You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001443_01363
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001443_01363
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
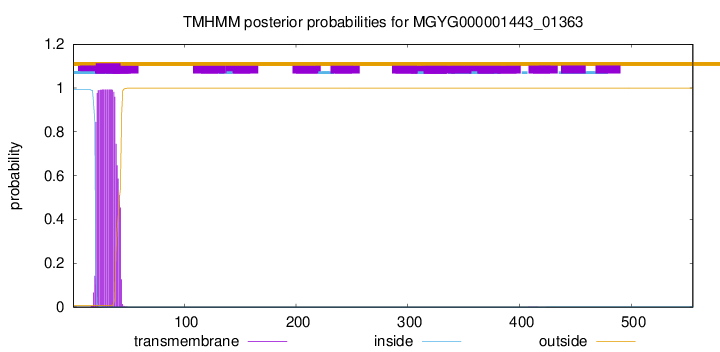
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Streptomyces albus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Actinobacteriota; Actinomycetia; Streptomycetales; Streptomycetaceae; Streptomyces; Streptomyces albus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001443_01363 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH23 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 1694750; End: 1696417 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH23 | 119 | 256 | 3.2e-22 | 0.8074074074074075 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd13399 | Slt35-like | 4.04e-28 | 116 | 252 | 1 | 105 | Slt35-like lytic transglycosylase. Lytic transglycosylase similar to Escherichia coli lytic transglycosylase Slt35 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Sltb1. Lytic transglycosylase (LT) catalyzes the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc) as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. Proteins similar to this this family include the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria, the LTs in bacteriophage lambda, as well as the eukaryotic "goose-type" lysozymes (goose egg-white lysozyme; GEWL). |
| COG2951 | MltB | 1.54e-26 | 22 | 268 | 30 | 289 | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase B [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
| pfam13406 | SLT_2 | 1.71e-07 | 168 | 219 | 150 | 196 | Transglycosylase SLT domain. This family is related to the SLT domain pfam01464. |
| cd00254 | LT-like | 7.58e-05 | 179 | 240 | 24 | 79 | lytic transglycosylase(LT)-like domain. Members include the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria and LTs in bacteriophage lambda. LTs catalyze the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc), as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QID35744.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 555 | 1 | 555 |
| QHF94046.1 | 7.56e-187 | 11 | 555 | 19 | 583 |
| QNF57914.1 | 1.40e-184 | 11 | 555 | 19 | 583 |
| QFR93060.1 | 3.81e-148 | 18 | 553 | 8 | 577 |
| AXK36456.1 | 7.49e-143 | 15 | 553 | 17 | 576 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
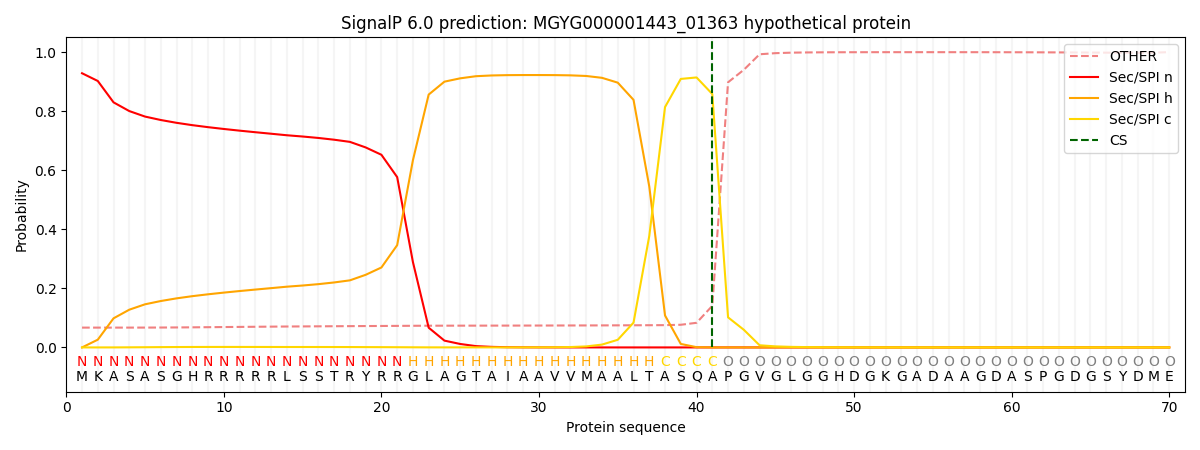
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.075877 | 0.916098 | 0.004953 | 0.002079 | 0.000577 | 0.000397 |