You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000097_01413
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000097_01413
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
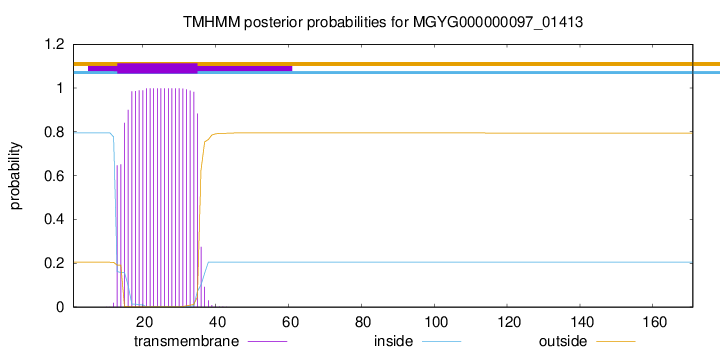
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Ligilactobacillus animalis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Lactobacillales; Lactobacillaceae; Ligilactobacillus; Ligilactobacillus animalis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000097_01413 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM50 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 24561; End: 25076 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam01476 | LysM | 4.69e-13 | 115 | 157 | 1 | 43 | LysM domain. The LysM (lysin motif) domain is about 40 residues long. It is found in a variety of enzymes involved in bacterial cell wall degradation. This domain may have a general peptidoglycan binding function. The structure of this domain is known. |
| cd00118 | LysM | 2.34e-12 | 114 | 156 | 2 | 45 | Lysin Motif is a small domain involved in binding peptidoglycan. LysM, a small globular domain with approximately 40 amino acids, is a widespread protein module involved in binding peptidoglycan in bacteria and chitin in eukaryotes. The domain was originally identified in enzymes that degrade bacterial cell walls, but proteins involved in many other biological functions also contain this domain. It has been reported that the LysM domain functions as a signal for specific plant-bacteria recognition in bacterial pathogenesis. Many of these enzymes are modular and are composed of catalytic units linked to one or several repeats of LysM domains. LysM domains are found in bacteria and eukaryotes. |
| smart00257 | LysM | 1.28e-09 | 114 | 156 | 1 | 44 | Lysin motif. |
| PRK10783 | mltD | 1.79e-08 | 113 | 156 | 344 | 387 | membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase D; Provisional |
| COG1388 | LysM | 9.74e-07 | 72 | 157 | 26 | 111 | LysM repeat [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QHQ69596.1 | 3.69e-107 | 1 | 171 | 1 | 171 |
| AWZ40421.1 | 2.02e-74 | 1 | 171 | 1 | 170 |
| QIA89727.1 | 2.02e-74 | 1 | 171 | 1 | 170 |
| AWZ38583.1 | 2.02e-74 | 1 | 171 | 1 | 170 |
| QCQ03518.1 | 1.37e-73 | 1 | 171 | 1 | 175 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4UZ2_A | 3.84e-07 | 114 | 160 | 4 | 50 | Crystalstructure of the N-terminal LysM domains from the putative NlpC/P60 D,L endopeptidase from T. thermophilus [Thermus thermophilus HB8],4UZ2_B Crystal structure of the N-terminal LysM domains from the putative NlpC/P60 D,L endopeptidase from T. thermophilus [Thermus thermophilus HB8],4UZ2_C Crystal structure of the N-terminal LysM domains from the putative NlpC/P60 D,L endopeptidase from T. thermophilus [Thermus thermophilus HB8],4UZ2_D Crystal structure of the N-terminal LysM domains from the putative NlpC/P60 D,L endopeptidase from T. thermophilus [Thermus thermophilus HB8],4UZ3_A Crystal structure of the N-terminal LysM domains from the putative NlpC/P60 D,L endopeptidase from T. thermophilus bound to N-acetyl-chitohexaose [Thermus thermophilus HB8],4UZ3_B Crystal structure of the N-terminal LysM domains from the putative NlpC/P60 D,L endopeptidase from T. thermophilus bound to N-acetyl-chitohexaose [Thermus thermophilus HB8],4UZ3_C Crystal structure of the N-terminal LysM domains from the putative NlpC/P60 D,L endopeptidase from T. thermophilus bound to N-acetyl-chitohexaose [Thermus thermophilus HB8] |
| 4XCM_A | 4.02e-06 | 114 | 160 | 4 | 50 | Crystalstructure of the putative NlpC/P60 D,L endopeptidase from T. thermophilus [Thermus thermophilus HB8],4XCM_B Crystal structure of the putative NlpC/P60 D,L endopeptidase from T. thermophilus [Thermus thermophilus HB8] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.995245 | 0.000231 | 0.000283 | 0.000002 | 0.000001 | 0.004274 |