You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001732_01316
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001732_01316
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | HGM11530 sp900751685 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes_A; Clostridia; Monoglobales_A; UBA1381; HGM11530; HGM11530 sp900751685 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001732_01316 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CE12 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 24216; End: 28064 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE12 | 233 | 448 | 2.6e-26 | 0.9904761904761905 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd01821 | Rhamnogalacturan_acetylesterase_like | 3.10e-26 | 233 | 449 | 2 | 198 | Rhamnogalacturan_acetylesterase_like subgroup of SGNH-hydrolases. Rhamnogalacturan acetylesterase removes acetyl esters from rhamnogalacturonan substrates, and renders them susceptible to degradation by rhamnogalacturonases. Rhamnogalacturonans are highly branched regions in pectic polysaccharides, consisting of repeating -(1,2)-L-Rha-(1,4)-D-GalUA disaccharide units, with many rhamnose residues substituted by neutral oligosaccharides such as arabinans, galactans and arabinogalactans. Extracellular enzymes participating in the degradation of plant cell wall polymers, such as Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase, would typically be found in saprophytic and plant pathogenic fungi and bacteria. |
| cd01834 | SGNH_hydrolase_like_2 | 8.16e-09 | 231 | 445 | 1 | 188 | SGNH_hydrolase subfamily. SGNH hydrolases are a diverse family of lipases and esterases. The tertiary fold of the enzyme is substantially different from that of the alpha/beta hydrolase family and unique among all known hydrolases; its active site closely resembles the Ser-His-Asp(Glu) triad found in other serine hydrolases. |
| cd00229 | SGNH_hydrolase | 1.54e-05 | 234 | 447 | 1 | 186 | SGNH_hydrolase, or GDSL_hydrolase, is a diverse family of lipases and esterases. The tertiary fold of the enzyme is substantially different from that of the alpha/beta hydrolase family and unique among all known hydrolases; its active site closely resembles the typical Ser-His-Asp(Glu) triad from other serine hydrolases, but may lack the carboxlic acid. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEI43346.1 | 4.33e-126 | 29 | 593 | 433 | 966 |
| AFH63317.1 | 4.20e-88 | 29 | 380 | 432 | 771 |
| AFK65394.1 | 4.88e-88 | 29 | 380 | 439 | 778 |
| APC40119.1 | 3.29e-30 | 37 | 451 | 5 | 392 |
| QNM03704.1 | 2.50e-20 | 110 | 451 | 81 | 399 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
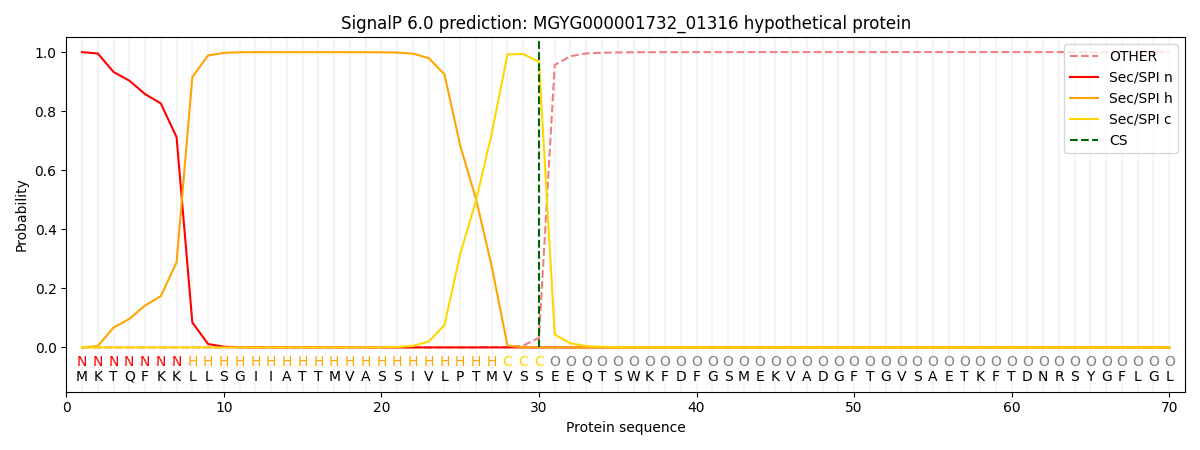
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.002275 | 0.996147 | 0.000402 | 0.000422 | 0.000376 | 0.000351 |
