You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001789_02025
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001789_02025
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Phocaeicola sp002161565 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; Phocaeicola; Phocaeicola sp002161565 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001789_02025 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CE1 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Carbohydrate acetyl esterase/feruloyl esterase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 27089; End: 28195 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE1 | 146 | 364 | 8.5e-58 | 0.9691629955947136 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd02858 | E_set_Esterase_N | 3.60e-38 | 45 | 121 | 1 | 78 | N-terminal Early set domain associated with the catalytic domain of esterase. E or "early" set domains are associated with the catalytic domain of esterase at the N-terminal end. Esterases catalyze the hydrolysis of organic esters to release an alcohol or thiol and acid. The term esterase can be applied to enzymes that hydrolyze carboxylate, phosphate and sulphate esters, but is more often restricted to the first class of substrate. The N-terminal domain of esterase may be related to the immunoglobulin and/or fibronectin type III superfamilies. These domains are associated with different types of catalytic domains at either the N-terminal or C-terminal end and may be involved in homodimeric/tetrameric/dodecameric interactions. Members of this family include members of the alpha amylase family, sialidase, galactose oxidase, cellulase, cellulose, hyaluronate lyase, chitobiase, and chitinase, among others. |
| COG2382 | Fes | 6.17e-38 | 96 | 368 | 30 | 297 | Enterochelin esterase or related enzyme [Inorganic ion transport and metabolism]. |
| pfam00756 | Esterase | 1.37e-18 | 153 | 359 | 8 | 239 | Putative esterase. This family contains Esterase D. However it is not clear if all members of the family have the same function. This family is related to the pfam00135 family. |
| cd02853 | E_set_MTHase_like_N | 1.28e-15 | 39 | 105 | 2 | 70 | N-terminal Early set domain associated with the catalytic domain of Maltooligosyl trehalose trehalohydrolase (also called Glycosyltrehalose trehalohydrolase) and similar proteins. E or "early" set domains are associated with the catalytic domain of Maltooligosyl trehalose trehalohydrolase (MTHase) and similar proteins at the N-terminal end. This subfamily also includes bacterial alpha amylases and 1,4-alpha-glucan branching enzymes which are highly similar to MTHase. Maltooligosyl trehalose synthase (MTSase) and MTHase work together to produce trehalose. MTSase is responsible for converting the alpha-1,4-glucosidic linkage to an alpha,alpha-1,1-glucosidic linkage at the reducing end of the maltooligosaccharide through an intramolecular transglucosylation reaction, while MTHase hydrolyzes the penultimate alpha-1,4 linkage of the reducing end, resulting in the release of trehalose. The N-terminal domain of MTHase may be related to the immunoglobulin and/or fibronectin type III superfamilies. These domains are associated with different types of catalytic domains at either the N-terminal or C-terminal end and may be involved in homodimeric/tetrameric/dodecameric interactions. Members of this family include members of the alpha amylase family, sialidase, galactose oxidase, cellulase, cellulose, hyaluronate lyase, chitobiase, and chitinase, among others. |
| cd11294 | E_set_Esterase_like_N | 9.26e-14 | 45 | 121 | 1 | 83 | N-terminal Early set domain associated with the catalytic domain of putative esterases. E or "early" set domains are associated with the catalytic domain of esterase at the N-terminal end. Esterases catalyze the hydrolysis of organic esters to release an alcohol or thiol and acid. The term esterase can be applied to enzymes that hydrolyze carboxylate, phosphate and sulphate esters, but is more often restricted to the first class of substrate. The N-terminal domain of esterase may be related to the immunoglobulin and/or fibronectin type III superfamilies. These domains are associated with different types of catalytic domains at either the N-terminal or C-terminal end and may be involved in homodimeric/tetrameric/dodecameric interactions. Members of this family include members of the alpha amylase family, sialidase, galactose oxidase, cellulase, cellulose, hyaluronate lyase, chitobiase, and chitinase, among others. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QRQ49052.1 | 8.59e-187 | 18 | 368 | 26 | 376 |
| QCD34664.1 | 2.32e-176 | 2 | 368 | 3 | 372 |
| ASB48760.1 | 7.48e-146 | 2 | 368 | 3 | 370 |
| AFK05655.1 | 6.36e-140 | 26 | 368 | 291 | 642 |
| AYQ33226.1 | 7.21e-139 | 26 | 368 | 291 | 642 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7B5V_A | 3.14e-107 | 32 | 368 | 33 | 386 | ChainA, Carbohydrate Esterase family 1 protein with an N-terminal carbohydrate binding module family 48 [Dysgonomonas mossii DSM 22836],7B5V_B Chain B, Carbohydrate Esterase family 1 protein with an N-terminal carbohydrate binding module family 48 [Dysgonomonas mossii DSM 22836],7B6B_A Chain A, Carbohydrate Esterase family 1 protein with an N-terminal carbohydrate binding module family 48 [Dysgonomonas mossii DSM 22836],7B6B_B Chain B, Carbohydrate Esterase family 1 protein with an N-terminal carbohydrate binding module family 48 [Dysgonomonas mossii DSM 22836] |
| 6NE9_A | 8.45e-78 | 12 | 368 | 15 | 382 | ChainA, Isoamylase protein [Bacteroides intestinalis],6NE9_B Chain B, Isoamylase protein [Bacteroides intestinalis] |
| 6RZO_A | 2.72e-72 | 37 | 368 | 15 | 344 | Crystalstructure of the N-terminal carbohydrate binding module family 48 and ferulic acid esterase from the multi-enzyme CE1-GH62-GH10 [uncultured bacterium] |
| 6RZO_B | 2.80e-72 | 37 | 368 | 15 | 344 | Crystalstructure of the N-terminal carbohydrate binding module family 48 and ferulic acid esterase from the multi-enzyme CE1-GH62-GH10 [uncultured bacterium] |
| 6MOT_A | 5.34e-70 | 32 | 368 | 12 | 359 | ChainA, Isoamylase N-terminal domain protein [Bacteroides intestinalis DSM 17393] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D5EXZ4 | 1.11e-77 | 32 | 368 | 322 | 670 | Carbohydrate acetyl esterase/feruloyl esterase OS=Prevotella ruminicola (strain ATCC 19189 / JCM 8958 / 23) OX=264731 GN=axe1-6A PE=1 SV=1 |
| D5EY13 | 1.11e-53 | 37 | 368 | 393 | 726 | Endo-1,4-beta-xylanase/feruloyl esterase OS=Prevotella ruminicola (strain ATCC 19189 / JCM 8958 / 23) OX=264731 GN=xyn10D-fae1A PE=1 SV=1 |
| P31471 | 8.78e-40 | 7 | 368 | 7 | 389 | Uncharacterized protein YieL OS=Escherichia coli (strain K12) OX=83333 GN=yieL PE=4 SV=3 |
| P10478 | 4.00e-25 | 134 | 276 | 46 | 197 | Endo-1,4-beta-xylanase Z OS=Acetivibrio thermocellus (strain ATCC 27405 / DSM 1237 / JCM 9322 / NBRC 103400 / NCIMB 10682 / NRRL B-4536 / VPI 7372) OX=203119 GN=xynZ PE=1 SV=3 |
| P55192 | 1.24e-12 | 141 | 337 | 1 | 202 | Uncharacterized protein YbbA OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=ybbA PE=2 SV=3 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
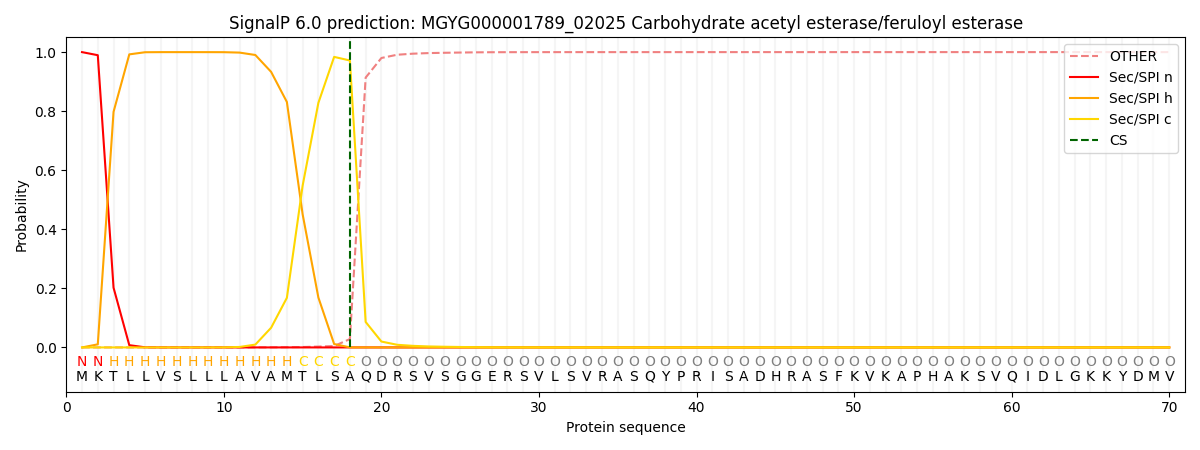
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000353 | 0.998699 | 0.000435 | 0.000172 | 0.000163 | 0.000152 |
