You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000666_00240
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000666_00240
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Verrucomicrobiota; Lentisphaeria; Victivallales; UBA1829; ; | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000666_00240 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH39 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 29428; End: 32382 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH39 | 353 | 628 | 4.9e-19 | 0.7169373549883991 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd09621 | CBM9_like_5 | 1.44e-49 | 795 | 981 | 1 | 188 | DOMON-like type 9 carbohydrate binding module. Family 9 carbohydrate-binding modules (CBM9) play a role in the microbial degradation of cellulose and hemicellulose (materials found in plants). The domain has previously been called cellulose-binding domain. The polysaccharide binding sites of CBMs with available 3D structure have been found to be either flat surfaces with interactions formed by predominantly aromatic residues (tryptophan and tyrosine), or extended shallow grooves. CBM9 domains found in this uncharacterized heterogeneous subfamily are often located at the C-terminus of longer proteins and may co-occur with various other functional domains such as glycosyl hydrolases. The CBM9 module in these architectures may be involved in binding to carbohydrates. |
| cd09619 | CBM9_like_4 | 2.25e-07 | 819 | 959 | 29 | 167 | DOMON-like type 9 carbohydrate binding module. Family 9 carbohydrate-binding modules (CBM9) play a role in the microbial degradation of cellulose and hemicellulose (materials found in plants). The domain has previously been called cellulose-binding domain. The polysaccharide binding sites of CBMs with available 3D structure have been found to be either flat surfaces with interactions formed by predominantly aromatic residues (tryptophan and tyrosine), or extended shallow grooves. CBM9 domains found in this uncharacterized heterogeneous subfamily are often located at the C-terminus of longer proteins and may co-occur with various other domains. |
| cd00241 | DOMON_like | 6.02e-04 | 841 | 961 | 33 | 156 | Domon-like ligand-binding domains. DOMON-like domains can be found in all three kindgoms of life and are a diverse group of ligand binding domains that have been shown to interact with sugars and hemes. DOMON domains were initially thought to confer protein-protein interactions. They were subsequently found as a heme-binding motif in cellobiose dehydrogenase, an extracellular fungal oxidoreductase that degrades both lignin and cellulose, and in ethylbenzene dehydrogenase, an enzyme that aids in the anaerobic degradation of hydrocarbons. The domain interacts with sugars in the type 9 carbohydrate binding modules (CBM9), which are present in a variety of glycosyl hydrolases, and it can also be found at the N-terminus of sensor histidine kinases. |
| cd21510 | agarase_cat | 0.003 | 393 | 463 | 85 | 159 | alpha-beta barrel catalytic domain of agarase, such as GH86-like endo-acting agarases identified in non-marine organisms. Typically, agarases (E.C. 3.2.1.81) are found in ocean-dwelling bacteria since agarose is a principle component of red algae cell wall polysaccharides. Agarose is a linear polymer of alternating D-galactose and 3,6-anhydro-L-galactopyranose. Endo-acting agarases, such as glycoside hydrolase 16 (GH16) and GH86 hydrolyze internal beta-1,4 linkages. GH86-like endo-acting agarase of this protein family has been identified in the human intestinal bacterium Bacteroides uniformis. This acquired metabolic pathway, as demonstrated by the prevalence of agar-specific genetic cluster called polysaccharide utilization loci (PULs), varies considerably between human populations, being much more prevalent in a Japanese sample than in North America, European, or Chinese samples. Agarase activity was also identified in the non-marine bacterium Cellvibrio sp. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVM46276.1 | 1.97e-177 | 163 | 982 | 306 | 1137 |
| AVM47149.1 | 1.66e-169 | 49 | 982 | 213 | 1307 |
| AHF94342.1 | 1.20e-156 | 46 | 982 | 79 | 1033 |
| AVM44759.1 | 3.04e-156 | 231 | 982 | 202 | 965 |
| AHF90198.1 | 2.14e-139 | 35 | 981 | 39 | 1005 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5JVK_A | 2.39e-11 | 304 | 675 | 107 | 499 | Structuralinsights into a family 39 glycoside hydrolase from the gut symbiont Bacteroides cellulosilyticus WH2. [Bacteroides cellulosilyticus],5JVK_B Structural insights into a family 39 glycoside hydrolase from the gut symbiont Bacteroides cellulosilyticus WH2. [Bacteroides cellulosilyticus],5JVK_C Structural insights into a family 39 glycoside hydrolase from the gut symbiont Bacteroides cellulosilyticus WH2. [Bacteroides cellulosilyticus] |
| 4ZN2_A | 3.63e-07 | 310 | 581 | 29 | 323 | Glycosylhydrolase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa [Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1],4ZN2_B Glycosyl hydrolase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa [Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1],4ZN2_C Glycosyl hydrolase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa [Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1],4ZN2_D Glycosyl hydrolase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa [Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1] |
| 5BX9_A | 3.63e-07 | 310 | 581 | 29 | 323 | Structureof PslG from Pseudomonas aeruginosa [Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1],5BXA_A Structure of PslG from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in complex with mannose [Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
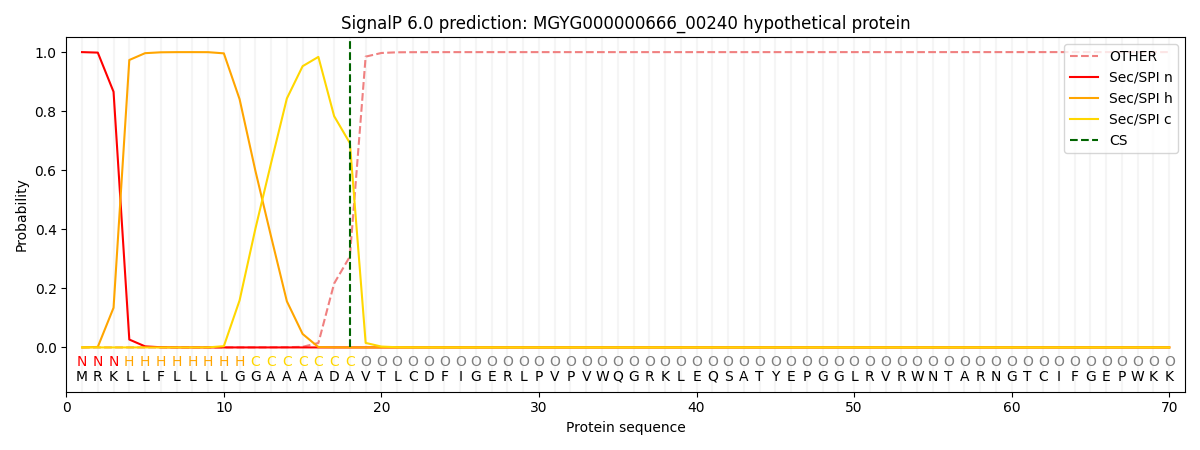
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000292 | 0.999055 | 0.000150 | 0.000159 | 0.000141 | 0.000138 |
