You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000204_02028
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000204_02028
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
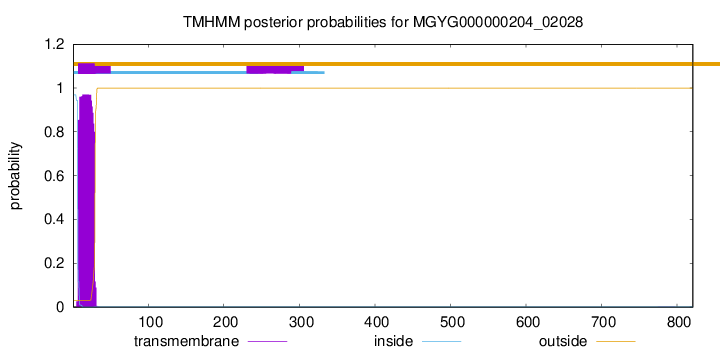
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Eubacterium_G sp000435815 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes_A; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; Lachnospiraceae; Eubacterium_G; Eubacterium_G sp000435815 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000204_02028 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH64 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 52144; End: 54609 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH64 | 468 | 819 | 2e-95 | 0.9863760217983651 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd09214 | GH64-like | 1.50e-109 | 468 | 819 | 1 | 318 | glycosyl hydrolase 64 family. This family is represented by the laminaripentaose-producing, beta-1,3-glucanase (LPHase) of Streptomyces matensis and related bacterial and ascomycete proteins. LPHase is a member of glycoside hydrolase family 64 (GH64), it is an inverting enzyme involved in the cleavage of long-chain polysaccharide beta-1,3-glucans, into specific pentasaccharide oligomers. LPHase is a two-domain crescent fold structure: one domain is composed of 10 beta-strands, eight coming from the N-terminus of the protein and two from the C-terminal region, and the protein has a second inserted domain; this cd includes both domains. This protein has an electronegative, substrate-binding cleft, and conserved Glu and Asp residues involved in the cleavage of the beta-1,3-glucan, laminarin, a plant and fungal cell wall component. Among bacteria, many beta-1,3-glucanases are implicated in fungal cell wall degradation. Also included in this family is GluB , the beta-1,3-glucanase B from Lysobacter enzymogenes Strain N4-7. Recombinant GluB demonstrated higher relative activity toward the branched-chain beta-1,3 glucan substrate zymosan A than toward linear beta-1,3 glucan substrates. Sometimes these two domains are found associated with other domains such as in the Catenulispora acidiphila DSM 44928 carbohydrate binding family 6 protein in which they are positioned N-terminal of a carbohydrate binding module, family 6 (CBM_6) domain. In the Cellulosimicrobium cellulans, glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase, they are positioned N-terminal of a RICIN, carbohydrate-binding domain, and in the Salinispora tropica CNB-440, coagulation factor 5/8 C-terminal domain (FA58C) protein, they are positioned C-terminal of two FA58C domains which are proposed to function as cell surface-attached, carbohydrate-binding domain. This FA58C-containing protein has an internal peptide deletion (of approx. 44 residues) in the LPHase domain II. |
| pfam16483 | Glyco_hydro_64 | 5.49e-89 | 470 | 819 | 5 | 370 | Beta-1,3-glucanase. Family 64 glycoside hydrolases have beta-1,3-glucanase activity. |
| cd09216 | GH64-LPHase-like | 2.25e-49 | 476 | 819 | 6 | 352 | glycoside hydrolase family 64: laminaripentaose-producing, beta-1,3-glucanase (LPHase)-like. This subfamily is represented by the laminaripentaose-producing, beta-1,3-glucanase (LPHase) of Streptomyces matensis and related bacterial and ascomycete proteins. LPHase is a member of glycoside hydrolase family 64 (GH64), it is an inverting enzyme involved in the cleavage of long-chain polysaccharide beta-1,3-glucans, into specific pentasaccharide oligomers. LPHase is a two-domain crescent fold structure: one domain is composed of 10 beta-strands, eight coming from the N-terminus of the protein and two from the C-terminal region, and the protein has a second inserted domain; this cd includes both domains. This protein has an electronegative, substrate-binding cleft, and conserved Glu and Asp residues involved in the cleavage of the beta-1,3-glucan, laminarin, a plant and fungal cell wall component. Among bacteria, many beta-1,3-glucanases are implicated in fungal cell wall degradation. Also included in this family is GluB , the beta-1,3-glucanase B from Lysobacter enzymogenes Strain N4-7. Recombinant GluB demonstrated higher relative activity toward the branched-chain beta-1,3 glucan substrate zymosan A than toward linear beta-1,3 glucan substrates. Sometimes these two domains are found associated with other domains such as in the Catenulispora acidiphila DSM 44928 carbohydrate binding family 6 protein in which they are positioned N-terminal of a carbohydrate binding module, family 6 (CBM_6) domain. In the Cellulosimicrobium cellulans, glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase, they are positioned N-terminal of a RICIN, carbohydrate-binding domain. |
| cd09220 | GH64-GluB-like | 8.52e-35 | 470 | 817 | 3 | 366 | glycoside hydrolase family 64: beta-1,3-glucanase B (GluB)-like. This subfamily is represented by GluB, beta-1,3-glucanase B , from Lysobacter enzymogenes Strain N4-7 and related bacterial and ascomycete proteins. GluB is a member of the glycoside hydrolase family 64 (GH64) involved in the cleavage of long-chain polysaccharide beta-1,3-glucans, into specific pentasaccharide oligomers. Among bacteria, many beta-1,3-glucanases are implicated in fungal cell wall degradation. GluB possesses the conserved Glu and Asp residues required to cleave substrate beta-1,3-glucans. Recombinant GluB demonstrated higher relative activity toward the branched-chain beta-1,3 glucan substrate zymosan A than toward linear beta-1,3 glucan substrates. Based on the structure of laminaripentaose-producing, beta-1,3-glucanase (LPHase) of Streptomyces matensis, which belongs to the same family as GluB but to a different subfamily, this cd is a two-domain model. Sometimes these two domains are found associated with other domains such as in the Catenulispora acidiphila DSM 44928 carbohydrate binding family 6 protein in which they are positioned N-terminal of a carbohydrate binding module, family 6 (CBM_6) domain. |
| NF033909 | opacity_OapA | 4.50e-07 | 108 | 202 | 182 | 283 | opacity-associated protein OapA. This family consists of full-length homologs to OapA, opacity-associated protein A as described in Haemophilus influenzae. OapA shares a C-terminal homology domain, called the OapA domain, with the Escherichia coli protein YtfB, which is now known to bind peptidoglycan through its OapA domain and to act as a cell division protein. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWI66982.1 | 1.21e-138 | 444 | 821 | 89 | 477 |
| CUU48451.1 | 1.51e-87 | 462 | 821 | 217 | 589 |
| ARN22775.1 | 2.16e-87 | 461 | 821 | 207 | 577 |
| ATU67471.1 | 2.16e-87 | 461 | 821 | 207 | 577 |
| AJG99223.1 | 4.10e-87 | 462 | 821 | 217 | 589 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5H4E_A | 2.56e-90 | 462 | 821 | 3 | 375 | Crystalstructure of a beta-1,3-glucanase domain (GH64) from Clostridium beijerinckii [Clostridium beijerinckii NCIMB 8052] |
| 5H9X_A | 5.41e-66 | 468 | 821 | 137 | 444 | Crystalstructure of GH family 64 laminaripentaose-producing beta-1,3-glucanase from Paenibacillus barengoltzii [Paenibacillus barengoltzii] |
| 5H9Y_A | 3.81e-65 | 468 | 821 | 137 | 444 | Crystalstructure of GH family 64 laminaripentaose-producing beta-1,3-glucanase from Paenibacillus barengoltzii complexed with laminarihexaose. [Paenibacillus barengoltzii] |
| 3GD0_A | 5.94e-27 | 544 | 807 | 79 | 351 | ChainA, Laminaripentaose-producing beta-1,3-guluase (LPHase) [Streptomyces matensis],3GD9_A Chain A, Laminaripentaose-producing beta-1,3-guluase (LPHase) [Streptomyces matensis] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q59146 | 5.96e-16 | 544 | 819 | 111 | 394 | Glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase OS=Arthrobacter sp. (strain YCWD3) OX=79671 GN=glcI PE=3 SV=1 |
| P22222 | 7.88e-16 | 544 | 819 | 111 | 394 | Glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase OS=Cellulosimicrobium cellulans OX=1710 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
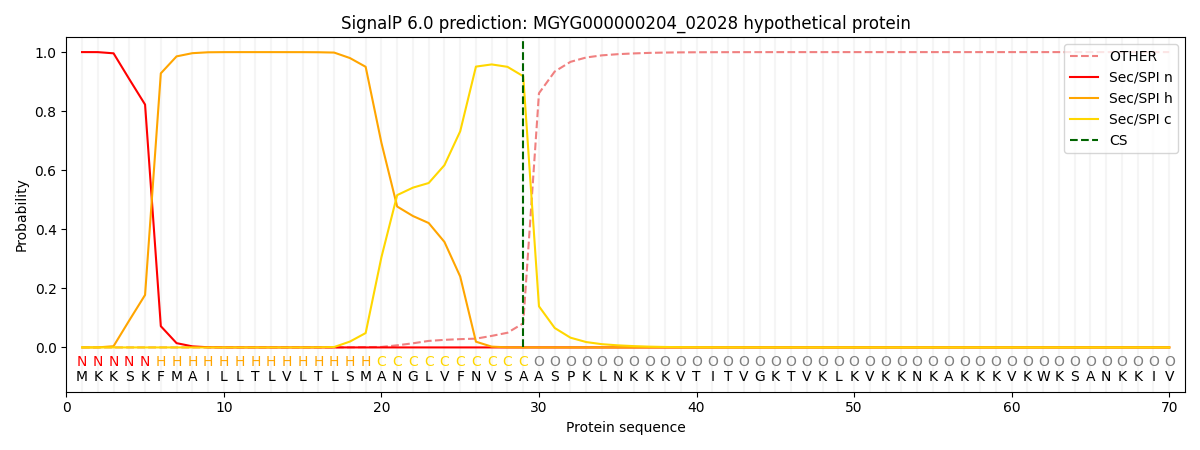
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000281 | 0.999107 | 0.000180 | 0.000148 | 0.000139 | 0.000127 |