You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001512_02150
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001512_02150
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Coprobacter secundus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Coprobacteraceae; Coprobacter; Coprobacter secundus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001512_02150 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH43 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 112493; End: 113680 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH43 | 79 | 374 | 1.5e-41 | 0.9435483870967742 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam04616 | Glyco_hydro_43 | 8.82e-34 | 80 | 373 | 10 | 279 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 43. The glycosyl hydrolase family 43 contains members that are arabinanases. Arabinanases hydrolyze the alpha-1,5-linked L-arabinofuranoside backbone of plant cell wall arabinans. The structure of arabinanase Arb43A from Cellvibrio japonicus reveals a five-bladed beta-propeller fold. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd08991 | GH43_HoAraf43-like | 2.52e-32 | 82 | 376 | 2 | 279 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as Halothermothrix orenii H 168 alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (HoAraf43;Hore_20580). This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes Halothermothrix orenii H 168 alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55) (HoAraf43;Hore_20580). It belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) which includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62) families. This GH43_ HoAraf43-like subgroup includes enzymes that have been annotated as having xylan-digesting beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37) and xylanase (endo-alpha-L-arabinanase, EC 3.2.1.8) activities. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd08978 | GH_F | 3.35e-24 | 81 | 350 | 1 | 248 | Glycosyl hydrolase families 43 and 62 form CAZY clan GH-F. This glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62). GH43 includes enzymes with beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37), beta-1,3-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.-), alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55), arabinanase (EC 3.2.1.99), xylanase (EC 3.2.1.8), endo-alpha-L-arabinanases (beta-xylanases) and galactan 1,3-beta-galactosidase (EC 3.2.1.145) activities. GH62 includes enzymes characterized as arabinofuranosidases (alpha-L-arabinofuranosidases; EC 3.2.1.55) that specifically cleave either alpha-1,2 or alpha-1,3-L-arabinofuranose side chains from xylans. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many of the enzymes in this family display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. GH62 are also predicted to be inverting enzymes. A common structural feature of both, GH43 and GH62 enzymes, is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd08999 | GH43_ABN-like | 5.04e-23 | 82 | 370 | 10 | 279 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as endo-alpha-L-arabinanase. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes mostly enzymes with alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (ABF; EC 3.2.1.55) and endo-alpha-L-arabinanase (ABN; EC 3.2.1.99) activities. These are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. The GH43 ABN enzymes hydrolyze alpha-1,5-L-arabinofuranoside linkages while the ABF enzymes cleave arabinose side chains so that the combined actions of these two enzymes reduce arabinan to L-arabinose and/or arabinooligosaccharides. These arabinan-degrading enzymes are important in the food industry for efficient production of L-arabinose from agricultural waste; L-arabinose is often used as a bioactive sweetener. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd09000 | GH43_SXA-like | 5.45e-23 | 82 | 348 | 10 | 256 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43, such as Selenomonas ruminantium beta-D-xylosidase SXA. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) includes enzymes that have been characterized to mainly have beta-1,4-xylosidase (beta-D-xylosidase;xylan 1,4-beta-xylosidase; EC 3.2.1.37) activity, including Selenomonas ruminantium (Xsa;Sxa;SXA), Bifidobacterium adolescentis ATCC 15703 (XylC;XynB;BAD_0428) and Bacillus sp. KK-1 XylB. They are part of an array of hemicellulases that are involved in the final breakdown of plant cell-wall whereby they degrade xylan. They hydrolyze beta-1,4 glycosidic bonds between two xylose units in short xylooligosaccharides. These are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. These enzymes possess an additional C-terminal beta-sandwich domain that restricts access for substrates to a portion of the active site to form a pocket. The active-site pockets comprise of two subsites, with binding capacity for two monosaccharide moieties and a single route of access for small molecules such as substrate. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCI63974.1 | 2.90e-298 | 1 | 395 | 1 | 396 |
| BCI63975.1 | 4.70e-199 | 50 | 389 | 31 | 371 |
| BCI63971.1 | 7.09e-71 | 56 | 381 | 31 | 338 |
| QGY47516.1 | 3.35e-38 | 63 | 389 | 24 | 375 |
| AWB65485.1 | 9.65e-34 | 80 | 387 | 48 | 378 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2EXH_A | 2.17e-17 | 82 | 329 | 15 | 230 | Structureof the family43 beta-Xylosidase from geobacillus stearothermophilus [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],2EXH_B Structure of the family43 beta-Xylosidase from geobacillus stearothermophilus [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],2EXH_C Structure of the family43 beta-Xylosidase from geobacillus stearothermophilus [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],2EXH_D Structure of the family43 beta-Xylosidase from geobacillus stearothermophilus [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
| 2EXI_A | 1.24e-16 | 83 | 329 | 16 | 230 | ChainA, beta-D-xylosidase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],2EXI_B Chain B, beta-D-xylosidase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],2EXI_C Chain C, beta-D-xylosidase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],2EXI_D Chain D, beta-D-xylosidase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
| 2EXJ_A | 1.66e-16 | 82 | 329 | 15 | 230 | ChainA, beta-D-xylosidase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],2EXJ_B Chain B, beta-D-xylosidase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],2EXJ_C Chain C, beta-D-xylosidase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],2EXJ_D Chain D, beta-D-xylosidase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
| 2EXK_A | 1.66e-16 | 82 | 329 | 15 | 230 | ChainA, beta-D-xylosidase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],2EXK_B Chain B, beta-D-xylosidase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],2EXK_C Chain C, beta-D-xylosidase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],2EXK_D Chain D, beta-D-xylosidase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
| 3C2U_A | 9.60e-15 | 82 | 329 | 14 | 229 | Structureof the two subsite D-xylosidase from Selenomonas ruminantium in complex with 1,3-bis[tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamino]propane [Selenomonas ruminantium],3C2U_B Structure of the two subsite D-xylosidase from Selenomonas ruminantium in complex with 1,3-bis[tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamino]propane [Selenomonas ruminantium],3C2U_C Structure of the two subsite D-xylosidase from Selenomonas ruminantium in complex with 1,3-bis[tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamino]propane [Selenomonas ruminantium],3C2U_D Structure of the two subsite D-xylosidase from Selenomonas ruminantium in complex with 1,3-bis[tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamino]propane [Selenomonas ruminantium] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
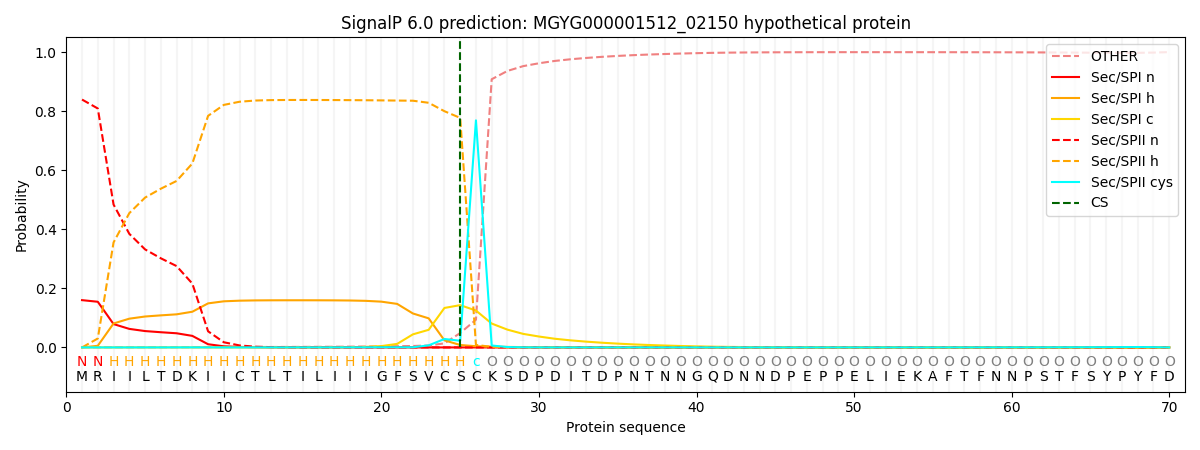
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.001319 | 0.153703 | 0.844263 | 0.000237 | 0.000263 | 0.000200 |
