You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001624_02463
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001624_02463
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
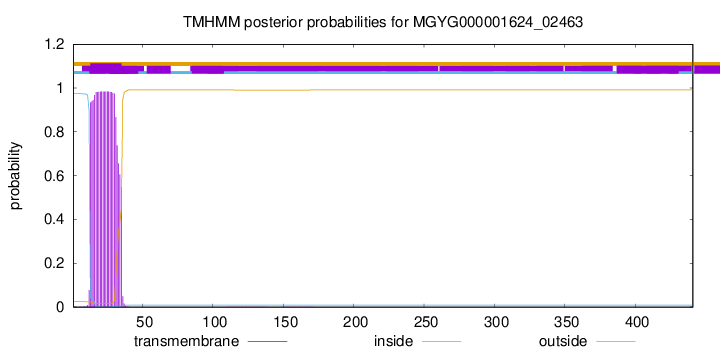
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Proteus cibarius | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Enterobacterales; Enterobacteriaceae; Proteus; Proteus cibarius | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001624_02463 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM50 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase AmiB | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 25455; End: 26780 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRK10431 | PRK10431 | 5.34e-166 | 19 | 440 | 9 | 425 | N-acetylmuramoyl-l-alanine amidase II; Provisional |
| COG0860 | AmiC | 1.59e-73 | 192 | 434 | 26 | 231 | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
| cd02696 | MurNAc-LAA | 1.91e-60 | 210 | 427 | 1 | 171 | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase or MurNAc-LAA (also known as peptidoglycan aminohydrolase, NAMLA amidase, NAMLAA, Amidase 3, and peptidoglycan amidase; EC 3.5.1.28) is an autolysin that hydrolyzes the amide bond between N-acetylmuramoyl and L-amino acids in certain cell wall glycopeptides. These proteins are Zn-dependent peptidases with highly conserved residues involved in cation co-ordination. MurNAc-LAA in this family is one of several peptidoglycan hydrolases (PGHs) found in bacterial and bacteriophage or prophage genomes that are involved in the degradation of the peptidoglycan. In Escherichia coli, there are five MurNAc-LAAs present: AmiA, AmiB, AmiC and AmiD that are periplasmic, and AmpD that is cytoplasmic. Three of these (AmiA, AmiB and AmiC) belong to this family, the other two (AmiD and AmpD) do not. E. coli AmiA, AmiB and AmiC play an important role in cleaving the septum to release daughter cells after cell division. In general, bacterial MurNAc-LAAs are members of the bacterial autolytic system and carry a signal peptide in their N-termini that allows their transport across the cytoplasmic membrane. However, the bacteriophage MurNAc-LAAs are endolysins since these phage-encoded enzymes break down bacterial peptidoglycan at the terminal stage of the phage reproduction cycle. As opposed to autolysins, almost all endolysins have no signal peptides and their translocation through the cytoplasmic membrane is thought to proceed with the help of phage-encoded holin proteins. The amidase catalytic module is fused to another functional module (cell wall binding module or CWBM) either at the N- or C-terminus, which is responsible for high affinity binding of the protein to the cell wall. |
| PRK10319 | PRK10319 | 3.12e-57 | 195 | 440 | 44 | 285 | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase AmiA. |
| pfam01520 | Amidase_3 | 4.89e-52 | 211 | 427 | 1 | 172 | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase. This enzyme domain cleaves the amide bond between N-acetylmuramoyl and L-amino acids in bacterial cell walls. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADV97335.1 | 3.90e-145 | 20 | 440 | 5 | 430 |
| QOW12656.1 | 3.90e-145 | 20 | 440 | 5 | 430 |
| ACY57230.1 | 3.90e-145 | 20 | 440 | 5 | 430 |
| QFR75324.1 | 3.90e-145 | 20 | 440 | 5 | 430 |
| QFS74615.1 | 3.90e-145 | 20 | 440 | 5 | 430 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4BIN_A | 1.81e-48 | 61 | 431 | 46 | 393 | Crystalstructure of the E. coli N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase AmiC [Escherichia coli K-12] |
| 3NE8_A | 2.95e-29 | 211 | 430 | 7 | 223 | Thecrystal structure of a domain from N-acetylmuramoyl-l-alanine amidase of Bartonella henselae str. Houston-1 [Bartonella henselae] |
| 5EMI_A | 2.34e-20 | 205 | 430 | 1 | 177 | ChainA, Cell wall hydrolase/autolysin [Nostoc punctiforme PCC 73102] |
| 1JWQ_A | 2.84e-19 | 210 | 430 | 3 | 175 | Structureof the catalytic domain of CwlV, N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase from Bacillus(Paenibacillus) polymyxa var.colistinus [Paenibacillus polymyxa] |
| 4RN7_A | 2.29e-18 | 206 | 430 | 1 | 181 | ChainA, N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase [Clostridioides difficile 630] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P26365 | 8.28e-128 | 33 | 440 | 22 | 425 | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase AmiB OS=Escherichia coli (strain K12) OX=83333 GN=amiB PE=1 SV=2 |
| P26366 | 7.11e-125 | 31 | 440 | 20 | 419 | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase AmiB OS=Salmonella typhimurium (strain LT2 / SGSC1412 / ATCC 700720) OX=99287 GN=amiB PE=3 SV=2 |
| P44493 | 3.40e-79 | 209 | 427 | 23 | 243 | Probable N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase AmiB OS=Haemophilus influenzae (strain ATCC 51907 / DSM 11121 / KW20 / Rd) OX=71421 GN=amiB PE=3 SV=1 |
| P57638 | 3.55e-54 | 206 | 431 | 2 | 228 | Putative N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase OS=Buchnera aphidicola subsp. Acyrthosiphon pisum (strain APS) OX=107806 GN=amiB PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q89A33 | 2.03e-49 | 209 | 432 | 1 | 210 | Putative N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase OS=Buchnera aphidicola subsp. Baizongia pistaciae (strain Bp) OX=224915 GN=amiB PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
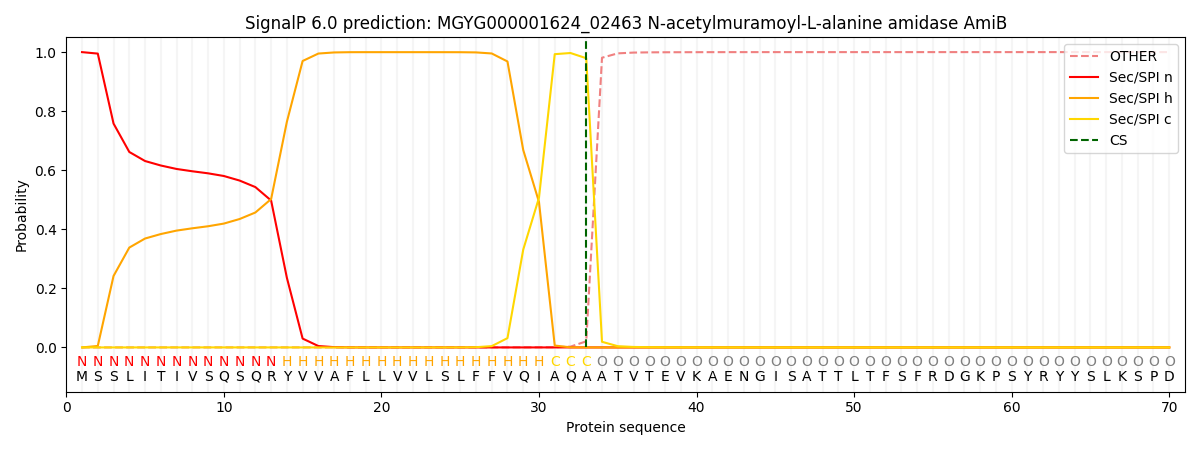
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000285 | 0.999099 | 0.000165 | 0.000152 | 0.000133 | 0.000126 |