You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001376_00022
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001376_00022
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
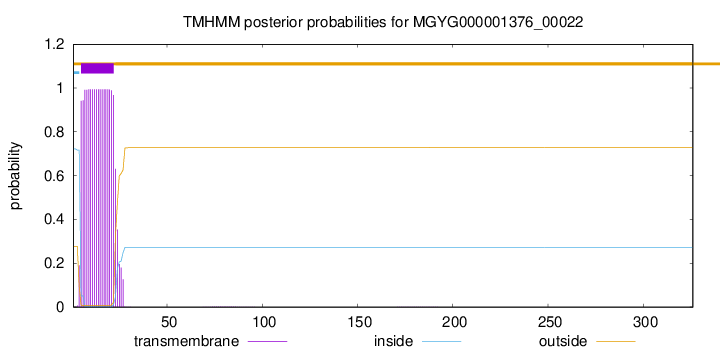
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Dysgonomonas gadei | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Dysgonomonadaceae; Dysgonomonas; Dysgonomonas gadei | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001376_00022 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH23 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 22765; End: 23745 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH23 | 92 | 227 | 1.3e-23 | 0.9037037037037037 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd16894 | MltD-like | 8.15e-58 | 100 | 225 | 1 | 129 | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase D and similar proteins. Lytic transglycosylases (LT) catalyze the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc). Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase D protein (MltD) family members may have one or more small LysM domains, which may contribute to peptidoglycan binding. Unlike the similar "goose-type" lysozymes, LTs also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. Proteins similar to this family include the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria, the LTs in bacteriophage lambda, as well as the eukaryotic "goose-type" lysozymes (goose egg-white lysozyme; GEWL). |
| PRK10783 | mltD | 4.85e-28 | 52 | 301 | 65 | 311 | membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase D; Provisional |
| pfam01464 | SLT | 3.86e-24 | 95 | 192 | 1 | 99 | Transglycosylase SLT domain. This family is distantly related to pfam00062. Members are found in phages, type II, type III and type IV secretion systems. |
| cd00254 | LT-like | 1.35e-18 | 112 | 222 | 5 | 108 | lytic transglycosylase(LT)-like domain. Members include the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria and LTs in bacteriophage lambda. LTs catalyze the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc), as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. |
| cd13401 | Slt70-like | 8.28e-15 | 92 | 217 | 6 | 138 | 70kDa soluble lytic transglycosylase (Slt70) and similar proteins. Catalytic domain of the 70kda soluble lytic transglycosylase (LT)-like proteins, which also have an N-terminal U-shaped U-domain and a linker L-domain. LTs catalyze the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc), as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. Proteins similar to this family include the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria and the LTs in bacteriophage lambda. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QIK56176.1 | 4.45e-168 | 1 | 322 | 1 | 322 |
| QIK58445.1 | 2.66e-167 | 1 | 322 | 2 | 323 |
| BBD44537.1 | 2.20e-149 | 1 | 324 | 1 | 323 |
| SCM59513.1 | 1.61e-144 | 22 | 322 | 23 | 321 |
| CEA15013.1 | 9.61e-144 | 1 | 322 | 1 | 322 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P32820 | 1.47e-09 | 68 | 192 | 2 | 126 | Putative tributyltin chloride resistance protein OS=Alteromonas sp. (strain M-1) OX=29457 GN=tbtA PE=3 SV=1 |
| O31608 | 9.90e-08 | 116 | 192 | 85 | 156 | Putative murein lytic transglycosylase YjbJ OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=yjbJ PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
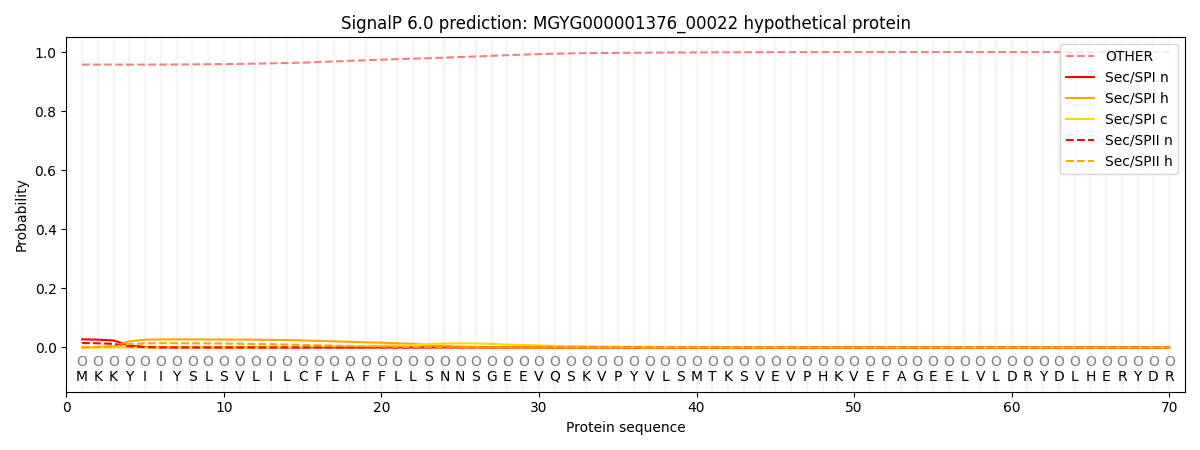
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.959107 | 0.025635 | 0.015062 | 0.000040 | 0.000032 | 0.000137 |