You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002082_01398
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002082_01398
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Alistipes sp900544265 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Rikenellaceae; Alistipes; Alistipes sp900544265 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002082_01398 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH18 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 91047; End: 92669 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd06542 | GH18_EndoS-like | 1.35e-16 | 269 | 468 | 47 | 231 | Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases are bacterial chitinases that hydrolyze the chitin core of various asparagine (N)-linked glycans and glycoproteins. The endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases have a glycosyl hydrolase family 18 (GH18) catalytic domain. Some members also have an additional C-terminal glycosyl hydrolase family 20 (GH20) domain while others have an N-terminal domain of unknown function (pfam08522). Members of this family include endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase S (EndoS) from Streptococcus pyogenes, EndoF1, EndoF2, EndoF3, and EndoH from Flavobacterium meningosepticum, and EndoE from Enterococcus faecalis. EndoS is a secreted endoglycosidase from Streptococcus pyogenes that specifically hydrolyzes the glycan on human IgG between two core N-acetylglucosamine residues. EndoE is a secreted endoglycosidase, encoded by the ndoE gene in Enterococcus faecalis, that hydrolyzes the glycan on human RNase B. |
| pfam08522 | DUF1735 | 3.80e-12 | 71 | 171 | 20 | 120 | Domain of unknown function (DUF1735). This domain of unknown function is found in a number of bacterial proteins including acylhydrolases. The structure of this domain has a beta-sandwich fold. |
| cd00598 | GH18_chitinase-like | 2.09e-06 | 221 | 397 | 5 | 170 | The GH18 (glycosyl hydrolase, family 18) type II chitinases hydrolyze chitin, an abundant polymer of beta-1,4-linked N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) which is a major component of the cell wall of fungi and the exoskeleton of arthropods. Chitinases have been identified in viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoan parasites, insects, and plants. The structure of the GH18 domain is an eight-stranded beta/alpha barrel with a pronounced active-site cleft at the C-terminal end of the beta-barrel. The GH18 family includes chitotriosidase, chitobiase, hevamine, zymocin-alpha, narbonin, SI-CLP (stabilin-1 interacting chitinase-like protein), IDGF (imaginal disc growth factor), CFLE (cortical fragment-lytic enzyme) spore hydrolase, the type III and type V plant chitinases, the endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases, and the chitolectins. The GH85 (glycosyl hydrolase, family 85) ENGases (endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases) are closely related to the GH18 chitinases and are included in this alignment model. |
| cd02871 | GH18_chitinase_D-like | 3.45e-04 | 242 | 403 | 29 | 175 | GH18 domain of Chitinase D (ChiD). ChiD, a chitinase found in Bacillus circulans, hydrolyzes the 1,4-beta-linkages of N-acetylglucosamine in chitin and chitodextrins. The domain architecture of ChiD includes a catalytic glycosyl hydrolase family 18 (GH18) domain, a chitin-binding domain, and a fibronectin type III domain. The chitin-binding and fibronectin type III domains are located either N-terminal or C-terminal to the catalytic domain. This family includes exochitinase Chi36 from Bacillus cereus. |
| cd06548 | GH18_chitinase | 4.68e-04 | 288 | 370 | 86 | 180 | The GH18 (glycosyl hydrolases, family 18) type II chitinases hydrolyze chitin, an abundant polymer of N-acetylglucosamine and have been identified in bacteria, fungi, insects, plants, viruses, and protozoan parasites. The structure of this domain is an eight-stranded alpha/beta barrel with a pronounced active-site cleft at the C-terminal end of the beta-barrel. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBL01830.1 | 2.70e-119 | 28 | 540 | 24 | 538 |
| ALJ47937.1 | 2.12e-114 | 1 | 513 | 1 | 517 |
| SCV07341.1 | 2.12e-114 | 1 | 513 | 1 | 517 |
| QRQ54816.1 | 2.12e-114 | 1 | 513 | 1 | 517 |
| BBL09700.1 | 6.94e-112 | 1 | 540 | 1 | 544 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2EBN_A | 1.83e-12 | 240 | 402 | 38 | 199 | CRYSTALSTRUCTURE OF ENDO-BETA-N-ACETYLGLUCOSAMINIDASE F1, AN ALPHA(SLASH)BETA-BARREL ENZYME ADAPTED FOR A COMPLEX SUBSTRATE [Elizabethkingia meningoseptica] |
| 1C8X_A | 3.36e-12 | 222 | 402 | 7 | 190 | ChainA, ENDO-BETA-N-ACETYLGLUCOSAMINIDASE H [Streptomyces plicatus] |
| 1C8Y_A | 3.36e-12 | 222 | 402 | 7 | 190 | ChainA, ENDO-BETA-N-ACETYLGLUCOSAMINIDASE H [Streptomyces plicatus] |
| 1C90_A | 3.36e-12 | 222 | 402 | 7 | 190 | ChainA, ENDO-BETA-N-ACETYLGLUCOSAMINIDASE H [Streptomyces plicatus],1C90_B Chain B, ENDO-BETA-N-ACETYLGLUCOSAMINIDASE H [Streptomyces plicatus] |
| 1C93_A | 3.36e-12 | 222 | 402 | 7 | 190 | ChainA, ENDO-BETA-N-ACETYLGLUCOSAMINIDASE H [Streptomyces plicatus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P36911 | 1.60e-11 | 240 | 402 | 88 | 249 | Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F1 OS=Elizabethkingia meningoseptica OX=238 GN=endOF1 PE=1 SV=1 |
| P04067 | 4.13e-11 | 222 | 402 | 54 | 237 | Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H OS=Streptomyces plicatus OX=1922 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
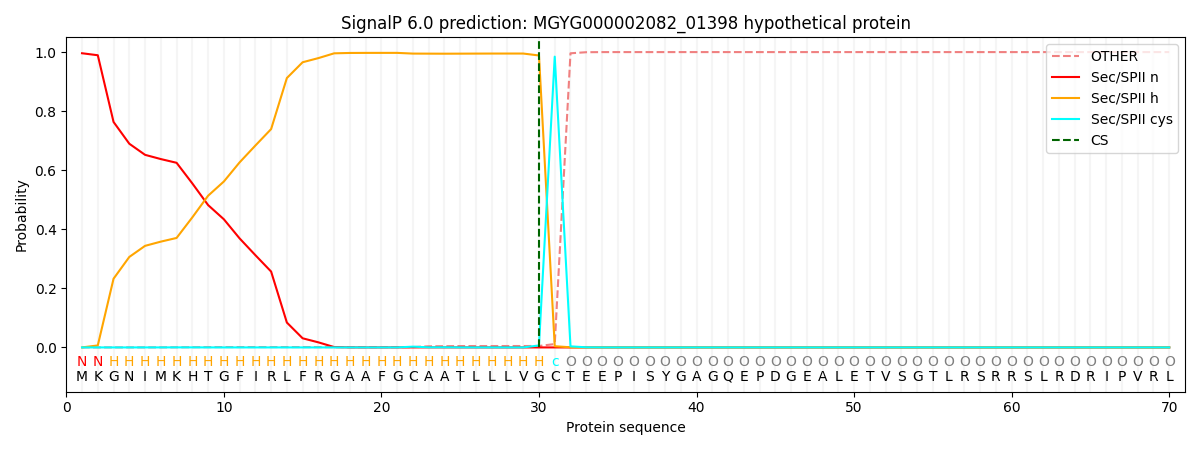
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000020 | 0.001004 | 0.999000 | 0.000004 | 0.000002 | 0.000000 |
