You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001058_01261
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001058_01261
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | UBA6398 sp900550635 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; UBA6398; UBA6398 sp900550635 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001058_01261 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH43 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Intracellular endo-alpha-(1->5)-L-arabinanase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 18; End: 1043 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH43 | 33 | 321 | 1.4e-99 | 0.9966555183946488 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd18616 | GH43_ABN-like | 4.74e-131 | 35 | 316 | 1 | 291 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 such as arabinan endo-1 5-alpha-L-arabinosidase. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes mostly enzymes with endo-alpha-L-arabinanase (ABN; EC 3.2.1.99) activity. These are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. The GH43 ABN enzymes hydrolyze alpha-1,5-L-arabinofuranoside linkages. These arabinan-degrading enzymes are important in the food industry for efficient production of L-arabinose from agricultural waste; L-arabinose is often used as a bioactive sweetener. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd08998 | GH43_Arb43a-like | 7.41e-76 | 42 | 309 | 1 | 269 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168 endo-alpha-1,5-L-arabinanase Arb43A. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) which includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62) families. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. The GH43 ABN enzymes hydrolyze alpha-1,5-L-arabinofuranoside linkages while the ABF enzymes cleave arabinose side chains so that the combined actions of these two enzymes reduce arabinan to L-arabinose and/or arabinooligosaccharides. Many of these enzymes such as the Bacillus subtilis arabinanase Abn2, that hydrolyzes sugar beet arabinan (branched), linear alpha-1,5-L-arabinan and pectin, are different from other arabinases; they are organized into two different domains with a divalent metal cluster close to the catalytic residues to guarantee the correct protonation state of the catalytic residues and consequently the enzyme activity. These arabinan-degrading enzymes are important in the food industry for efficient production of L-arabinose from agricultural waste; L-arabinose is often used as a bioactive sweetener. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| pfam04616 | Glyco_hydro_43 | 1.10e-67 | 33 | 321 | 1 | 281 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 43. The glycosyl hydrolase family 43 contains members that are arabinanases. Arabinanases hydrolyze the alpha-1,5-linked L-arabinofuranoside backbone of plant cell wall arabinans. The structure of arabinanase Arb43A from Cellvibrio japonicus reveals a five-bladed beta-propeller fold. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd08988 | GH43_ABN | 9.33e-64 | 43 | 316 | 1 | 277 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes mostly enzymes with alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (ABF; EC 3.2.1.55) and endo-alpha-L-arabinanase (ABN; EC 3.2.1.99) activities. These are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. The GH43 ABN enzymes hydrolyze alpha-1,5-L-arabinofuranoside linkages while the ABF enzymes cleave arabinose side chains so that the combined actions of these two enzymes reduce arabinan to L-arabinose and/or arabinooligosaccharides. These arabinan-degrading enzymes are important in the food industry for efficient production of L-arabinose from agricultural waste; L-arabinose is often used as a bioactive sweetener. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd08999 | GH43_ABN-like | 1.10e-58 | 35 | 322 | 1 | 284 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as endo-alpha-L-arabinanase. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes mostly enzymes with alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (ABF; EC 3.2.1.55) and endo-alpha-L-arabinanase (ABN; EC 3.2.1.99) activities. These are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. The GH43 ABN enzymes hydrolyze alpha-1,5-L-arabinofuranoside linkages while the ABF enzymes cleave arabinose side chains so that the combined actions of these two enzymes reduce arabinan to L-arabinose and/or arabinooligosaccharides. These arabinan-degrading enzymes are important in the food industry for efficient production of L-arabinose from agricultural waste; L-arabinose is often used as a bioactive sweetener. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEA16128.1 | 1.56e-124 | 1 | 337 | 1 | 333 |
| SCM57950.1 | 2.52e-121 | 11 | 339 | 17 | 340 |
| QIA07413.1 | 5.87e-121 | 26 | 338 | 32 | 339 |
| QIK58373.1 | 8.95e-120 | 1 | 338 | 1 | 334 |
| BBD45555.1 | 1.23e-119 | 32 | 337 | 35 | 335 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6B7K_A | 2.21e-35 | 42 | 323 | 21 | 301 | GH43Endo-Arabinanase from Bacillus licheniformis [Bacillus licheniformis DSM 13 = ATCC 14580],6B7K_B GH43 Endo-Arabinanase from Bacillus licheniformis [Bacillus licheniformis DSM 13 = ATCC 14580],6B7K_C GH43 Endo-Arabinanase from Bacillus licheniformis [Bacillus licheniformis DSM 13 = ATCC 14580],6B7K_D GH43 Endo-Arabinanase from Bacillus licheniformis [Bacillus licheniformis DSM 13 = ATCC 14580] |
| 4KCB_A | 1.44e-31 | 29 | 325 | 119 | 442 | CrystalStructure of Exo-1,5-alpha-L-arabinanase from Bovine Ruminal Metagenomic Library [uncultured bacterium],4KCB_B Crystal Structure of Exo-1,5-alpha-L-arabinanase from Bovine Ruminal Metagenomic Library [uncultured bacterium] |
| 3CU9_A | 1.65e-31 | 44 | 322 | 26 | 311 | Highresolution crystal structure of 1,5-alpha-L-arabinanase from Geobacillus Stearothermophilus [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
| 3D60_A | 6.17e-31 | 50 | 322 | 30 | 311 | ChainA, Intracellular arabinanase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
| 3D5Y_A | 8.58e-31 | 44 | 322 | 26 | 311 | ChainA, Intracellular arabinanase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],3D5Z_A Chain A, Intracellular arabinanase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1CLG4 | 3.73e-33 | 41 | 321 | 31 | 319 | Probable arabinan endo-1,5-alpha-L-arabinosidase A OS=Aspergillus clavatus (strain ATCC 1007 / CBS 513.65 / DSM 816 / NCTC 3887 / NRRL 1 / QM 1276 / 107) OX=344612 GN=abnA PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q4WYX7 | 1.03e-31 | 41 | 321 | 31 | 319 | Probable arabinan endo-1,5-alpha-L-arabinosidase A OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain ATCC MYA-4609 / Af293 / CBS 101355 / FGSC A1100) OX=330879 GN=abnA PE=3 SV=1 |
| B0XZW5 | 1.03e-31 | 41 | 321 | 31 | 319 | Probable arabinan endo-1,5-alpha-L-arabinosidase A OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain CEA10 / CBS 144.89 / FGSC A1163) OX=451804 GN=abnA PE=3 SV=1 |
| A1D5W1 | 1.99e-31 | 41 | 321 | 31 | 319 | Probable arabinan endo-1,5-alpha-L-arabinosidase A OS=Neosartorya fischeri (strain ATCC 1020 / DSM 3700 / CBS 544.65 / FGSC A1164 / JCM 1740 / NRRL 181 / WB 181) OX=331117 GN=abnA PE=3 SV=1 |
| B3EYM8 | 9.20e-31 | 44 | 322 | 27 | 312 | Intracellular endo-alpha-(1->5)-L-arabinanase OS=Geobacillus stearothermophilus OX=1422 GN=abnB PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
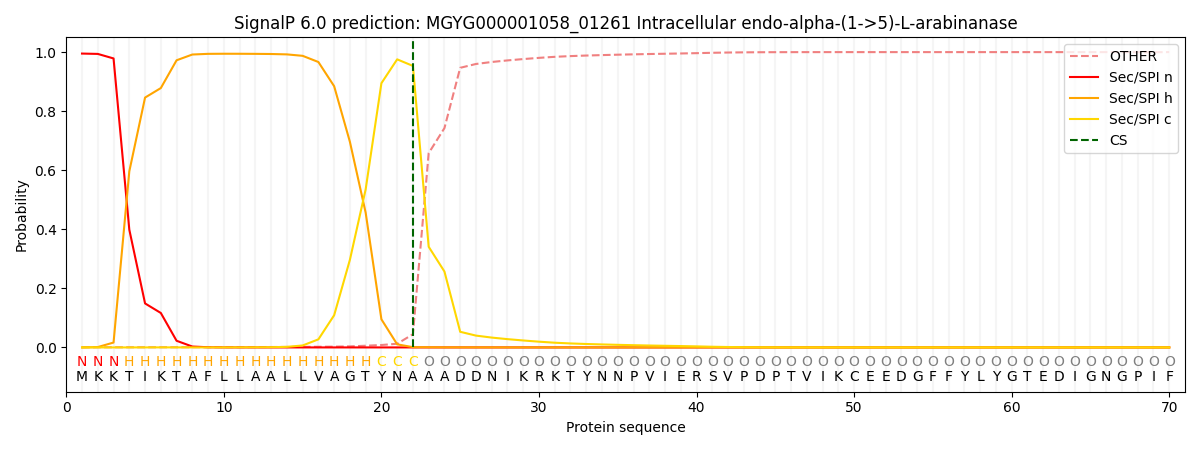
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.001691 | 0.992471 | 0.005065 | 0.000282 | 0.000233 | 0.000217 |

