You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001713_04164
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001713_04164
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Vibrio furnissii | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Enterobacterales; Vibrionaceae; Vibrio; Vibrio furnissii | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001713_04164 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH23 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase F | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 12496; End: 13941 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH23 | 316 | 453 | 2.6e-21 | 0.7925925925925926 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd01009 | PBP2_YfhD_N | 1.81e-63 | 43 | 277 | 1 | 221 | The solute binding domain of YfhD proteins, a member of the type 2 periplasmic binding fold protein superfamily. This subfamily includes the solute binding domain YfhD_N. These domains are found in the YfhD proteins that are predicted to function as lytic transglycosylases that cleave the glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetylglucosamin in peptidoglycan, while the YfhD_N domain might act as an auxiliary or regulatory subunit. In addition to periplasmic solute binding domain, they have an SLT domain, typically found in soluble lytic transglycosylases, and a C-terminal low complexity domain. The YfhD proteins might have been recruited to create localized cell wall openings required for transport of large substrates such as DNA. They belong to the PBP2 superfamily of periplasmic binding proteins that differ in size and ligand specificity, but have similar tertiary structures consisting of two globular subdomains connected by a flexible hinge. They have been shown to bind their ligand in the cleft between these domains in a manner resembling a Venus flytrap. |
| cd13403 | MLTF-like | 2.38e-62 | 303 | 454 | 1 | 161 | membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase F (MLTF) and similar proteins. This subfamily includes membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase F (MltF, murein lyase F) that degrades murein glycan strands. It is responsible for catalyzing the release of 1,6-anhydromuropeptides from peptidoglycan. Lytic transglycosylase catalyzes the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc) as do goose-type lysozymes. However, in addition, it also makes a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. |
| COG4623 | MltF | 4.95e-49 | 31 | 450 | 11 | 429 | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase MltF [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis, Signal transduction mechanisms]. |
| PRK10859 | PRK10859 | 2.15e-48 | 40 | 481 | 40 | 473 | membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase MltF. |
| cd13530 | PBP2_peptides_like | 1.80e-23 | 44 | 277 | 1 | 217 | Peptide-binding protein and related homologs; type 2 periplasmic binding protein fold. This domain is found in solute binding proteins that serve as initial receptors in the ABC transport, signal transduction and channel gating. The PBP2 proteins share the same architecture as periplasmic binding proteins type 1, but have a different topology. They are typically comprised of two globular subdomains connected by a flexible hinge and bind their ligand in the cleft between these domains in a manner resembling a Venus flytrap. The majority of PBP2 proteins function in the uptake of small soluble substrates in eubacteria and archaea. After binding their specific ligand with high affinity, they can interact with a cognate membrane transport complex comprised of two integral membrane domains and two cytoplasmically-located ATPase domains. This interaction triggers the ligand translocation across the cytoplasmic membrane energized by ATP hydrolysis. Besides transport proteins, the family includes ionotropic glutamate receptors and unorthodox sensor proteins involved in signal transduction. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QDC94210.1 | 0.0 | 6 | 481 | 1 | 476 |
| ADT86198.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 481 | 1 | 481 |
| QTG97312.1 | 0.0 | 6 | 481 | 1 | 476 |
| QTG89961.1 | 0.0 | 6 | 481 | 1 | 476 |
| QTH09343.1 | 5.99e-277 | 1 | 469 | 1 | 469 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5AA2_B | 8.91e-21 | 39 | 449 | 48 | 459 | Crystalstructure of MltF from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in complex with NAM-pentapeptide. [Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWHPSA013] |
| 4OZ9_A | 1.39e-20 | 39 | 449 | 7 | 418 | Crystalstructure of MltF from Pseudomonas aeruginosa complexed with isoleucine [Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1] |
| 4OYV_A | 1.47e-20 | 39 | 449 | 14 | 425 | Crystalstructure of MltF from Pseudomonas aeruginosa complexed with leucine [Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1] |
| 4OWD_A | 1.47e-20 | 39 | 449 | 14 | 425 | Crystalstructure of MltF from Pseudomonas aeruginosa complexed with cysteine [Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1],4OXV_A Crystal structure of MltF from Pseudomonas aeruginosa complexed with valine [Pseudomonas aeruginosa PADK2_CF510],4P0G_A Crystal structure of MltF from Pseudomonas aeruginosa complexed with bulgecin and muropeptide [Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1],4P11_A Native crystal structure of MltF Pseudomonas aeruginosa [Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1] |
| 5AA2_A | 2.14e-20 | 39 | 462 | 48 | 477 | Crystalstructure of MltF from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in complex with NAM-pentapeptide. [Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWHPSA013],5AA2_C Crystal structure of MltF from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in complex with NAM-pentapeptide. [Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWHPSA013] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A8ZWR8 | 6.21e-35 | 39 | 458 | 37 | 454 | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase F OS=Desulfococcus oleovorans (strain DSM 6200 / JCM 39069 / Hxd3) OX=96561 GN=mltF PE=3 SV=2 |
| Q4KHS7 | 2.55e-29 | 39 | 449 | 37 | 448 | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase F OS=Pseudomonas fluorescens (strain ATCC BAA-477 / NRRL B-23932 / Pf-5) OX=220664 GN=mltF PE=3 SV=2 |
| Q886W7 | 3.77e-27 | 39 | 481 | 37 | 485 | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase F OS=Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (strain ATCC BAA-871 / DC3000) OX=223283 GN=mltF PE=3 SV=2 |
| A8FY01 | 4.38e-27 | 42 | 468 | 34 | 457 | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase F OS=Shewanella sediminis (strain HAW-EB3) OX=425104 GN=mltF PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q3KHL5 | 6.28e-27 | 22 | 481 | 22 | 485 | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase F OS=Pseudomonas fluorescens (strain Pf0-1) OX=205922 GN=mltF PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
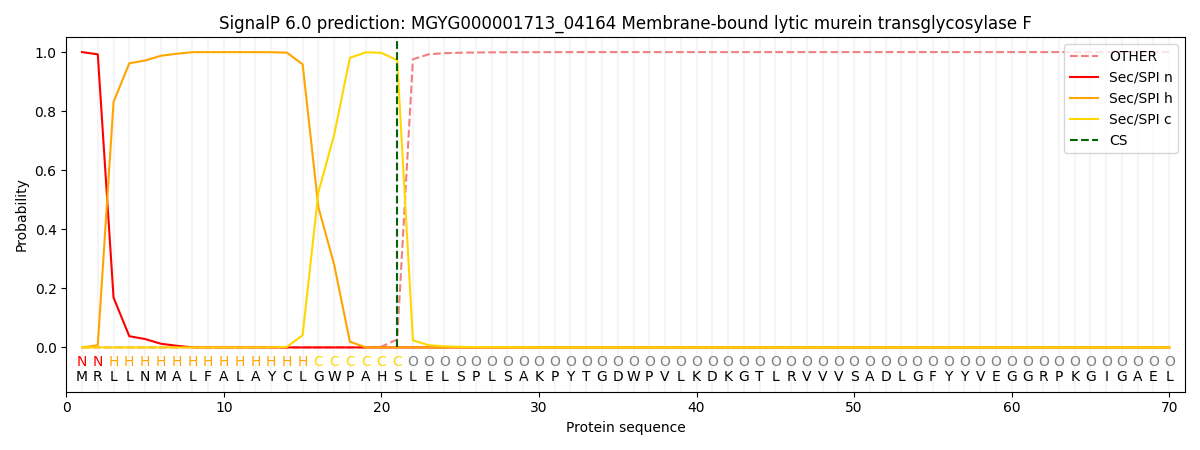
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000281 | 0.999063 | 0.000172 | 0.000162 | 0.000150 | 0.000141 |
