You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000670_02717
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000670_02717
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
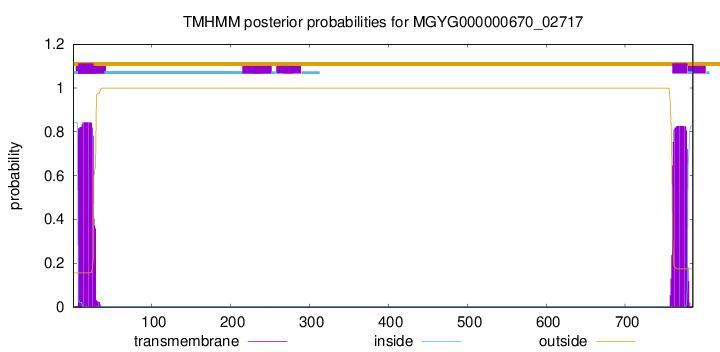
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Faecalibacillus sp900544435 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Erysipelotrichales; Erysipelatoclostridiaceae; Faecalibacillus; Faecalibacillus sp900544435 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000670_02717 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH92 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 1262; End: 3622 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd00839 | MPP_PAPs | 2.45e-18 | 349 | 650 | 5 | 296 | purple acid phosphatases of the metallophosphatase superfamily, metallophosphatase domain. Purple acid phosphatases (PAPs) belong to a diverse family of binuclear metallohydrolases that have been identified and characterized in plants, animals, and fungi. PAPs contain a binuclear metal center and their characteristic pink or purple color derives from a charge-transfer transition between a tyrosine residue and a chromophoric ferric ion within the binuclear center. PAPs catalyze the hydrolysis of a wide range of activated phosphoric acid mono- and di-esters and anhydrides. PAPs are distinguished from the other phosphatases by their insensitivity to L-(+) tartrate inhibition and are therefore also known as tartrate resistant acid phosphatases (TRAPs). While only a few copies of PAP-like genes are present in mammalian and fungal genomes, multiple copies are present in plant genomes. PAPs belong to the metallophosphatase (MPP) superfamily. MPPs are functionally diverse, but all share a conserved domain with an active site consisting of two metal ions (usually manganese, iron, or zinc) coordinated with octahedral geometry by a cage of histidine, aspartate, and asparagine residues. The MPP superfamily includes: Mre11/SbcD-like exonucleases, Dbr1-like RNA lariat debranching enzymes, YfcE-like phosphodiesterases, purple acid phosphatases (PAPs), YbbF-like UDP-2,3-diacylglucosamine hydrolases, and acid sphingomyelinases (ASMases). The conserved domain is a double beta-sheet sandwich with a di-metal active site made up of residues located at the C-terminal side of the sheets. This domain is thought to allow for productive metal coordination. |
| pfam16656 | Pur_ac_phosph_N | 6.23e-13 | 251 | 343 | 4 | 94 | Purple acid Phosphatase, N-terminal domain. This domain is found at the N-terminus of Purple acid phosphatase proteins. |
| pfam00149 | Metallophos | 7.52e-11 | 349 | 551 | 1 | 191 | Calcineurin-like phosphoesterase. This family includes a diverse range of phosphoesterases, including protein phosphoserine phosphatases, nucleotidases, sphingomyelin phosphodiesterases and 2'-3' cAMP phosphodiesterases as well as nucleases such as bacterial SbcD or yeast MRE11. The most conserved regions in this superfamily centre around the metal chelating residues. |
| cd07378 | MPP_ACP5 | 1.74e-10 | 386 | 549 | 35 | 217 | Homo sapiens acid phosphatase 5 and related proteins, metallophosphatase domain. Acid phosphatase 5 (ACP5) removes the mannose 6-phosphate recognition marker from lysosomal proteins. The exact site of dephosphorylation is not clear. Evidence suggests dephosphorylation may take place in a prelysosomal compartment as well as in the lysosome. ACP5 belongs to the metallophosphatase (MPP) superfamily. MPPs are functionally diverse, but all share a conserved domain with an active site consisting of two metal ions (usually manganese, iron, or zinc) coordinated with octahedral geometry by a cage of histidine, aspartate, and asparagine residues. The MPP superfamily includes: Mre11/SbcD-like exonucleases, Dbr1-like RNA lariat debranching enzymes, YfcE-like phosphodiesterases, purple acid phosphatases (PAPs), YbbF-like UDP-2,3-diacylglucosamine hydrolases, and acid sphingomyelinases (ASMases). The conserved domain is a double beta-sheet sandwich with a di-metal active site made up of residues located at the C-terminal side of the sheets. This domain is thought to allow for productive metal coordination. |
| PLN02533 | PLN02533 | 2.95e-10 | 235 | 553 | 33 | 336 | probable purple acid phosphatase |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCI59828.1 | 8.68e-125 | 41 | 655 | 777 | 1369 |
| QNL45026.1 | 2.34e-113 | 47 | 656 | 1570 | 2154 |
| QMW74468.1 | 6.13e-07 | 661 | 785 | 975 | 1092 |
| QPS12259.1 | 6.13e-07 | 661 | 785 | 975 | 1092 |
| QQY28952.1 | 6.13e-07 | 661 | 785 | 975 | 1092 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P9WL80 | 2.38e-09 | 260 | 559 | 78 | 397 | Uncharacterized protein MT2654 OS=Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain CDC 1551 / Oshkosh) OX=83331 GN=MT2654 PE=3 SV=1 |
| P9WL81 | 2.38e-09 | 260 | 559 | 78 | 397 | Uncharacterized protein Rv2577 OS=Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv) OX=83332 GN=Rv2577 PE=3 SV=1 |
| A5D6U8 | 2.09e-06 | 251 | 616 | 34 | 400 | Acid phosphatase type 7 OS=Danio rerio OX=7955 GN=acp7 PE=2 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
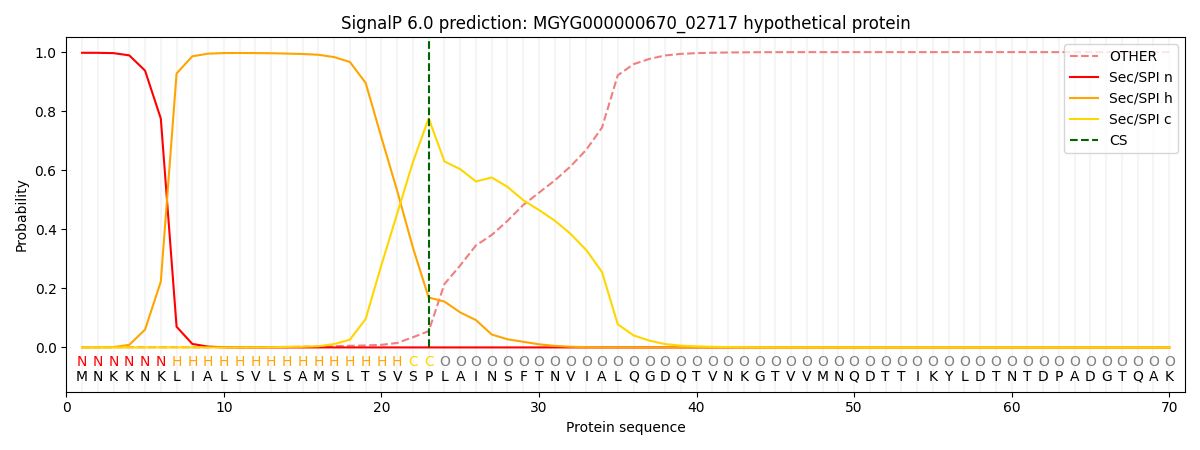
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.001410 | 0.995635 | 0.002248 | 0.000279 | 0.000217 | 0.000191 |