You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001548_02778
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001548_02778
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
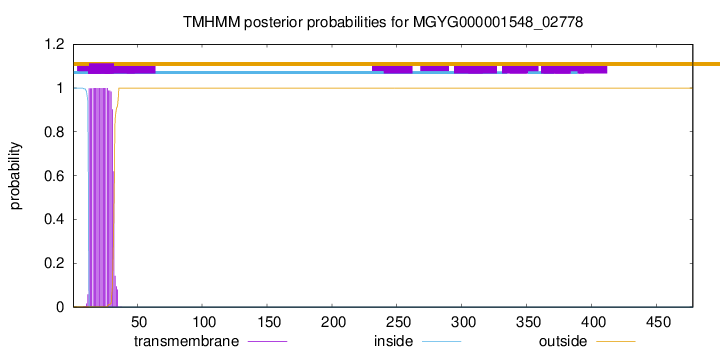
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Paenibacillus_A tuaregi | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Paenibacillales; Paenibacillaceae; Paenibacillus_A; Paenibacillus_A tuaregi | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001548_02778 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CE4 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 3003061; End: 3004497 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd10917 | CE4_NodB_like_6s_7s | 7.28e-77 | 282 | 457 | 1 | 171 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of rhizobial NodB-like proteins. This family belongs to the large and functionally diverse carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily, whose members show strong sequence similarity with some variability due to their distinct carbohydrate substrates. It includes many rhizobial NodB chitooligosaccharide N-deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.-)-like proteins, mainly from bacteria and eukaryotes, such as chitin deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.41), bacterial peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.-), and acetylxylan esterases (EC 3.1.1.72), which catalyze the N- or O-deacetylation of substrates such as acetylated chitin, peptidoglycan, and acetylated xylan. All members of this family contain a catalytic NodB homology domain with the same overall topology and a deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold with 6- or 7 strands. Their catalytic activity is dependent on the presence of a divalent cation, preferably cobalt or zinc, and they employ a conserved His-His-Asp zinc-binding triad closely associated with the conserved catalytic base (aspartic acid) and acid (histidine) to carry out acid/base catalysis. Several family members show diversity both in metal ion specificities and in the residues that coordinate the metal. |
| cd10962 | CE4_GT2-like | 6.46e-73 | 282 | 471 | 1 | 196 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of uncharacterized bacterial glycosyl transferase, group 2-like family proteins. This family includes many uncharacterized bacterial proteins containing an N-terminal GH18 (glycosyl hydrolase, family 18) domain, a middle NodB-like homology domain, and a C-terminal GT2-like (glycosyl transferase group 2) domain. Although their biological function is unknown, members in this family contain a middle NodB homology domain that is similar to the catalytic domain of Streptococcus pneumoniae polysaccharide deacetylase PgdA (SpPgdA), an extracellular metal-dependent polysaccharide deacetylase with de-N-acetylase activity toward a hexamer of chitooligosaccharide N-acetylglucosamine, but not shorter chitooligosaccharides or a synthetic peptidoglycan tetrasaccharide. Like SpPgdA, this family is a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. The presence of three domains suggests that members of this family may be multifunctional. |
| cd02696 | MurNAc-LAA | 1.90e-69 | 66 | 235 | 1 | 172 | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase or MurNAc-LAA (also known as peptidoglycan aminohydrolase, NAMLA amidase, NAMLAA, Amidase 3, and peptidoglycan amidase; EC 3.5.1.28) is an autolysin that hydrolyzes the amide bond between N-acetylmuramoyl and L-amino acids in certain cell wall glycopeptides. These proteins are Zn-dependent peptidases with highly conserved residues involved in cation co-ordination. MurNAc-LAA in this family is one of several peptidoglycan hydrolases (PGHs) found in bacterial and bacteriophage or prophage genomes that are involved in the degradation of the peptidoglycan. In Escherichia coli, there are five MurNAc-LAAs present: AmiA, AmiB, AmiC and AmiD that are periplasmic, and AmpD that is cytoplasmic. Three of these (AmiA, AmiB and AmiC) belong to this family, the other two (AmiD and AmpD) do not. E. coli AmiA, AmiB and AmiC play an important role in cleaving the septum to release daughter cells after cell division. In general, bacterial MurNAc-LAAs are members of the bacterial autolytic system and carry a signal peptide in their N-termini that allows their transport across the cytoplasmic membrane. However, the bacteriophage MurNAc-LAAs are endolysins since these phage-encoded enzymes break down bacterial peptidoglycan at the terminal stage of the phage reproduction cycle. As opposed to autolysins, almost all endolysins have no signal peptides and their translocation through the cytoplasmic membrane is thought to proceed with the help of phage-encoded holin proteins. The amidase catalytic module is fused to another functional module (cell wall binding module or CWBM) either at the N- or C-terminus, which is responsible for high affinity binding of the protein to the cell wall. |
| cd10959 | CE4_NodB_like_3 | 2.17e-69 | 282 | 466 | 1 | 187 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of uncharacterized bacterial polysaccharide deacetylases. This family includes many uncharacterized bacterial polysaccharide deacetylases. Although their biological function still remains unknown, members in this family show high sequence homology to the catalytic NodB homology domain of Streptococcus pneumoniae polysaccharide deacetylase PgdA (SpPgdA), which is an extracellular metal-dependent polysaccharide deacetylase with de-N-acetylase activity toward a hexamer of chitooligosaccharide N-acetylglucosamine, but not shorter chitooligosaccharides or a synthetic peptidoglycan tetrasaccharide. Like SpPgdA, this family is a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. |
| cd10947 | CE4_SpPgdA_BsYjeA_like | 1.10e-67 | 282 | 466 | 1 | 177 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of Streptococcus pneumoniae peptidoglycan deacetylase PgdA, Bacillus subtilis BsYjeA protein, and their bacterial homologs. This family is represented by Streptococcus pneumoniae peptidoglycan GlcNAc deacetylase (SpPgdA), a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. SpPgdA protects gram-positive bacterial cell wall from host lysozymes by deacetylating peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) residues. It consists of three separate domains: N-terminal, middle and C-terminal (catalytic) domains. The catalytic NodB homology domain is similar to the deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold adopted by other CE4 esterases, which harbors a mononuclear metalloenzyme employing a conserved His-His-Asp zinc-binding triad closely associated with conserved catalytic base (aspartic acid) and acid (histidine) to carry out acid/base catalysis. The enzyme is able to accept GlcNAc3 as a substrate, with the N-acetyl of the middle sugar being removed by the enzyme. This family also includes Bacillus subtilis BsYjeA protein encoded by the yjeA gene, which is one of the six polysaccharide deacetylase gene homologs (pdaA, pdaB/ybaN, yheN, yjeA, yxkH and ylxY) in the Bacillus subtilis genome. Although homology comparison shows that the BsYjeA protein contains a polysaccharide deacetylase domain, and was predicted to be a membrane-bound xylanase or a membrane-bound chitooligosaccharide deacetylase, more recent research indicates BsYjeA might be a novel non-specific secretory endonuclease which creates random nicks progressively on the two strands of dsDNA, resulting in highly distinguishable intermediates/products very different in chemical and physical compositions over time. In addition, BsYjeA shares several enzymatic properties with the well-understood DNase I endonuclease. Both enzymes are active on ssDNA and dsDNA, both generate random nicks, and both require Mg2+ or Mn2+ for hydrolytic activity. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWP28024.1 | 1.29e-210 | 1 | 476 | 1 | 476 |
| ANA82425.1 | 6.50e-209 | 1 | 476 | 1 | 478 |
| AVV58836.1 | 6.50e-209 | 1 | 476 | 1 | 478 |
| AYB44783.1 | 3.03e-193 | 1 | 478 | 1 | 480 |
| QOT12681.1 | 1.23e-192 | 1 | 478 | 1 | 480 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5O6Y_A | 2.10e-54 | 268 | 469 | 7 | 207 | Crystalstructure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase in complex with 4-naphthalen-1-yl-~{N}-oxidanyl-benzamide [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579] |
| 5O6Y_B | 3.16e-53 | 268 | 469 | 7 | 207 | Crystalstructure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase in complex with 4-naphthalen-1-yl-~{N}-oxidanyl-benzamide [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579],5O6Y_C Crystal structure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase in complex with 4-naphthalen-1-yl-~{N}-oxidanyl-benzamide [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579],5O6Y_D Crystal structure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase in complex with 4-naphthalen-1-yl-~{N}-oxidanyl-benzamide [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579] |
| 4L1G_A | 1.82e-52 | 268 | 469 | 59 | 259 | Crystalstructure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase from Bacillus cereus [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579],4L1G_B Crystal structure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase from Bacillus cereus [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579],4L1G_C Crystal structure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase from Bacillus cereus [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579],4L1G_D Crystal structure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase from Bacillus cereus [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579] |
| 7FBW_A | 1.99e-47 | 270 | 474 | 105 | 304 | ChainA, Predicted xylanase/chitin deacetylase [Caldanaerobacter subterraneus subsp. tengcongensis MB4] |
| 2C1G_A | 1.04e-46 | 208 | 471 | 159 | 417 | Structureof Streptococcus pneumoniae peptidoglycan deacetylase (SpPgdA) [Streptococcus pneumoniae R6] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q81EK9 | 7.08e-53 | 268 | 469 | 67 | 267 | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase BC_1960 OS=Bacillus cereus (strain ATCC 14579 / DSM 31 / CCUG 7414 / JCM 2152 / NBRC 15305 / NCIMB 9373 / NCTC 2599 / NRRL B-3711) OX=226900 GN=BC_1960 PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q8DP63 | 1.07e-45 | 208 | 471 | 191 | 449 | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase OS=Streptococcus pneumoniae (strain ATCC BAA-255 / R6) OX=171101 GN=pgdA PE=1 SV=1 |
| O34798 | 2.59e-39 | 282 | 469 | 278 | 457 | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylmuramic acid deacetylase PdaC OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=pdaC PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q52845 | 5.27e-38 | 264 | 468 | 6 | 217 | Chitooligosaccharide deacetylase OS=Mesorhizobium japonicum (strain LMG 29417 / CECT 9101 / MAFF 303099) OX=266835 GN=nodB PE=3 SV=2 |
| Q8Y9V5 | 5.95e-37 | 278 | 469 | 262 | 445 | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase PgdA OS=Listeria monocytogenes serovar 1/2a (strain ATCC BAA-679 / EGD-e) OX=169963 GN=pgdA PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
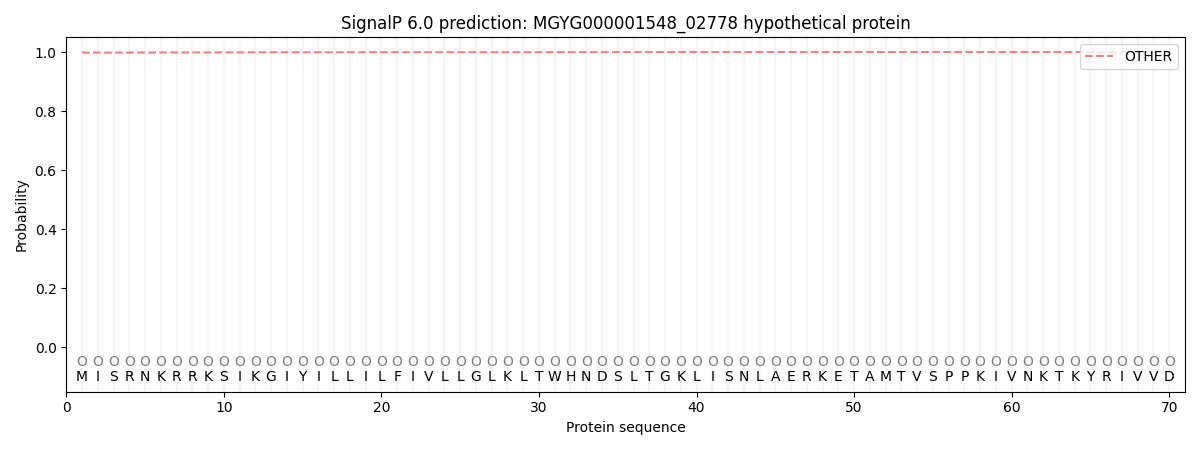
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.998451 | 0.000758 | 0.000135 | 0.000004 | 0.000002 | 0.000685 |