You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000678_01802
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000678_01802
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | CAG-485 sp002491165 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Muribaculaceae; CAG-485; CAG-485 sp002491165 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000678_01802 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH13 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | 1,4-alpha-glucan branching enzyme GlgB | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 2390; End: 5179 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH13 | 409 | 713 | 6e-46 | 0.9331103678929766 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd11350 | AmyAc_4 | 8.60e-126 | 374 | 763 | 1 | 390 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in an uncharacterized protein family. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| cd11325 | AmyAc_GTHase | 1.46e-51 | 374 | 705 | 23 | 355 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in Glycosyltrehalose trehalohydrolase (also called Maltooligosyl trehalose Trehalohydrolase). Glycosyltrehalose trehalohydrolase (GTHase) was discovered as part of a coupled system for the production of trehalose from soluble starch. In the first half of the reaction, glycosyltrehalose synthase (GTSase), an intramolecular glycosyl transferase, converts the glycosidic bond between the last two glucose residues of amylose from an alpha-1,4 bond to an alpha-1,1 bond, making a non-reducing glycosyl trehaloside. In the second half of the reaction, GTHase cleaves the alpha-1,4 glycosidic bond adjacent to the trehalose moiety to release trehalose and malto-oligosaccharide. Like isoamylase and other glycosidases that recognize branched oligosaccharides, GTHase contains an N-terminal extension and does not have the conserved calcium ion present in other alpha amylase family enzymes. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. Glycosyltrehalose Trehalohydrolase Maltooligosyltrehalose Trehalohydrolase |
| COG0296 | GlgB | 3.76e-48 | 250 | 558 | 25 | 312 | 1,4-alpha-glucan branching enzyme [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| COG1523 | PulA | 6.97e-37 | 320 | 550 | 100 | 360 | Pullulanase/glycogen debranching enzyme [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| cd00551 | AmyAc_family | 9.30e-37 | 391 | 711 | 2 | 259 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain family. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; and C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost this catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QIM10833.1 | 0.0 | 21 | 929 | 8 | 908 |
| QCD35300.1 | 2.52e-311 | 3 | 929 | 2 | 927 |
| QQR08212.1 | 1.08e-250 | 24 | 796 | 30 | 730 |
| ANU64421.1 | 1.08e-250 | 24 | 796 | 30 | 730 |
| ASB37479.1 | 1.08e-250 | 24 | 796 | 30 | 730 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3M07_A | 1.79e-27 | 374 | 551 | 122 | 287 | 1.4Angstrom Resolution Crystal Structure of Putative alpha Amylase from Salmonella typhimurium. [Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2] |
| 4J7R_A | 3.15e-25 | 321 | 554 | 154 | 422 | CrystalStructure of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Isoamylase 1 (ISA1) [Chlamydomonas reinhardtii],4J7R_B Crystal Structure of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Isoamylase 1 (ISA1) [Chlamydomonas reinhardtii],4OKD_A Crystal Structure of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Isoamylase 1 (ISA1) in complex with maltoheptaose [Chlamydomonas reinhardtii],4OKD_B Crystal Structure of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Isoamylase 1 (ISA1) in complex with maltoheptaose [Chlamydomonas reinhardtii] |
| 2BHU_A | 6.01e-24 | 307 | 551 | 70 | 277 | Crystalstructure of Deinococcus radiodurans maltooligosyltrehalose trehalohydrolase [Deinococcus radiodurans] |
| 2BHY_A | 1.86e-23 | 307 | 551 | 70 | 277 | Crystalstructure of Deinococcus radiodurans maltooligosyltrehalose trehalohydrolase in complex with trehalose [Deinococcus radiodurans],2BHZ_A Crystal structure of Deinococcus radiodurans maltooligosyltrehalose trehalohydrolase in complex with maltose [Deinococcus radiodurans R1],2BXY_A Is radiation damage dependent on the dose-rate used during macromolecular crystallography data collection [Deinococcus radiodurans],2BXZ_A Is radiation damage dependent on the dose-rate used during macromolecular crystallography data collection [Deinococcus radiodurans],2BY0_A Is radiation damage dependent on the dose-rate used during macromolecular crystallography data collection [Deinococcus radiodurans],2BY1_A Is radiation damage dependent on the dose-rate used during macromolecular crystallography data collection [Deinococcus radiodurans R1],2BY2_A Is radiation damage dependent on the dose-rate used during macromolecular crystallography data collection [Deinococcus radiodurans R1],2BY3_A Is radiation damage dependent on the dose-rate used during macromolecular crystallography data collection [Deinococcus radiodurans] |
| 1EH9_A | 7.46e-21 | 384 | 554 | 97 | 257 | CrystalStructure Of Sulfolobus Solfataricus Glycosyltrehalose Trehalohydrolase [Saccharolobus solfataricus],3VGB_A Crystal structure of glycosyltrehalose trehalohydrolase (GTHase) from Sulfolobus solfataricus KM1 [Saccharolobus solfataricus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O22637 | 2.26e-25 | 331 | 554 | 174 | 422 | Isoamylase SU1, chloroplastic OS=Zea mays OX=4577 GN=SU1 PE=1 SV=1 |
| D0TZF0 | 8.51e-24 | 331 | 551 | 189 | 434 | Isoamylase 1, chloroplastic OS=Oryza sativa subsp. japonica OX=39947 GN=ISA1 PE=1 SV=1 |
| O04196 | 1.88e-23 | 315 | 550 | 142 | 411 | Isoamylase 1, chloroplastic OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=ISA1 PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q8D4P0 | 2.13e-23 | 261 | 554 | 127 | 401 | 1,4-alpha-glucan branching enzyme GlgB OS=Vibrio vulnificus (strain CMCP6) OX=216895 GN=glgB PE=3 SV=1 |
| P95867 | 2.64e-23 | 300 | 554 | 43 | 260 | Malto-oligosyltrehalose trehalohydrolase OS=Saccharolobus solfataricus (strain ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2) OX=273057 GN=treZ PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
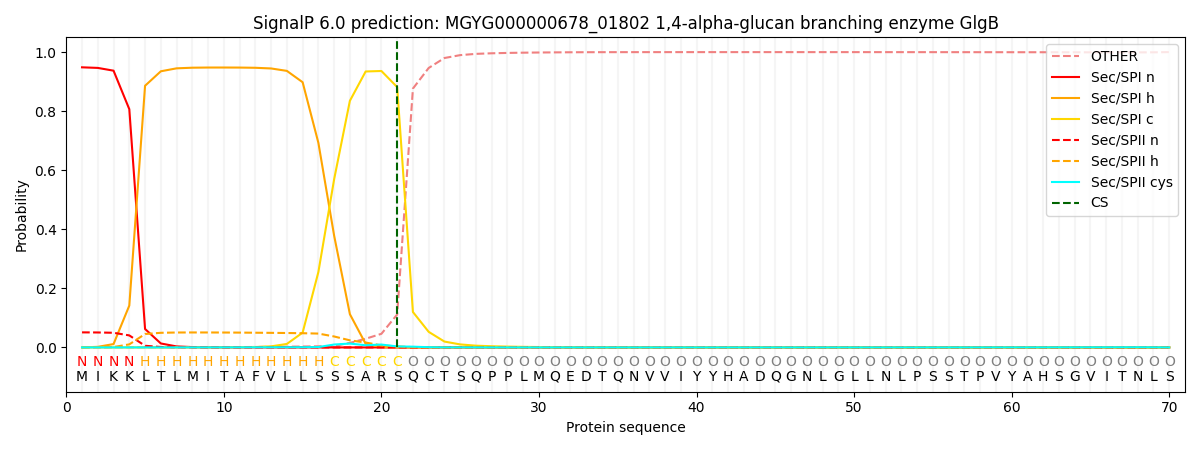
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.002085 | 0.941497 | 0.055503 | 0.000353 | 0.000272 | 0.000265 |
