You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001663_01350
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001663_01350
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Alistipes sp900760675 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Rikenellaceae; Alistipes; Alistipes sp900760675 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001663_01350 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH0 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 8870; End: 11119 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam17389 | Bac_rhamnosid6H | 2.58e-07 | 165 | 303 | 87 | 222 | Bacterial alpha-L-rhamnosidase 6 hairpin glycosidase domain. This family consists of bacterial rhamnosidase A and B enzymes. L-Rhamnose is abundant in biomass as a common constituent of glycolipids and glycosides, such as plant pigments, pectic polysaccharides, gums or biosurfactants. Some rhamnosides are important bioactive compounds. For example, terpenyl glycosides, the glycosidic precursor of aromatic terpenoids, act as important flavouring substances in grapes. Other rhamnosides act as cytotoxic rhamnosylated terpenoids, as signal substances in plants or play a role in the antigenicity of pathogenic bacteria. |
| pfam06202 | GDE_C | 6.07e-06 | 172 | 394 | 82 | 324 | Amylo-alpha-1,6-glucosidase. This family includes human glycogen branching enzyme AGL. This enzyme contains a number of distinct catalytic activities. It has been shown for the yeast homolog GDB1 that mutations in this region disrupt the enzymes Amylo-alpha-1,6-glucosidase (EC:3.2.1.33). |
| cd04083 | CBM35_Lmo2446-like | 9.80e-06 | 612 | 745 | 2 | 125 | Carbohydrate Binding Module 35 (CBM35) domains similar to Lmo2446. This family includes carbohydrate binding module 35 (CBM35) domains that are appended to several carbohydrate binding enzymes. Some CBM35 domains belonging to this family are appended to glycoside hydrolase (GH) family domains, including glycoside hydrolase family 31 (GH31), for example the CBM35 domain of Lmo2446, an uncharacterized protein from Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e. These CBM35s are non-catalytic carbohydrate binding domains that facilitate the strong binding of the GH catalytic modules with their dedicated, insoluble substrates. GH31 has a wide range of hydrolytic activities such as alpha-glucosidase, alpha-xylosidase, 6-alpha-glucosyltransferase, or alpha-1,4-glucan lyase, cleaving a terminal carbohydrate moiety from a substrate that may be a starch or a glycoprotein. Most characterized GH31 enzymes are alpha-glucosidases. |
| cd04082 | CBM35_pectate_lyase-like | 3.29e-05 | 627 | 723 | 20 | 109 | Carbohydrate Binding Module family 35 (CBM35), pectate lyase-like; appended mainly to enzymes that bind mannan (Man), xylan, glucuronic acid (GlcA) and possibly glucans. This family includes carbohydrate binding module family 35 (CBM35) domains that are non-catalytic carbohydrate binding domains that are appended mainly to enzymes that bind mannan (Man), xylan, glucuronic acid (GlcA) and possibly glucans. Included in this family are CBM35s of pectate lyases, including pectate lyase 10A from Cellvibrio japonicas, these enzymes release delta-4,5-anhydrogalaturonic acid (delta4,5-GalA) from pectin, thus identifying a signature molecule for plant cell wall degradation. CBM35s are unique in that they display conserved specificity through extensive sequence similarity but divergent function through their appended catalytic modules. They are known to bind alpha-D-galactose (Gal), mannan (Man), xylan, glucuronic acid (GlcA), a beta-polymer of mannose, and possibly glucans, forming four subfamilies based on general ligand specificities (galacto, urono, manno, and gluco configurations). In contrast to most CBMs that are generally rigid proteins, CBM35 undergoes significant conformational change upon ligand binding. Some CBM35s bind their ligands in a calcium-dependent manner, especially those binding uronic acids. |
| pfam01204 | Trehalase | 7.61e-04 | 265 | 346 | 320 | 398 | Trehalase. Trehalase (EC:3.2.1.28) is known to recycle trehalose to glucose. Trehalose is a physiological hallmark of heat-shock response in yeast and protects of proteins and membranes against a variety of stresses. This family is found in conjunction with pfam07492 in fungi. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QEC42842.1 | 4.46e-185 | 74 | 741 | 216 | 888 |
| QNE41784.1 | 3.34e-177 | 74 | 747 | 215 | 891 |
| QEC58493.1 | 2.09e-176 | 67 | 741 | 191 | 870 |
| AYA38918.1 | 3.88e-175 | 67 | 747 | 228 | 914 |
| QDA62675.1 | 1.67e-174 | 67 | 747 | 193 | 880 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
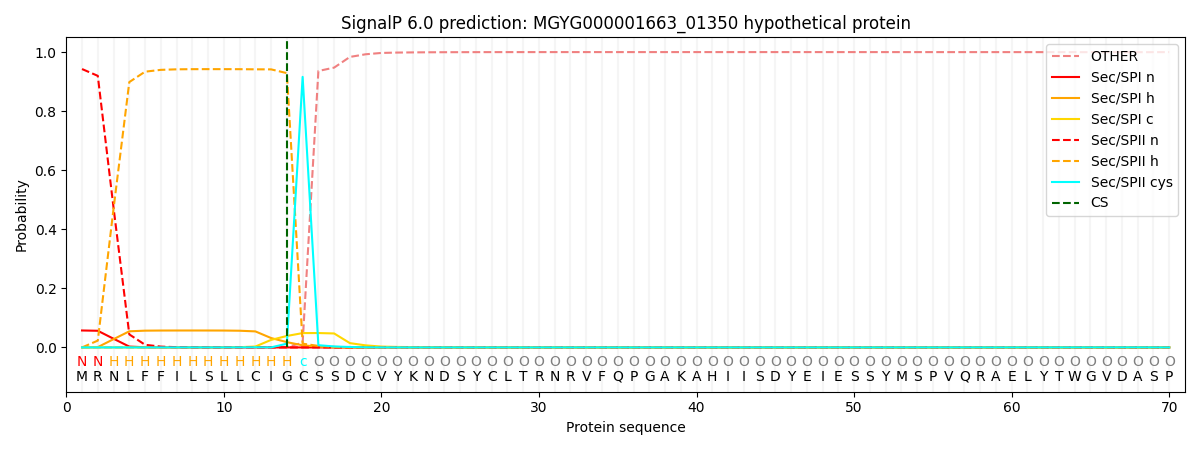
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000234 | 0.055371 | 0.944313 | 0.000026 | 0.000044 | 0.000034 |
