You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001522_00201
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001522_00201
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Pauljensenia radingae_A | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Actinobacteriota; Actinomycetia; Actinomycetales; Actinomycetaceae; Pauljensenia; Pauljensenia radingae_A | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001522_00201 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH23 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 201257; End: 202720 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COG3583 | YabE | 1.09e-28 | 60 | 323 | 23 | 288 | Uncharacterized conserved protein YabE, contains G5 and tandem DUF348 domains [Function unknown]. |
| pfam07501 | G5 | 9.26e-09 | 247 | 319 | 3 | 75 | G5 domain. This domain is found in a wide range of extracellular proteins. It is found tandemly repeated in up to 8 copies. It is found in the N-terminus of peptidases belonging to the M26 family which cleave human IgA. The domain is also found in proteins involved in metabolism of bacterial cell walls suggesting this domain may have an adhesive function. |
| pfam03990 | DUF348 | 3.88e-07 | 77 | 117 | 1 | 41 | Domain of unknown function (DUF348). This domain normally occurs as tandem repeats; however it is found as a single copy in the S. cerevisiae DNA-binding nuclear protein YCR593. This protein is involved in sporulation part of the SET3C complex, which is required to repress early/middle sporulation genes during meiosis. The bacterial proteins are likely to be involved in a cell wall function as they are found in conjunction with the pfam07501 domain, which is involved in various cell surface processes. |
| cd13399 | Slt35-like | 5.98e-05 | 415 | 443 | 11 | 39 | Slt35-like lytic transglycosylase. Lytic transglycosylase similar to Escherichia coli lytic transglycosylase Slt35 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Sltb1. Lytic transglycosylase (LT) catalyzes the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc) as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. Proteins similar to this this family include the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria, the LTs in bacteriophage lambda, as well as the eukaryotic "goose-type" lysozymes (goose egg-white lysozyme; GEWL). |
| cd21441 | KLF12_N | 0.010 | 116 | 214 | 39 | 137 | N-terminal domain of Kruppel-like factor 12. Kruppel-like factor 12 (also known as Krueppel-like transcription factor 12, KLF12) regulates, by transcriptionally repressing Nur77 expression, endometrial decidualization, which is a prerequisite for successful implantation and the establishment of pregnancy. It is involved in the maturation processes of kidney collecting ducts after birth, and is able to increase the promoter activity of the UT-A1 urea transporter promoter by binding to the CACCC motif. KLF12 has also been found to promote colorectal cancer growth is also involved in the invasion and apoptosis of basal-like breast carcinoma. KLF12 belongs to a family of proteins called the Specificity Protein (SP)/KLF family, characterized by a C-terminal DNA-binding domain of 81 amino acids consisting of three Kruppel-like C2H2 zinc fingers. These factors bind to a loose consensus motif, namely NNRCRCCYY (where N is any nucleotide; R is A/G, and Y is C/T), such as the recurring motifs in GC and GT boxes (5'-GGGGCGGGG-3' and 5-GGTGTGGGG-3') that are present in promoters and more distal regulatory elements of mammalian genes. Although these factors bind to similar elements in vitro, they have distinct activities in vivo depending on their expression profile and the sequence of the N-terminal activation/repression domain, which differ between members. KLF12 contains an N-terminal domain that is related to the N-terminal repression domain of KLF8. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDT86987.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 487 | 1 | 487 |
| QPK82169.1 | 1.54e-146 | 78 | 487 | 1 | 412 |
| AKU65287.1 | 2.61e-146 | 45 | 487 | 28 | 469 |
| QQC44019.1 | 2.61e-146 | 45 | 487 | 28 | 469 |
| QCT35005.1 | 1.03e-145 | 45 | 487 | 28 | 479 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q6M6N7 | 1.14e-15 | 67 | 340 | 33 | 306 | Resuscitation-promoting factor Rpf2 OS=Corynebacterium glutamicum (strain ATCC 13032 / DSM 20300 / BCRC 11384 / JCM 1318 / LMG 3730 / NCIMB 10025) OX=196627 GN=rpf2 PE=1 SV=1 |
| A0R3E0 | 3.71e-10 | 68 | 340 | 17 | 294 | Resuscitation-promoting factor RpfB OS=Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) OX=246196 GN=rpfB PE=3 SV=2 |
| P37546 | 1.87e-09 | 50 | 394 | 13 | 355 | Putative cell wall shaping protein YabE OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=yabE PE=2 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
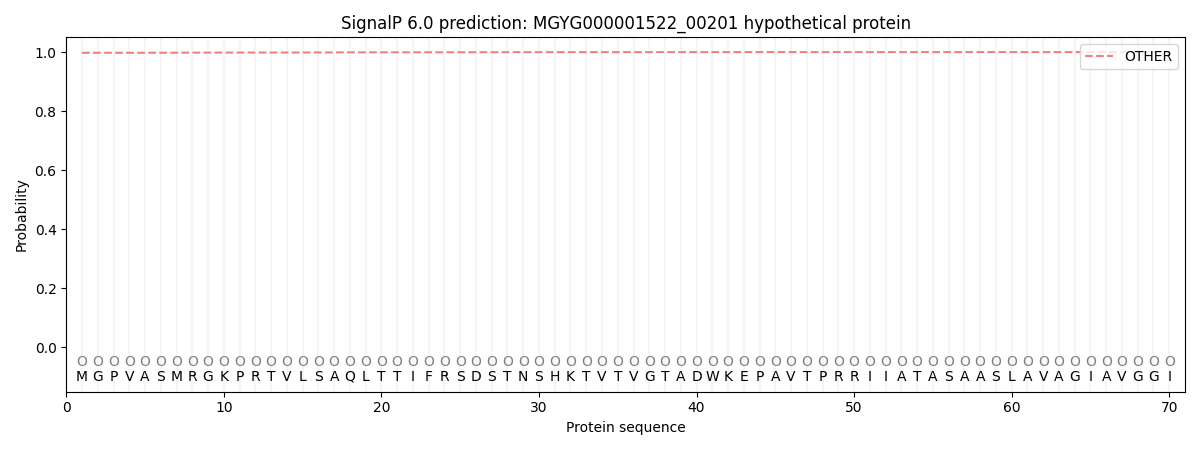
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.997977 | 0.001955 | 0.000027 | 0.000009 | 0.000008 | 0.000010 |
