You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001534_00431
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001534_00431
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Xanthomonas_B massiliensis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Xanthomonadales; Xanthomonadaceae; Xanthomonas_B; Xanthomonas_B massiliensis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001534_00431 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH20 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 71183; End: 73393 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH20 | 170 | 512 | 6.1e-107 | 0.9762611275964391 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd06570 | GH20_chitobiase-like_1 | 2.05e-143 | 175 | 524 | 1 | 311 | A functionally uncharacterized subgroup of the Glycosyl hydrolase family 20 (GH20) catalytic domain found in proteins similar to the chitobiase of Serratia marcescens, a beta-N-1,4-acetylhexosaminidase that hydrolyzes the beta-1,4-glycosidic linkages in oligomers derived from chitin. Chitin is degraded by a two step process: i) a chitinase hydrolyzes the chitin to oligosaccharides and disaccharides such as di-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and chitobiose, ii) chitobiase then further degrades these oligomers into monomers. This subgroup lacks the C-terminal PKD (polycystic kidney disease I)-like domain found in the chitobiases. The GH20 hexosaminidases are thought to act via a catalytic mechanism in which the catalytic nucleophile is not provided by solvent or the enzyme, but by the substrate itself. |
| cd06563 | GH20_chitobiase-like | 3.52e-129 | 175 | 524 | 1 | 357 | The chitobiase of Serratia marcescens is a beta-N-1,4-acetylhexosaminidase with a glycosyl hydrolase family 20 (GH20) domain that hydrolyzes the beta-1,4-glycosidic linkages in oligomers derived from chitin. Chitin is degraded by a two step process: i) a chitinase hydrolyzes the chitin to oligosaccharides and disaccharides such as di-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and chitobiose, ii) chitobiase then further degrades these oligomers into monomers. This GH20 domain family includes an N-acetylglucosamidase (GlcNAcase A) from Pseudoalteromonas piscicida and an N-acetylhexosaminidase (SpHex) from Streptomyces plicatus. SpHex lacks the C-terminal PKD (polycystic kidney disease I)-like domain found in the chitobiases. The GH20 hexosaminidases are thought to act via a catalytic mechanism in which the catalytic nucleophile is not provided by solvent or the enzyme, but by the substrate itself. |
| pfam00728 | Glyco_hydro_20 | 1.31e-122 | 175 | 511 | 1 | 345 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 20, catalytic domain. This domain has a TIM barrel fold. |
| cd06562 | GH20_HexA_HexB-like | 3.56e-111 | 175 | 525 | 1 | 338 | Beta-N-acetylhexosaminidases catalyze the removal of beta-1,4-linked N-acetyl-D-hexosamine residues from the non-reducing ends of N-acetyl-beta-D-hexosaminides including N-acetylglucosides and N-acetylgalactosides. The hexA and hexB genes encode the alpha- and beta-subunits of the two major beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase isoenzymes, N-acetyl-beta-D-hexosaminidase A (HexA) and beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase B (HexB). Both the alpha and the beta catalytic subunits have a TIM-barrel fold and belong to the glycosyl hydrolase family 20 (GH20). The HexA enzyme is a heterodimer containing one alpha and one beta subunit while the HexB enzyme is a homodimer containing two beta-subunits. Hexosaminidase mutations cause an inability to properly hydrolyze certain sphingolipids which accumulate in lysosomes within the brain, resulting in the lipid storage disorders Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff. Mutations in the alpha subunit cause in a deficiency in the HexA enzyme and result in Tay-Sachs, mutations in the beta-subunit cause in a deficiency in both HexA and HexB enzymes and result in Sandhoff disease. In both disorders GM(2) gangliosides accumulate in lysosomes. The GH20 hexosaminidases are thought to act via a catalytic mechanism in which the catalytic nucleophile is not provided by solvent or the enzyme, but by the substrate itself. |
| COG3525 | Chb | 1.25e-86 | 123 | 537 | 206 | 638 | N-acetyl-beta-hexosaminidase [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKC88203.1 | 0.0 | 67 | 736 | 1 | 670 |
| QKR98531.1 | 5.60e-200 | 31 | 736 | 9 | 708 |
| ARW18249.1 | 3.08e-181 | 40 | 736 | 28 | 714 |
| AQU88477.1 | 4.34e-181 | 28 | 730 | 17 | 710 |
| AXY21037.1 | 1.48e-180 | 32 | 733 | 30 | 722 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6YHH_A | 1.68e-99 | 121 | 656 | 90 | 620 | X-rayStructure of Flavobacterium johnsoniae chitobiase (FjGH20) [Flavobacterium johnsoniae UW101],6YHH_B X-ray Structure of Flavobacterium johnsoniae chitobiase (FjGH20) [Flavobacterium johnsoniae UW101] |
| 6EZR_A | 1.13e-65 | 122 | 537 | 207 | 633 | Crystalstructure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi [Vibrio harveyi],6EZR_B Crystal structure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi [Vibrio harveyi],6EZS_A Crystal structure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi in complex with N-acetylglucosamine [Vibrio harveyi],6EZS_B Crystal structure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi in complex with N-acetylglucosamine [Vibrio harveyi],6K35_A Crystal structure of GH20 exo beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi in complex with NAG-thiazoline [Vibrio harveyi],6K35_B Crystal structure of GH20 exo beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi in complex with NAG-thiazoline [Vibrio harveyi] |
| 6EZT_A | 1.41e-64 | 122 | 537 | 204 | 630 | Crystalstructure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase D437A inactive mutant from Vibrio harveyi [Vibrio harveyi],6EZT_B Crystal structure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase D437A inactive mutant from Vibrio harveyi [Vibrio harveyi] |
| 7CBN_A | 4.76e-61 | 123 | 558 | 78 | 526 | Crystalstructure of beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase Am0868 from Akkermansia muciniphila [Akkermansia muciniphila ATCC BAA-835],7CBO_A Crystal structure of beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase Am0868 from Akkermansia muciniphila in complex with GlcNAc [Akkermansia muciniphila ATCC BAA-835] |
| 5BRO_A | 1.97e-60 | 121 | 524 | 103 | 487 | Crystalstructure of modified HexB (modB) [Homo sapiens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P49008 | 6.38e-68 | 118 | 562 | 106 | 551 | Beta-hexosaminidase OS=Porphyromonas gingivalis (strain ATCC BAA-308 / W83) OX=242619 GN=nahA PE=3 SV=2 |
| P96155 | 7.80e-67 | 107 | 505 | 191 | 601 | Beta-hexosaminidase OS=Vibrio furnissii OX=29494 GN=exoI PE=1 SV=1 |
| P20060 | 7.59e-65 | 121 | 526 | 124 | 510 | Beta-hexosaminidase subunit beta OS=Mus musculus OX=10090 GN=Hexb PE=1 SV=2 |
| P49614 | 8.77e-62 | 121 | 538 | 119 | 517 | Beta-hexosaminidase subunit beta OS=Felis catus OX=9685 GN=HEXB PE=2 SV=2 |
| Q29548 | 1.21e-61 | 121 | 538 | 119 | 517 | Beta-hexosaminidase subunit beta OS=Sus scrofa OX=9823 GN=HEXB PE=1 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
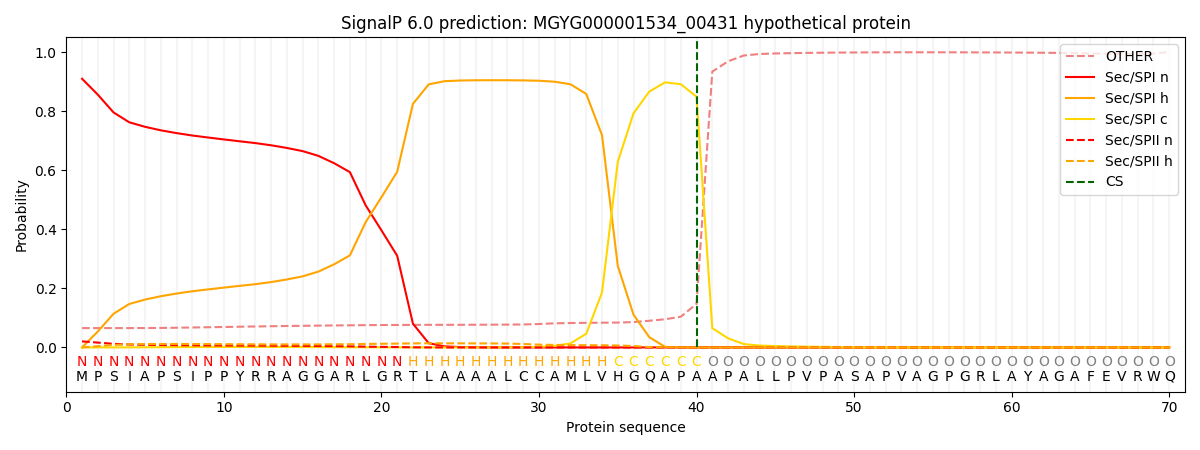
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.075319 | 0.891885 | 0.024559 | 0.006418 | 0.001101 | 0.000700 |
