You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000211_00343
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000211_00343
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
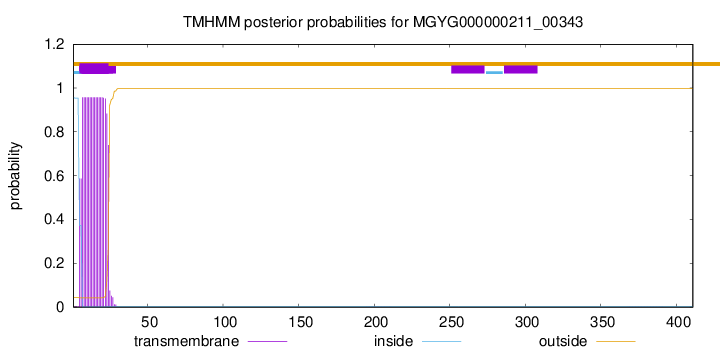
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Bacteroides sp900556215 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; Bacteroides; Bacteroides sp900556215 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000211_00343 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH43 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 515675; End: 516910 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH43 | 90 | 358 | 6.9e-35 | 0.9633699633699634 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd11576 | GH99_GH71_like_2 | 0.0 | 28 | 400 | 1 | 378 | Uncharacterized glycoside hydrolase family 99-like domain. This family of putative glycoside hydrolases resembles glycosyl hydrolase families 71 and 99 (following the CAZY nomenclature) and may share a similar catalytic site and mechanism. The domain may co-occur with other domains involved in the binding/processing of glycans. |
| cd11573 | GH99_GH71_like | 1.48e-41 | 100 | 393 | 8 | 282 | Glycoside hydrolase families 71, 99, and related domains. This superfamily of glycoside hydrolases contains families GH71 and GH99 (following the CAZY nomenclature), as well as other members with undefined function and specificity. |
| cd11578 | GH99_GH71_like_1 | 2.93e-06 | 82 | 360 | 12 | 290 | Uncharacterized glycoside hydrolase family 99-like domain. This family of putative glycoside hydrolases resembles glycosyl hydrolase families 71 and 99 (following the CAZY nomenclature) and may share a similar catalytic site and mechanism. |
| cd11574 | GH99 | 8.54e-05 | 38 | 206 | 5 | 161 | Glycoside hydrolase family 99, an endo-alpha-1,2-mannosidase. This family of glycoside hydrolases 99 (following the CAZY nomenclature) includes endo-alpha-1,2-mannosidase (EC 3.2.1.130), which is an important membrane-associated eukaryotic enzyme involved in the maturation of N-linked glycans. Specifically, it cleaves mannoside linkages internal to N-linked glycan chains by hydrolyzing an alpha-1,2-mannosidic bond between a glucose-substituted mannose and the remainder of the chain. The biological function and significance of the soluble bacterial orthologs, which may have obtained the genes via horizontal transfer, is not clear. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QUT39634.1 | 1.24e-253 | 1 | 401 | 1 | 401 |
| QUT72097.1 | 1.24e-253 | 1 | 401 | 1 | 401 |
| ALJ40802.1 | 3.53e-253 | 1 | 401 | 1 | 401 |
| QQA09893.1 | 3.53e-253 | 1 | 401 | 1 | 401 |
| QIU96999.1 | 1.89e-244 | 1 | 401 | 1 | 401 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
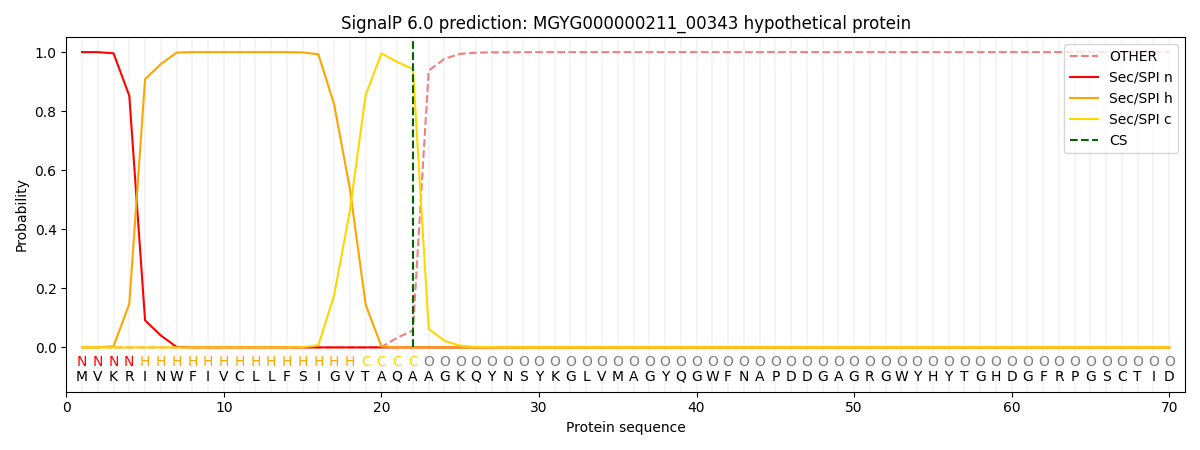
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000220 | 0.999138 | 0.000152 | 0.000163 | 0.000151 | 0.000140 |