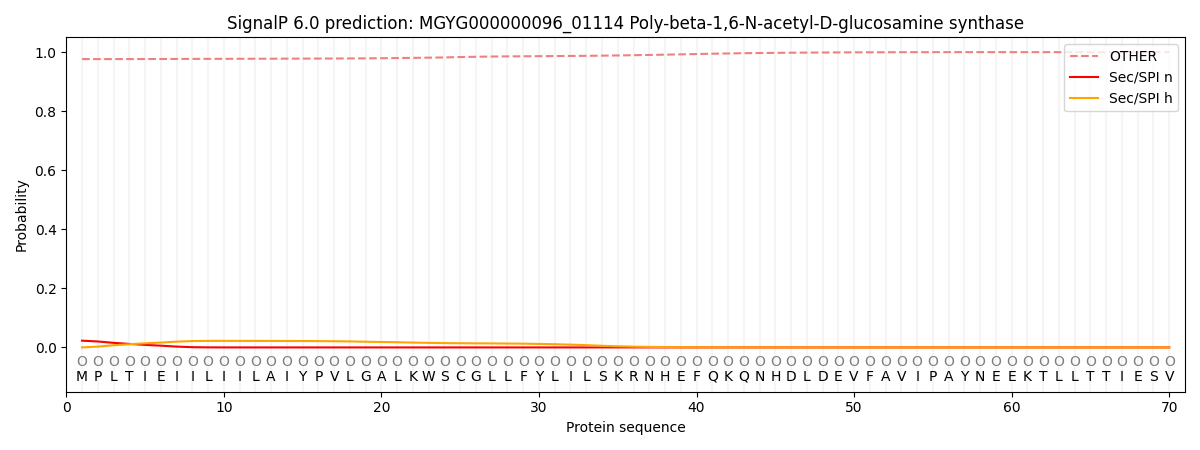
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.977677 | 0.021035 | 0.000857 | 0.000093 | 0.000060 | 0.000309 |