You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002300_00892
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002300_00892
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
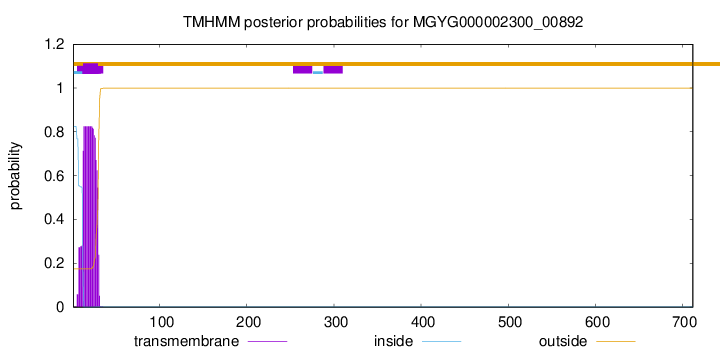
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Bacteroides cutis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; Bacteroides; Bacteroides cutis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002300_00892 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | PL29 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 135586; End: 137724 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL29 | 262 | 536 | 8.7e-19 | 0.8870431893687708 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd14948 | BACON | 1.74e-16 | 37 | 118 | 1 | 83 | Bacteroidetes-Associated Carbohydrate-binding (putative) Often N-terminal (BACON) domain. The BACON domain is found in diverse domain architectures and accociated with a wide variety of domains, including carbohydrate-active enzymes and proteases. It was named for its suggested function of carbohydrate binding; the latter was inferred from domain architectures, sequence conservation, and phyletic distribution. However, recent experimental data suggest that its primary function in Bacteroides ovatus endo-xyloglucanase BoGH5A is to distance the catalytic module from the cell surface and confer additional mobility to the catalytic domain for attack of the polysaccharide. No evidence for a direct role in carbohydrate binding could be found in that case. The large majority of BACON domains are found in Bacteroidetes. |
| cd14948 | BACON | 8.32e-14 | 124 | 207 | 2 | 83 | Bacteroidetes-Associated Carbohydrate-binding (putative) Often N-terminal (BACON) domain. The BACON domain is found in diverse domain architectures and accociated with a wide variety of domains, including carbohydrate-active enzymes and proteases. It was named for its suggested function of carbohydrate binding; the latter was inferred from domain architectures, sequence conservation, and phyletic distribution. However, recent experimental data suggest that its primary function in Bacteroides ovatus endo-xyloglucanase BoGH5A is to distance the catalytic module from the cell surface and confer additional mobility to the catalytic domain for attack of the polysaccharide. No evidence for a direct role in carbohydrate binding could be found in that case. The large majority of BACON domains are found in Bacteroidetes. |
| pfam13004 | BACON | 6.88e-06 | 64 | 118 | 1 | 61 | Putative binding domain, N-terminal. The BACON (Bacteroidetes-Associated Carbohydrate-binding Often N-terminal) domain is an all-beta domain found in diverse architectures, principally in combination with carbohydrate-active enzymes and proteases. These architectures suggest a carbohydrate-binding function which is also supported by the nature of BACON's few conserved amino-acids. The phyletic distribution of BACON and other data tentatively suggest that it may frequently function to bind mucin. Further work with the characterized structure of a member of glycoside hydrolase family 5 enzyme, Structure 3ZMR, has found no evidence for carbohydrate-binding for this domain. |
| pfam19190 | BACON_2 | 0.002 | 124 | 207 | 2 | 89 | Viral BACON domain. This family represents a distinct class of BACON domains found in crAss-like phages, the most common viral family in the human gut, in which they are found in tail fiber genes. This suggests they may play a role in phage-host interactions. |
| pfam19190 | BACON_2 | 0.009 | 38 | 118 | 2 | 89 | Viral BACON domain. This family represents a distinct class of BACON domains found in crAss-like phages, the most common viral family in the human gut, in which they are found in tail fiber genes. This suggests they may play a role in phage-host interactions. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QQT62233.1 | 2.18e-124 | 217 | 698 | 427 | 894 |
| QMV68341.1 | 3.06e-124 | 217 | 698 | 427 | 894 |
| QQT45112.1 | 4.29e-124 | 217 | 698 | 427 | 894 |
| QRY56719.1 | 5.10e-123 | 229 | 698 | 415 | 870 |
| QQT32413.1 | 3.47e-122 | 217 | 698 | 427 | 894 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
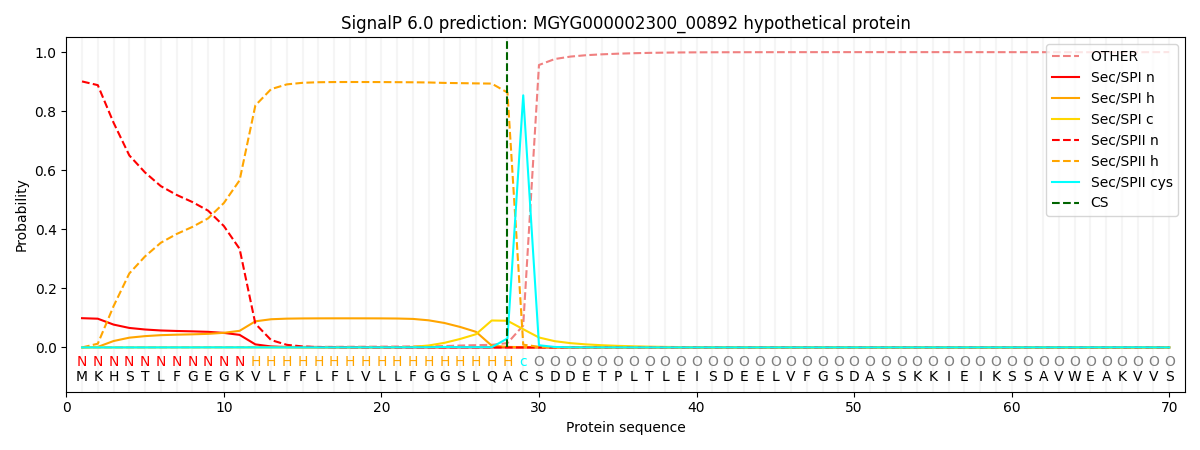
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000479 | 0.096848 | 0.902534 | 0.000042 | 0.000053 | 0.000045 |