You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001929_01789
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001929_01789
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Paramuribaculum sp900752995 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Muribaculaceae; Paramuribaculum; Paramuribaculum sp900752995 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001929_01789 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM32 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 34547; End: 37126 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam13402 | Peptidase_M60 | 5.67e-28 | 447 | 710 | 1 | 268 | Peptidase M60, enhancin and enhancin-like. This family of peptidases contains a zinc metallopeptidase motif (HEXXHX(8,28)E) and possesses mucinase activity. It includes the viral enhancins as well as enhancin-like peptidases from bacterial species. Enhancins are a class of metalloproteases found in some baculoviruses that enhance viral infection by degrading the peritrophic membrane (PM) of the insect midgut. Bacterial enhancins are found to be cytotoxic when compared to viral enhancin, however, suggesting that the bacterial enhancins do not enhance infection in the same way as viral enhancin. Bacterial enhancins may have evolved a distinct biochemical function. These bacterial domains are peptidases targetting host glycoproteins and thus probably play an important role in successful colonisation of both vertebrate mucosal surfaces and the invertebrate digestive tract by both mutualistic and pathogenic microbes. This family has been augmented by a merge with the sequences in the Enhancin Pfam family. |
| pfam18630 | Peptidase_M60_C | 7.92e-20 | 790 | 854 | 1 | 64 | Peptidase M60 C-terminal domain. This is C-terminal domain (CTD) of M60-peptidases pfam13402. It Can also be found at the C-terminal region of gingipain B (RgpB) from P. gingivalis. It was found to possess a typical Ig-like fold encompassing seven antiparallel beta-strands organized in two beta-sheets, packed into a beta-sandwich structure that can spontaneously dimerize through C-terminal strand swapping. Translocation of gingipains from the periplasm across the OM is dependent on the conserved CTD, which appears to be important for secretion of the proteins and in particular, truncation of the last few C-terminal residues of this domain leads to accumulation of gingipains in the periplasm. Subsequently, the T9SS targeting signal was demonstrated to reside within the last 22 residues at the C-terminus of the CTD. During gingipain translocation across the OM, the CTD is cleaved off by PorU. |
| cd14948 | BACON | 2.55e-11 | 46 | 129 | 8 | 83 | Bacteroidetes-Associated Carbohydrate-binding (putative) Often N-terminal (BACON) domain. The BACON domain is found in diverse domain architectures and accociated with a wide variety of domains, including carbohydrate-active enzymes and proteases. It was named for its suggested function of carbohydrate binding; the latter was inferred from domain architectures, sequence conservation, and phyletic distribution. However, recent experimental data suggest that its primary function in Bacteroides ovatus endo-xyloglucanase BoGH5A is to distance the catalytic module from the cell surface and confer additional mobility to the catalytic domain for attack of the polysaccharide. No evidence for a direct role in carbohydrate binding could be found in that case. The large majority of BACON domains are found in Bacteroidetes. |
| pfam13004 | BACON | 1.28e-06 | 74 | 129 | 7 | 61 | Putative binding domain, N-terminal. The BACON (Bacteroidetes-Associated Carbohydrate-binding Often N-terminal) domain is an all-beta domain found in diverse architectures, principally in combination with carbohydrate-active enzymes and proteases. These architectures suggest a carbohydrate-binding function which is also supported by the nature of BACON's few conserved amino-acids. The phyletic distribution of BACON and other data tentatively suggest that it may frequently function to bind mucin. Further work with the characterized structure of a member of glycoside hydrolase family 5 enzyme, Structure 3ZMR, has found no evidence for carbohydrate-binding for this domain. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAO79349.1 | 0.0 | 13 | 856 | 13 | 857 |
| QQA07622.1 | 0.0 | 13 | 856 | 13 | 857 |
| QUT42145.1 | 0.0 | 13 | 856 | 13 | 857 |
| QUT69943.1 | 0.0 | 13 | 856 | 13 | 857 |
| QUU10001.1 | 0.0 | 50 | 858 | 142 | 953 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5KD2_A | 1.10e-311 | 275 | 856 | 23 | 607 | BT_4244metallopeptidase from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482] |
| 5KD5_A | 2.26e-291 | 324 | 856 | 24 | 559 | BT_4244metallopeptidase from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482],5KD8_A BT_4244 metallopeptidase in complex with Tn antigen. [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482] |
| 7SCI_A | 1.27e-37 | 284 | 748 | 12 | 479 | ChainA, Peptidase M60 domain-containing protein [Akkermansia muciniphila ATCC BAA-835] |
| 7BLG_A | 1.66e-20 | 139 | 271 | 22 | 160 | ChainA, family 32 carbohydrate-binding module from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482],7BLH_AAAA Chain AAAA, family 32 carbohydrate-binding module from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482],7BLJ_A Chain A, family 32 carbohydrate-binding module from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482],7BLK_A Chain A, family 32 carbohydrate-binding module from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482] |
| 5EV7_A | 7.70e-16 | 327 | 710 | 11 | 379 | Thecrystal structure of a functionally unknown conserved protein mutant from Bacillus anthracis str. Ames [Bacillus anthracis str. Ames] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
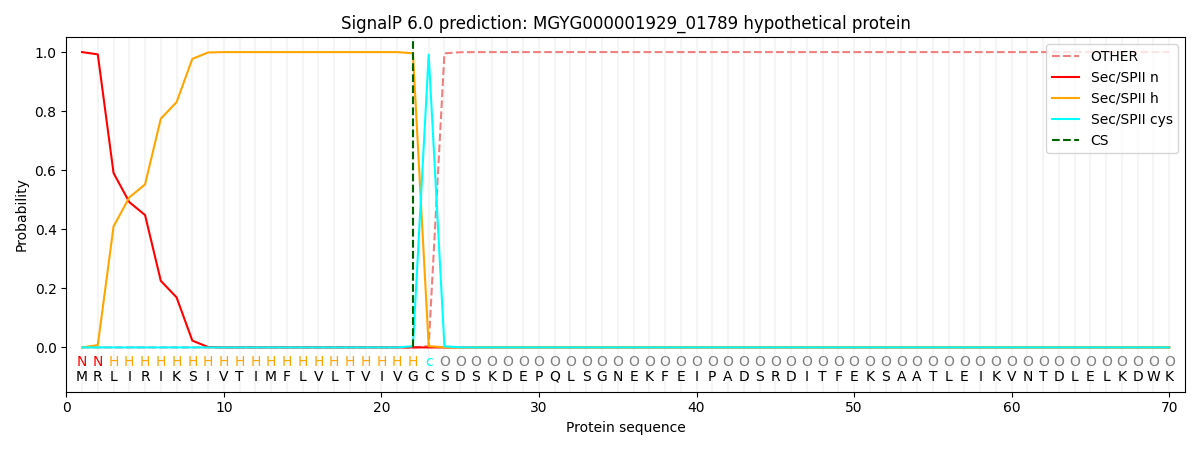
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000053 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
