You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000971_01890
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000971_01890
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
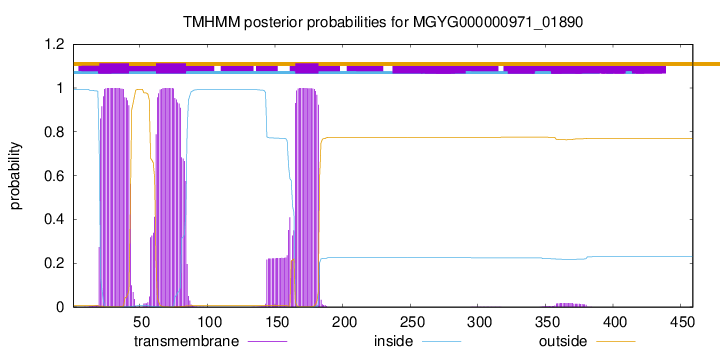
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | UMGS1518 sp900552575 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Verrucomicrobiota; Lentisphaeria; Victivallales; Victivallaceae; UMGS1518; UMGS1518 sp900552575 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000971_01890 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT4 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | D-inositol-3-phosphate glycosyltransferase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 198; End: 1577 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd18549 | ABC_6TM_YwjA_like | 8.81e-111 | 22 | 227 | 1 | 206 | Six-transmembrane helical domain of an uncharacterized ABC transporter YwjA and similar proteins. This group represents the six-transmembrane helical domain of an uncharacterized ABC transporter YwjA from Bacillus subtilis and similar proteins. This transmembrane (TM) subunit possesses the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) exporter fold, which is characterized by 6 TM helices per subunit (domain), or a total of 12 TM helices for the complete transporter. The ABC exporters are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, where they mediate the cellular secretion of toxic compounds, a various type of lipids and polypeptides. ABC transporters typically consist of two transmembrane domains (TMDs) and two nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs). The sequences and structures of the TMDs are quite varied between the different type of transporters, suggesting significant structural diversity of the translocated substrates, while NBDs are conserved among all ABC transporters. The two NBDs together bind and hydrolyze ATP, thereby providing the driving force for transport, while the TMDs participate in substrate recognition and translocation across the lipid membrane by alternating between inward- and outward-facing conformations. Moreover, some ABC genes are organized as half-transporters, which must form either homodimers or heterodimers to form a functional transporter. The ABC exporters play a role in multidrug resistance to antibiotics and anticancer agents, and mutations in these proteins have been shown to cause severe human diseases such as cystic fibrosis. |
| cd07346 | ABC_6TM_exporters | 6.40e-53 | 25 | 227 | 1 | 203 | Six-transmembrane helical domain of the ATP-binding cassette transporters. This family represents a subunit of six transmembrane (TM) helices typically found in the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters that function as exporters, which contain 6 TM helices per subunit (domain), or a total of 12 TM helices for the complete transporter. The ABC exporters are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, where they mediate the cellular secretion of toxic compounds and a various type of lipids. In addition to ABC exporters, ABC transporters include two classes of ABC importers, classified depending on details of their architecture and mechanism. Only the ABC exporters are included in this family. ABC transporters typically consist of two transmembrane domains (TMDs) and two nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs). The sequences and structures of the TMDs are quite varied between the different type of transporters, suggesting chemical diversity of the translocated substrates, whereas NBDs are conserved among all ABC transporters. The two NBDs together bind and hydrolyze ATP, thereby providing the driving force for transport, while the TMDs participate in substrate recognition and translocation across the lipid membrane. However, some ABC genes are organized as half-transporters, which must form either homodimers or heterodimers to form a functional unit. The ABC exporters play a role in multidrug resistance to antibiotics and anticancer agents, and mutations in these proteins have been shown to cause severe human diseases such as cystic fibrosis. |
| COG1132 | MdlB | 1.19e-47 | 11 | 228 | 4 | 217 | ABC-type multidrug transport system, ATPase and permease component [Defense mechanisms]. |
| cd03801 | GT4_PimA-like | 1.10e-46 | 223 | 441 | 153 | 366 | phosphatidyl-myo-inositol mannosyltransferase. This family is most closely related to the GT4 family of glycosyltransferases and named after PimA in Propionibacterium freudenreichii, which is involved in the biosynthesis of phosphatidyl-myo-inositol mannosides (PIM) which are early precursors in the biosynthesis of lipomannans (LM) and lipoarabinomannans (LAM), and catalyzes the addition of a mannosyl residue from GDP-D-mannose (GDP-Man) to the position 2 of the carrier lipid phosphatidyl-myo-inositol (PI) to generate a phosphatidyl-myo-inositol bearing an alpha-1,2-linked mannose residue (PIM1). Glycosyltransferases catalyze the transfer of sugar moieties from activated donor molecules to specific acceptor molecules, forming glycosidic bonds. The acceptor molecule can be a lipid, a protein, a heterocyclic compound, or another carbohydrate residue. This group of glycosyltransferases is most closely related to the previously defined glycosyltransferase family 1 (GT1). The members of this family may transfer UDP, ADP, GDP, or CMP linked sugars. The diverse enzymatic activities among members of this family reflect a wide range of biological functions. The protein structure available for this family has the GTB topology, one of the two protein topologies observed for nucleotide-sugar-dependent glycosyltransferases. GTB proteins have distinct N- and C- terminal domains each containing a typical Rossmann fold. The two domains have high structural homology despite minimal sequence homology. The large cleft that separates the two domains includes the catalytic center and permits a high degree of flexibility. The members of this family are found mainly in certain bacteria and archaea. |
| cd18563 | ABC_6TM_exporter_like | 1.23e-43 | 25 | 227 | 1 | 207 | Six-transmembrane helical domain (TMD) of an uncharacterized ABC exporter, and similar proteins. This group includes a subunit of six transmembrane (TM) helices typically found in the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters that function as exporters, which contain 6 TM helices per subunit (domain), or a total of 12 TM helices for the complete transporter. The ABC exporters are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, where they mediate the cellular secretion of toxic compounds and a various type of lipids. ABC transporters typically consist of two transmembrane domains (TMDs) and two nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs). The sequences and structures of the TMDs are quite varied between the different type of transporters, suggesting the chemical diversity of the translocated substrates, while NBDs are conserved among all ABC transporters. The two NBDs together bind and hydrolyze ATP, thereby providing the driving force for transport, while the TMDs participate in substrate recognition and translocation across the lipid membrane. However, some ABC genes are organized as half-transporters, which must form either homodimers or heterodimers to form a functional transporter. The ABC exporters play a role in multidrug resistance to antibiotics and anticancer agents, and mutations in these proteins have been shown to cause severe human diseases such as cystic fibrosis. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVM46739.1 | 3.73e-68 | 231 | 443 | 299 | 514 |
| AVM47131.1 | 1.40e-64 | 225 | 444 | 186 | 407 |
| QSH41982.1 | 1.66e-57 | 220 | 444 | 180 | 407 |
| SQH77395.1 | 2.98e-53 | 220 | 443 | 211 | 438 |
| AQS38746.1 | 7.36e-49 | 220 | 443 | 186 | 413 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6KIH_A | 1.65e-22 | 221 | 445 | 202 | 426 | Sucrose-phosphatesynthase (tll1590) from Thermosynechococcus elongatus [Thermosynechococcus vestitus],6KIH_B Sucrose-phosphate synthase (tll1590) from Thermosynechococcus elongatus [Thermosynechococcus vestitus],6KIH_C Sucrose-phosphate synthase (tll1590) from Thermosynechococcus elongatus [Thermosynechococcus vestitus],6KIH_D Sucrose-phosphate synthase (tll1590) from Thermosynechococcus elongatus [Thermosynechococcus vestitus],6KIH_E Sucrose-phosphate synthase (tll1590) from Thermosynechococcus elongatus [Thermosynechococcus vestitus],6KIH_F Sucrose-phosphate synthase (tll1590) from Thermosynechococcus elongatus [Thermosynechococcus vestitus],6KIH_G Sucrose-phosphate synthase (tll1590) from Thermosynechococcus elongatus [Thermosynechococcus vestitus],6KIH_H Sucrose-phosphate synthase (tll1590) from Thermosynechococcus elongatus [Thermosynechococcus vestitus],6KIH_I Sucrose-phosphate synthase (tll1590) from Thermosynechococcus elongatus [Thermosynechococcus vestitus],6KIH_J Sucrose-phosphate synthase (tll1590) from Thermosynechococcus elongatus [Thermosynechococcus vestitus],6KIH_K Sucrose-phosphate synthase (tll1590) from Thermosynechococcus elongatus [Thermosynechococcus vestitus],6KIH_L Sucrose-phosphate synthase (tll1590) from Thermosynechococcus elongatus [Thermosynechococcus vestitus] |
| 3C4Q_A | 3.81e-20 | 230 | 445 | 187 | 407 | Structureof the retaining glycosyltransferase MshA : The first step in mycothiol biosynthesis. Organism : Corynebacterium glutamicum- Complex with UDP [Corynebacterium glutamicum],3C4Q_B Structure of the retaining glycosyltransferase MshA : The first step in mycothiol biosynthesis. Organism : Corynebacterium glutamicum- Complex with UDP [Corynebacterium glutamicum],3C4V_A Structure of the retaining glycosyltransferase MshA:The first step in mycothiol biosynthesis. Organism: Corynebacterium glutamicum : Complex with UDP and 1L-INS-1-P. [Corynebacterium glutamicum],3C4V_B Structure of the retaining glycosyltransferase MshA:The first step in mycothiol biosynthesis. Organism: Corynebacterium glutamicum : Complex with UDP and 1L-INS-1-P. [Corynebacterium glutamicum] |
| 3C48_A | 4.15e-20 | 230 | 445 | 207 | 427 | Structureof the retaining glycosyltransferase MshA: The first step in mycothiol biosynthesis. Organism: Corynebacterium glutamicum- APO (OPEN) structure. [Corynebacterium glutamicum],3C48_B Structure of the retaining glycosyltransferase MshA: The first step in mycothiol biosynthesis. Organism: Corynebacterium glutamicum- APO (OPEN) structure. [Corynebacterium glutamicum] |
| 2HYD_A | 2.91e-14 | 69 | 241 | 67 | 238 | MultidrugABC transporter SAV1866 [Staphylococcus aureus],2HYD_B Multidrug ABC transporter SAV1866 [Staphylococcus aureus],2ONJ_A Structure of the multidrug ABC transporter Sav1866 from S. aureus in complex with AMP-PNP [Staphylococcus aureus],2ONJ_B Structure of the multidrug ABC transporter Sav1866 from S. aureus in complex with AMP-PNP [Staphylococcus aureus],4A82_A Fitted model of staphylococcus aureus sav1866 model ABC transporter in the human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator volume map EMD-1966. [Homo sapiens],4A82_B Fitted model of staphylococcus aureus sav1866 model ABC transporter in the human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator volume map EMD-1966. [Homo sapiens],4A82_C Fitted model of staphylococcus aureus sav1866 model ABC transporter in the human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator volume map EMD-1966. [Homo sapiens],4A82_D Fitted model of staphylococcus aureus sav1866 model ABC transporter in the human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator volume map EMD-1966. [Homo sapiens] |
| 4Q4J_B | 1.57e-12 | 15 | 227 | 29 | 241 | Structureof crosslinked TM287/288_S498C_S520C mutant [Thermotoga maritima MSB8] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P45861 | 3.77e-49 | 14 | 227 | 5 | 218 | Uncharacterized ABC transporter ATP-binding protein YwjA OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=ywjA PE=1 SV=1 |
| D5UJ42 | 2.73e-21 | 191 | 440 | 183 | 436 | D-inositol 3-phosphate glycosyltransferase OS=Cellulomonas flavigena (strain ATCC 482 / DSM 20109 / BCRC 11376 / JCM 18109 / NBRC 3775 / NCIMB 8073 / NRS 134) OX=446466 GN=mshA PE=3 SV=1 |
| D6Z995 | 3.08e-20 | 179 | 444 | 168 | 436 | D-inositol 3-phosphate glycosyltransferase OS=Segniliparus rotundus (strain ATCC BAA-972 / CDC 1076 / CIP 108378 / DSM 44985 / JCM 13578) OX=640132 GN=mshA PE=3 SV=1 |
| D1BZ82 | 5.92e-20 | 179 | 442 | 140 | 409 | D-inositol 3-phosphate glycosyltransferase OS=Xylanimonas cellulosilytica (strain DSM 15894 / CECT 5975 / LMG 20990 / XIL07) OX=446471 GN=mshA PE=3 SV=1 |
| D7AW65 | 1.18e-19 | 220 | 445 | 186 | 419 | D-inositol 3-phosphate glycosyltransferase OS=Nocardiopsis dassonvillei (strain ATCC 23218 / DSM 43111 / CIP 107115 / JCM 7437 / KCTC 9190 / NBRC 14626 / NCTC 10488 / NRRL B-5397 / IMRU 509) OX=446468 GN=mshA PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
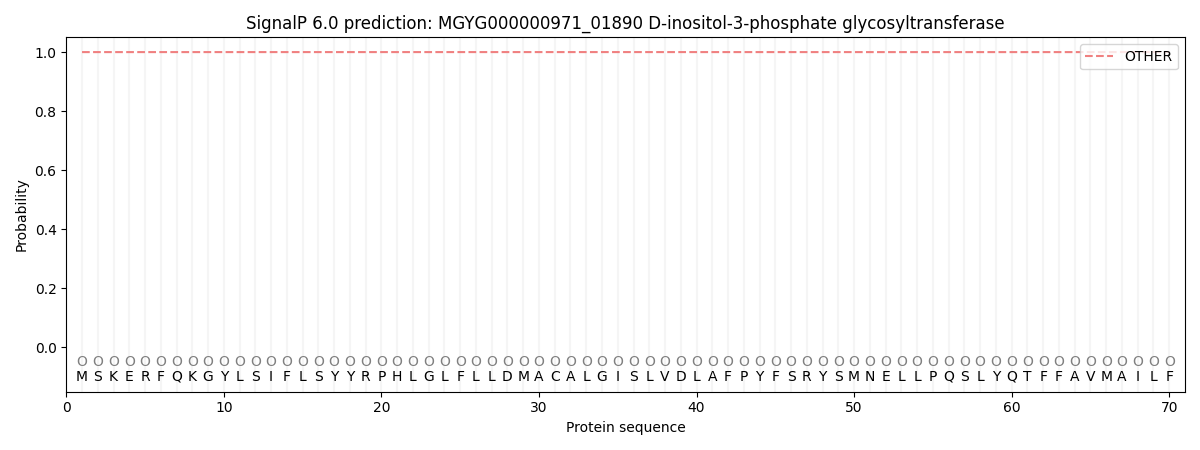
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.000026 | 0.000002 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |