You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000170_01892
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000170_01892
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Alistipes_A sp900240235 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Rikenellaceae; Alistipes_A; Alistipes_A sp900240235 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000170_01892 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH36 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 287329; End: 289404 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH36 | 79 | 668 | 1.1e-85 | 0.8604651162790697 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd14791 | GH36 | 2.41e-49 | 306 | 505 | 10 | 206 | glycosyl hydrolase family 36 (GH36). GH36 enzymes occur in prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and archaea with a wide range of hydrolytic activities, including alpha-galactosidase, alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase, stachyose synthase, and raffinose synthase. All GH36 enzymes cleave a terminal carbohydrate moiety from a substrate that varies considerably in size, depending on the enzyme, and may be either a starch or a glycoprotein. GH36 members are retaining enzymes that cleave their substrates via an acid/base-catalyzed, double-displacement mechanism involving a covalent glycosyl-enzyme intermediate. Two aspartic acid residues have been identified as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, respectively. |
| pfam02065 | Melibiase | 4.75e-33 | 291 | 505 | 30 | 247 | Melibiase. Glycoside hydrolase families GH27, GH31 and GH36 form the glycoside hydrolase clan GH-D. Glycoside hydrolase family 36 can be split into 11 families, GH36A to GH36K. This family includes enzymes from GH36A-B and GH36D-K and from GH27. |
| COG3345 | GalA | 4.72e-24 | 309 | 539 | 303 | 524 | Alpha-galactosidase [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| COG1501 | YicI | 8.43e-10 | 276 | 489 | 237 | 454 | Alpha-glucosidase, glycosyl hydrolase family GH31 [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| cd06589 | GH31 | 2.02e-08 | 315 | 423 | 24 | 118 | glycosyl hydrolase family 31 (GH31). GH31 enzymes occur in prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and archaea with a wide range of hydrolytic activities, including alpha-glucosidase (glucoamylase and sucrase-isomaltase), alpha-xylosidase, 6-alpha-glucosyltransferase, 3-alpha-isomaltosyltransferase and alpha-1,4-glucan lyase. All GH31 enzymes cleave a terminal carbohydrate moiety from a substrate that varies considerably in size, depending on the enzyme, and may be either a starch or a glycoprotein. In most cases, the pyranose moiety recognized in subsite -1 of the substrate binding site is an alpha-D-glucose, though some GH31 family members show a preference for alpha-D-xylose. Several GH31 enzymes can accommodate both glucose and xylose and different levels of discrimination between the two have been observed. Most characterized GH31 enzymes are alpha-glucosidases. In mammals, GH31 members with alpha-glucosidase activity are implicated in at least three distinct biological processes. The lysosomal acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA) is essential for glycogen degradation and a deficiency or malfunction of this enzyme causes glycogen storage disease II, also known as Pompe disease. In the endoplasmic reticulum, alpha-glucosidase II catalyzes the second step in the N-linked oligosaccharide processing pathway that constitutes part of the quality control system for glycoprotein folding and maturation. The intestinal enzymes sucrase-isomaltase (SI) and maltase-glucoamylase (MGAM) play key roles in the final stage of carbohydrate digestion, making alpha-glucosidase inhibitors useful in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. GH31 alpha-glycosidases are retaining enzymes that cleave their substrates via an acid/base-catalyzed, double-displacement mechanism involving a covalent glycosyl-enzyme intermediate. Two aspartic acid residues have been identified as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, respectively. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QGA23301.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 691 | 1 | 691 |
| QDM10797.1 | 0.0 | 20 | 690 | 9 | 692 |
| QQR15697.1 | 0.0 | 20 | 690 | 9 | 692 |
| ANU59398.1 | 0.0 | 20 | 690 | 9 | 692 |
| CBK67650.1 | 0.0 | 20 | 690 | 9 | 692 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3MI6_A | 1.05e-27 | 85 | 518 | 125 | 549 | ChainA, Alpha-galactosidase [Levilactobacillus brevis ATCC 367],3MI6_B Chain B, Alpha-galactosidase [Levilactobacillus brevis ATCC 367],3MI6_C Chain C, Alpha-galactosidase [Levilactobacillus brevis ATCC 367],3MI6_D Chain D, Alpha-galactosidase [Levilactobacillus brevis ATCC 367] |
| 6JHP_A | 5.30e-25 | 64 | 666 | 140 | 739 | Crystalstructure of the glycoside hydrolase family 36 alpha-galactosidase from Paecilomyces thermophila [Paecilomyces sp. 'thermophila'],6JHP_B Crystal structure of the glycoside hydrolase family 36 alpha-galactosidase from Paecilomyces thermophila [Paecilomyces sp. 'thermophila'],6JHP_C Crystal structure of the glycoside hydrolase family 36 alpha-galactosidase from Paecilomyces thermophila [Paecilomyces sp. 'thermophila'],6JHP_D Crystal structure of the glycoside hydrolase family 36 alpha-galactosidase from Paecilomyces thermophila [Paecilomyces sp. 'thermophila'] |
| 4FNQ_A | 1.10e-23 | 64 | 653 | 109 | 692 | Crystalstructure of GH36 alpha-galactosidase AgaB from Geobacillus stearothermophilus [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
| 2XN0_A | 1.93e-23 | 64 | 518 | 113 | 552 | Structureof alpha-galactosidase from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM, PtCl4 derivative [Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM],2XN0_B Structure of alpha-galactosidase from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM, PtCl4 derivative [Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM],2XN1_A Structure of alpha-galactosidase from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM with TRIS [Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM],2XN1_B Structure of alpha-galactosidase from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM with TRIS [Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM],2XN1_C Structure of alpha-galactosidase from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM with TRIS [Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM],2XN1_D Structure of alpha-galactosidase from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM with TRIS [Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM] |
| 2XN2_A | 4.47e-23 | 64 | 518 | 113 | 552 | Structureof alpha-galactosidase from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM with galactose [Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P43467 | 5.37e-26 | 320 | 651 | 353 | 692 | Alpha-galactosidase 1 OS=Pediococcus pentosaceus OX=1255 GN=agaR PE=3 SV=1 |
| P16551 | 6.68e-26 | 172 | 520 | 168 | 507 | Alpha-galactosidase OS=Escherichia coli OX=562 GN=rafA PE=1 SV=1 |
| G1UB44 | 1.06e-22 | 64 | 518 | 113 | 552 | Alpha-galactosidase Mel36A OS=Lactobacillus acidophilus (strain ATCC 700396 / NCK56 / N2 / NCFM) OX=272621 GN=melA PE=1 SV=1 |
| B8NWY6 | 1.92e-22 | 85 | 666 | 149 | 732 | Probable alpha-galactosidase C OS=Aspergillus flavus (strain ATCC 200026 / FGSC A1120 / IAM 13836 / NRRL 3357 / JCM 12722 / SRRC 167) OX=332952 GN=aglC PE=3 SV=2 |
| Q2TW69 | 1.92e-22 | 85 | 666 | 149 | 732 | Probable alpha-galactosidase C OS=Aspergillus oryzae (strain ATCC 42149 / RIB 40) OX=510516 GN=aglC PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
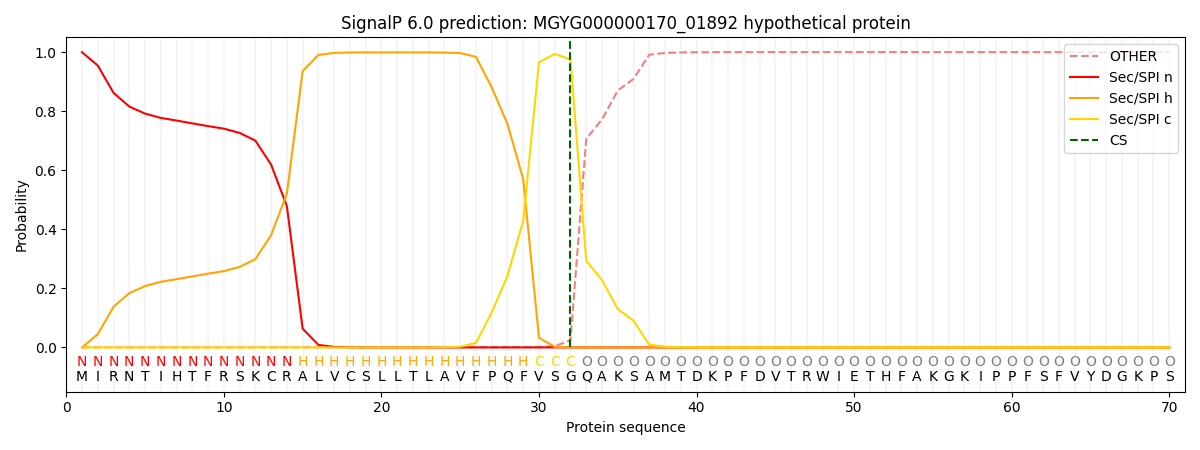
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.001111 | 0.996977 | 0.001061 | 0.000393 | 0.000224 | 0.000189 |
