You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000418_01704
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000418_01704
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | UBA1820 sp003150615 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Flavobacteriales; UBA1820; UBA1820; UBA1820 sp003150615 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000418_01704 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT9 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 29958; End: 30992 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT9 | 76 | 319 | 5.8e-34 | 0.9377777777777778 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd03789 | GT9_LPS_heptosyltransferase | 2.32e-45 | 3 | 341 | 1 | 275 | lipopolysaccharide heptosyltransferase and similar proteins. Lipopolysaccharide heptosyltransferase (2.4.99.B6) is involved in the biosynthesis of lipooligosaccharide (LOS). Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a major component of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. LPS heptosyltransferase transfers heptose molecules from ADP-heptose to 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO), a part of the inner core component of LPS. This family also contains lipopolysaccharide 1,2-N-acetylglucosaminetransferase EC 2.4.1.56 and belongs to the GT-B structural superfamily of glycoslytransferases, which have characteristic N- and C-terminal domains each containing a typical Rossmann fold. The two domains have high structural homology despite minimal sequence homology. The large cleft that separates the two domains includes the catalytic center and permits a high degree of flexibility. |
| COG0859 | RfaF | 5.75e-40 | 1 | 333 | 1 | 322 | ADP-heptose:LPS heptosyltransferase [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
| pfam01075 | Glyco_transf_9 | 3.80e-12 | 77 | 316 | 8 | 243 | Glycosyltransferase family 9 (heptosyltransferase). Members of this family belong to glycosyltransferase family 9. Lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the outer leaflet of the outer membrane in Gram-negative bacteria. It is composed of three domains; lipid A, Core oligosaccharide and the O-antigen. All of these enzymes transfer heptose to the lipopolysaccharide core. |
| cd08422 | PBP2_CrgA_like | 4.53e-05 | 6 | 50 | 2 | 49 | The C-terminal substrate binding domain of LysR-type transcriptional regulator CrgA and its related homologs, contains the type 2 periplasmic binding domain. This CD includes the substrate binding domain of LysR-type transcriptional regulator (LTTR) CrgA and its related homologs. The LTTRs are acting as both auto-repressors and activators of target promoters, controlling operons involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as amino acid biosynthesis, CO2 fixation, antibiotic resistance, degradation of aromatic compounds, nodule formation of nitrogen-fixing bacteria, and synthesis of virulence factors, to name a few. In contrast to the tetrameric form of other LTTRs, CrgA from Neisseria meningitides assembles into an octameric ring, which can bind up to four 63-bp DNA oligonucleotides. Phylogenetic cluster analysis further showed that the CrgA-like regulators form a subclass of the LTTRs that function as octamers. The CrgA is an auto-repressor of its own gene and activates the expression of the mdaB gene which coding for an NADPH-quinone reductase and that its action is increased by MBL (alpha-methylene-gamma-butyrolactone), an inducer of NADPH-quinone oxidoreductase. The structural topology of this substrate-binding domain is most similar to that of the type 2 periplasmic binding proteins (PBP2), which are responsible for the uptake of a variety of substrates such as phosphate, sulfate, polysaccharides, lysine/arginine/ornithine, and histidine. The PBP2 bind their ligand in the cleft between these domains in a manner resembling a Venus flytrap. After binding their specific ligand with high affinity, they can interact with a cognate membrane transport complex comprised of two integral membrane domains and two cytoplasmically located ATPase domains. This interaction triggers the ligand translocation across the cytoplasmic membrane energized by ATP hydrolysis. |
| cd08474 | PBP2_CrgA_like_5 | 7.90e-05 | 7 | 45 | 5 | 45 | The C-terminal substrate binding domain of an uncharacterized LysR-type transcriptional regulator CrgA-like, contains the type 2 periplasmic binding fold. This CD represents the substrate binding domain of an uncharacterized LysR-type transcriptional regulator (LTTR) CrgA-like 5. The LTTRs are acting as both auto-repressors and activators of target promoters, controlling operons involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as amino acid biosynthesis, CO2 fixation, antibiotic resistance, degradation of aromatic compounds, nodule formation of nitrogen-fixing bacteria, and synthesis of virulence factors, to name a few. In contrast to the tetrameric form of other LTTRs, CrgA from Neisseria meningitides assembles into an octameric ring, which can bind up to four 63-bp DNA oligonucleotides. Phylogenetic cluster analysis showed that the CrgA-like regulators form a subclass of the LTTRs that function as octamers. The CrgA is an auto-repressor of its own gene and activates the expression of the mdaB gene which coding for an NADPH-quinone reductase and that its action is increased by MBL (alpha-methylene-gamma-butyrolactone), an inducer of NADPH-quinone oxidoreductase. The structural topology of this substrate-binding domain is most similar to that of the type 2 periplasmic binding proteins (PBP2), which are responsible for the uptake of a variety of substrates such as phosphate, sulfate, polysaccharides, lysine/arginine/ornithine, and histidine. The PBP2 bind their ligand in the cleft between these domains in a manner resembling a Venus flytrap. After binding their specific ligand with high affinity, they can interact with a cognate membrane transport complex comprised of two integral membrane domains and two cytoplasmically located ATPase domains. This interaction triggers the ligand translocation across the cytoplasmic membrane energized by ATP hydrolysis. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDT21404.1 | 9.88e-96 | 2 | 339 | 5 | 340 |
| ASU33781.1 | 1.40e-95 | 2 | 339 | 5 | 340 |
| QWG06526.1 | 1.03e-93 | 2 | 340 | 3 | 344 |
| AZQ63461.1 | 1.33e-91 | 2 | 340 | 3 | 344 |
| ANQ50106.2 | 1.52e-90 | 2 | 333 | 3 | 337 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
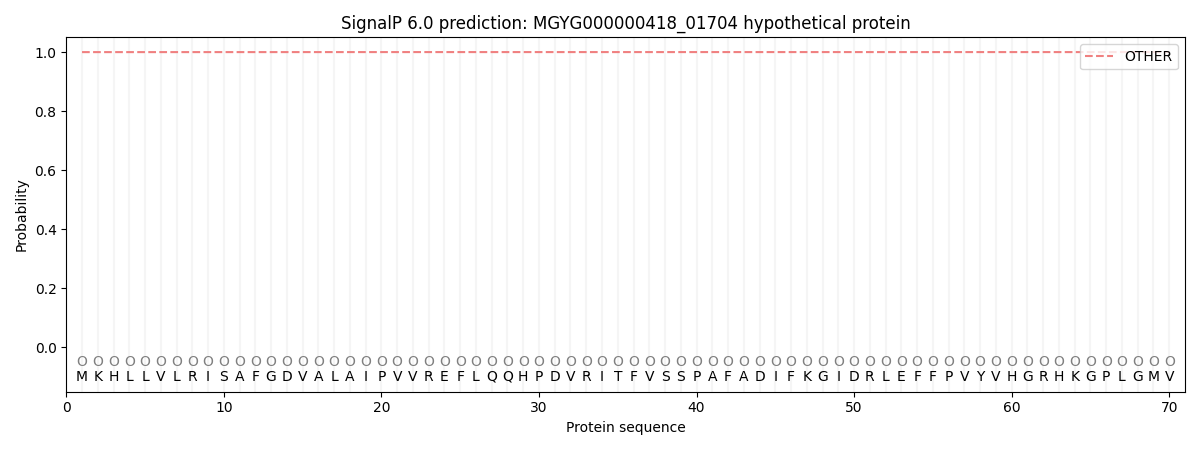
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.000000 | 0.000047 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
