You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000096_01183
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000096_01183
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Lactobacillales; Lactobacillaceae; Leuconostoc; Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000096_01183 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH23 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 478687; End: 479328 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd13402 | LT_TF-like | 7.66e-05 | 143 | 199 | 8 | 74 | lytic transglycosylase-like domain of tail fiber-like proteins and similar domains. These tail fiber-like proteins are multi-domain proteins that include a lytic transglycosylase (LT) domain. Members of the LT family include the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria, the LTs in bacteriophage lambda, and the eukaryotic "goose-type" lysozymes (goose egg-white lysozyme; GEWL). LTs catalyze the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc), as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QEA42983.1 | 1.94e-137 | 1 | 213 | 4 | 216 |
| QQB27098.1 | 1.94e-137 | 1 | 213 | 4 | 216 |
| QSB51572.1 | 2.08e-91 | 1 | 213 | 4 | 219 |
| QQB01678.1 | 1.11e-81 | 1 | 213 | 4 | 219 |
| QXC53734.1 | 1.96e-63 | 1 | 213 | 4 | 222 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
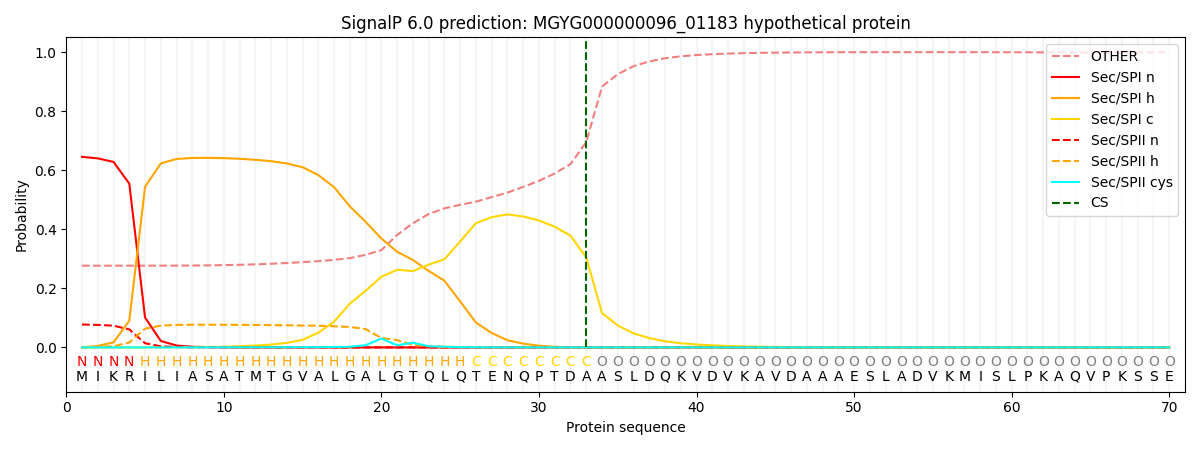
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.283924 | 0.635430 | 0.079001 | 0.000945 | 0.000383 | 0.000300 |
