You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000380_00623
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000380_00623
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
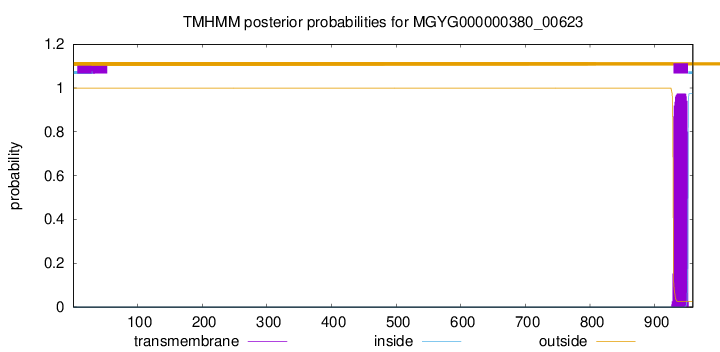
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Erysipelotrichales; Erysipelotrichaceae; Merdibacter; | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000380_00623 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH136 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 1203; End: 4082 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH136 | 12 | 534 | 3.3e-97 | 0.9775967413441955 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd04079 | CBM6_agarase-like | 4.15e-07 | 576 | 698 | 5 | 130 | Carbohydrate Binding Module 6 (CBM6); appended mainly to glycoside hydrolase (GH) family 16 alpha- and beta agarases. This family includes carbohydrate binding module 6 (CBM6) domains that are appended mainly to glycoside hydrolase (GH) family 16 agarases. These CBM6s are non-catalytic carbohydrate binding domains that facilitate the activity of alpha- and beta-agarase catalytic modules which are involved in the hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-D-galactosidic linkages. These CBM6s bind specifically to the non-reducing end of agarose chains, recognizing only the first repeat of the disaccharide, and directing the appended catalytic modules to areas of the plant cell wall attacked by beta-agarases. CBM6 is an unusual CBM as it represents a chimera of two distinct binding sites with different modes of binding: binding site I within the loop regions and binding site II on the concave face of the beta-sandwich fold. This family includes three tandem CBM6s from the Saccharophagus degradans agarase Aga86E, and three tandem CBM6s from Vibrio sp. strain PO-303 AgaA; in both these proteins these are appended to a GH16 domain. Vibrio AgaA also contains a Big-2-like protein-protein interaction domain. This family also includes two tandem CBM6s from an endo-type beta-agarase from a deep-sea Microbulbifer-like isolate, which are appended to a GH16 domain, and two of three CBM6s of Alteromonas agarilytica AgaA alpha-agarase, which are appended to a GH96 domain. |
| pfam13229 | Beta_helix | 4.64e-07 | 227 | 376 | 9 | 137 | Right handed beta helix region. This region contains a parallel beta helix region that shares some similarity with Pectate lyases. |
| pfam17996 | CE2_N | 3.19e-06 | 612 | 678 | 18 | 80 | Carbohydrate esterase 2 N-terminal. This is the N-terminal beta-sheet domain with jelly roll topology found in CE2 acetyl-esterase from the bacterium Clostridium thermocellum. This enzyme displays dual activities, it catalyses the deacetylation of plant polysaccharides and also potentiates the activity of its appended cellulase catalytic module through its noncatalytic cellulose binding function. This N-terminal jelly-roll domain appears to extend the substrate/cellulose binding cleft of the catalytic domain in C.thermocellum. |
| pfam12733 | Cadherin-like | 0.002 | 722 | 793 | 4 | 87 | Cadherin-like beta sandwich domain. This domain is found in several bacterial, metazoan and chlorophyte algal proteins. A profile-profile comparison recovered the cadherin domain and a comparison of the predicted structure of this domain with the crystal structure of the cadherin showed a congruent seven stranded secondary structure. The domain is widespread in bacteria and seen in the firmicutes, actinobacteria, certain proteobacteria, bacteroides and chlamydiae with an expansion in Clostridium. In contrast, it is limited in its distribution in eukaryotes suggesting that it was derived through lateral transfer from bacteria. In prokaryotes, this domain is widely fused to other domains such as FNIII (Fibronectin Type III), TIG, SLH (S-layer homology), discoidin, cell-wall-binding repeat domain and alpha-amylase-like glycohydrolases. These associations are suggestive of a carbohydrate-binding function for this cadherin-like domain. In animal proteins it is associated with an ATP-grasp domain. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AYE35145.1 | 6.50e-176 | 10 | 713 | 34 | 762 |
| AZG68471.1 | 5.02e-119 | 14 | 440 | 118 | 560 |
| QJD84649.1 | 2.95e-61 | 12 | 547 | 255 | 739 |
| QNK55089.1 | 5.68e-61 | 12 | 547 | 254 | 740 |
| QNK55088.1 | 5.58e-59 | 12 | 548 | 58 | 544 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7V6M_A | 5.09e-32 | 10 | 534 | 8 | 568 | ChainA, Fibronectin type III domain-containing protein [Tyzzerella nexilis] |
| 6KQT_A | 1.63e-25 | 14 | 384 | 247 | 620 | CrystalStructure of GH136 lacto-N-biosidase from Eubacterium ramulus - native protein [Eubacterium ramulus ATCC 29099] |
| 6KQS_A | 2.68e-24 | 14 | 356 | 247 | 595 | CrystalStructure of GH136 lacto-N-biosidase from Eubacterium ramulus - selenomethionine derivative [Eubacterium ramulus ATCC 29099] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
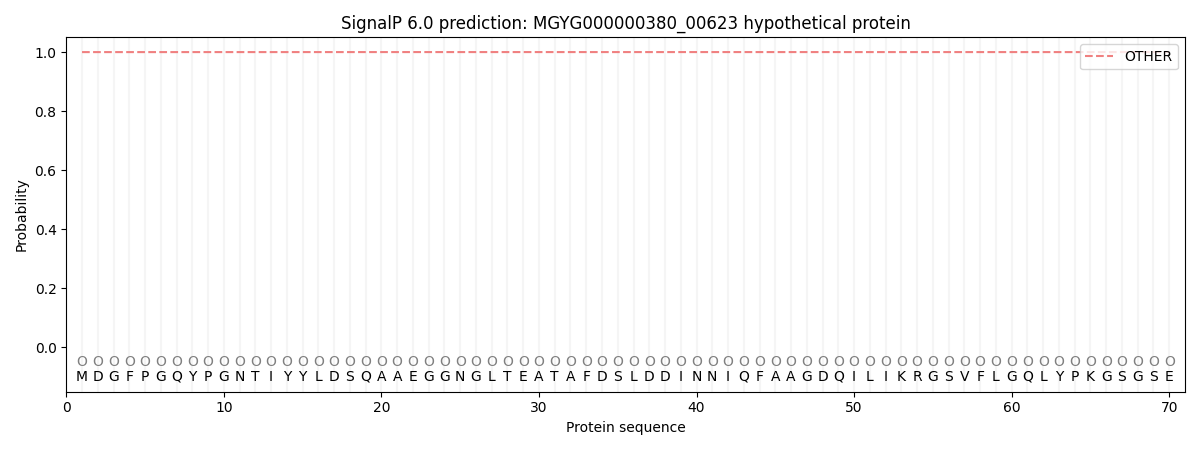
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.000059 | 0.000001 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |