You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000941_01417
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000941_01417
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | CAG-1031 sp000431215 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Muribaculaceae; CAG-1031; CAG-1031 sp000431215 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000941_01417 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH128 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 16609; End: 18003 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam11790 | Glyco_hydro_cc | 4.41e-53 | 45 | 269 | 19 | 235 | Glycosyl hydrolase catalytic core. This family is probably a glycosyl hydrolase, and is conserved in fungi and some Proteobacteria. The pombe member is annotated as being from IPR013781. |
| cd02795 | CBM6-CBM35-CBM36_like | 0.001 | 317 | 412 | 31 | 124 | Carbohydrate Binding Module 6 (CBM6) and CBM35_like superfamily. Carbohydrate binding module family 6 (CBM6, family 6 CBM), also known as cellulose binding domain family VI (CBD VI), and related CBMs (CBM35 and CBM36). These are non-catalytic carbohydrate binding domains found in a range of enzymes that display activities against a diverse range of carbohydrate targets, including mannan, xylan, beta-glucans, cellulose, agarose, and arabinans. These domains facilitate the strong binding of the appended catalytic modules to their dedicated, insoluble substrates. Many of these CBMs are associated with glycoside hydrolase (GH) domains. CBM6 is an unusual CBM as it represents a chimera of two distinct binding sites with different modes of binding: binding site I within the loop regions and binding site II on the concave face of the beta-sandwich fold. CBM36s are calcium-dependent xylan binding domains. CBM35s display conserved specificity through extensive sequence similarity, but divergent function through their appended catalytic modules. This alignment model also contains the C-terminal domains of bacterial insecticidal toxins, where they may be involved in determining insect specificity through carbohydrate binding functionality. |
| cd04082 | CBM35_pectate_lyase-like | 0.002 | 319 | 400 | 34 | 112 | Carbohydrate Binding Module family 35 (CBM35), pectate lyase-like; appended mainly to enzymes that bind mannan (Man), xylan, glucuronic acid (GlcA) and possibly glucans. This family includes carbohydrate binding module family 35 (CBM35) domains that are non-catalytic carbohydrate binding domains that are appended mainly to enzymes that bind mannan (Man), xylan, glucuronic acid (GlcA) and possibly glucans. Included in this family are CBM35s of pectate lyases, including pectate lyase 10A from Cellvibrio japonicas, these enzymes release delta-4,5-anhydrogalaturonic acid (delta4,5-GalA) from pectin, thus identifying a signature molecule for plant cell wall degradation. CBM35s are unique in that they display conserved specificity through extensive sequence similarity but divergent function through their appended catalytic modules. They are known to bind alpha-D-galactose (Gal), mannan (Man), xylan, glucuronic acid (GlcA), a beta-polymer of mannose, and possibly glucans, forming four subfamilies based on general ligand specificities (galacto, urono, manno, and gluco configurations). In contrast to most CBMs that are generally rigid proteins, CBM35 undergoes significant conformational change upon ligand binding. Some CBM35s bind their ligands in a calcium-dependent manner, especially those binding uronic acids. |
| cd04081 | CBM35_galactosidase-like | 0.005 | 317 | 400 | 34 | 114 | Carbohydrate Binding Module family 35 (CBM35); appended mainly to enzymes that bind alpha-D-galactose (CBM35-Gal), including glycoside hydrolase (GH) families GH27 and GH43. This family includes carbohydrate binding module family 35 (CBM35); these are non-catalytic carbohydrate binding domains that are appended mainly to enzymes that bind alpha-D-galactose (CBM35-Gal), including glycoside hydrolase (GH) families GH27 and GH43. Examples of proteins which contain CBM35s belonging to this family includes the CBM35 of an exo-beta-1,3-galactanase from Phanerochaete chrysosporium 9 (Pc1,3Gal43A) which is appended to a GH43 domain, and the CBM35 domain of two bifunctional proteins with beta-L-arabinopyranosidase/alpha-D-galactopyranosidase activities from Fusarium oxysporum 12S, Foap1 and Foap2 (Fo/AP1 and Fo/AP2), that are appended to GH27 domains. CBM35s are unique in that they display conserved specificity through extensive sequence similarity but divergent function through their appended catalytic modules. They are known to bind alpha-D-galactose (Gal), mannan (Man), xylan, glucuronic acid (GlcA), a beta-polymer of mannose, and possibly glucans, forming four subfamilies based on general ligand specificities (galacto, urono, manno, and gluco configurations). Some CBM35s bind their ligands in a calcium-dependent manner. In contrast to most CBMs that are generally rigid proteins, CBM35 undergoes significant conformational change upon ligand binding. GH43 includes beta-xylosidases and beta-xylanases, using aryl-glycosides as substrates, while family GH27 includes alpha-galactosidases, alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidases, and isomaltodextranases. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QIU93826.1 | 2.96e-55 | 21 | 399 | 51 | 430 |
| EAR10538.1 | 4.40e-44 | 22 | 276 | 31 | 290 |
| ARU26557.1 | 1.07e-43 | 22 | 396 | 115 | 483 |
| ABD80707.1 | 1.77e-43 | 21 | 396 | 88 | 457 |
| AYN96242.1 | 3.54e-41 | 4 | 239 | 14 | 262 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6UAV_A | 3.15e-37 | 21 | 232 | 2 | 226 | Crystalstructure of a GH128 (subgroup II) endo-beta-1,3-glucanase from Pseudomonas viridiflava (PvGH128_II) [Pseudomonas viridiflava] |
| 6UAW_A | 5.59e-37 | 21 | 232 | 24 | 248 | Crystalstructure of a GH128 (subgroup II) endo-beta-1,3-glucanase from Pseudomonas viridiflava (PvGH128_II) in complex with laminaritriose [Pseudomonas viridiflava] |
| 6UAX_A | 1.03e-29 | 24 | 237 | 95 | 321 | Crystalstructure of a GH128 (subgroup II) endo-beta-1,3-glucanase from Sorangium cellulosum (ScGH128_II) [Sorangium cellulosum So ce56],6UAX_B Crystal structure of a GH128 (subgroup II) endo-beta-1,3-glucanase from Sorangium cellulosum (ScGH128_II) [Sorangium cellulosum So ce56] |
| 6UAQ_A | 4.41e-20 | 24 | 232 | 25 | 235 | Crystalstructure of a GH128 (subgroup I) endo-beta-1,3-glucanase from Amycolatopsis mediterranei (AmGH128_I) [Amycolatopsis mediterranei],6UAR_A Crystal structure of a GH128 (subgroup I) endo-beta-1,3-glucanase from Amycolatopsis mediterranei (AmGH128_I) in complex with laminaritriose [Amycolatopsis mediterranei] |
| 6UFL_A | 1.11e-19 | 24 | 232 | 25 | 235 | Crystalstructure of a GH128 (subgroup I) endo-beta-1,3-glucanase (E199Q mutant) from Amycolatopsis mediterranei (AmGH128_I) in the complex with laminarihexaose [Amycolatopsis mediterranei],6UFZ_A Crystal structure of a GH128 (subgroup I) endo-beta-1,3-glucanase (E199Q mutant) from Amycolatopsis mediterranei (AmGH128_I) [Amycolatopsis mediterranei] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
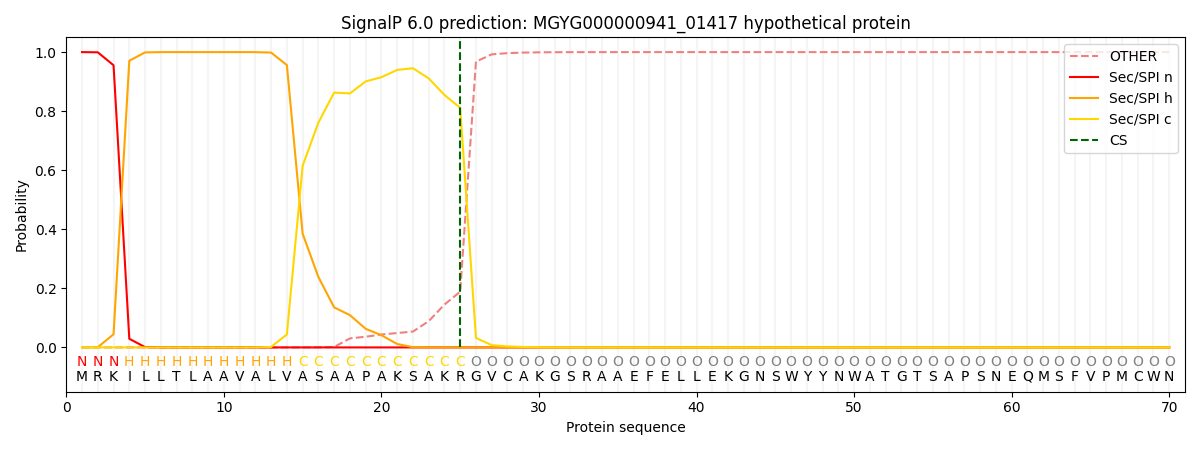
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000215 | 0.999209 | 0.000134 | 0.000157 | 0.000135 | 0.000127 |
