You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002455_03754
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002455_03754
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Bacteroides cellulosilyticus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; Bacteroides; Bacteroides cellulosilyticus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002455_03754 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH117 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Arylsulfatase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 81961; End: 83412 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd16026 | GALNS_like | 0.0 | 33 | 413 | 1 | 398 | galactosamine-6-sulfatase; also known as N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase (GALNS). Lysosomal galactosamine-6-sulfatase removes sulfate groups from a terminal N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate (or galactose-6-sulfate) in mucopolysaccharides such as keratan sulfate and chondroitin-6-sulfate. Defects in GALNS lead to accumulation of substrates, resulting in the development of the lysosomal storage disease mucopolysaccharidosis IV A. |
| cd16144 | ARS_like | 4.40e-133 | 34 | 431 | 1 | 421 | uncharacterized arylsulfatase subfamily. Sulfatases catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters from wide range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. The biological roles of sulfatase includes the cycling of sulfur in the environment, in the degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids in the lysosome, and in remodeling sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular space. The sulfatases are essential for human metabolism. At least eight human monogenic diseases are caused by the deficiency of individual sulfatases. |
| cd16142 | ARS_like | 5.88e-131 | 34 | 413 | 1 | 371 | uncharacterized arylsulfatase subfamily. Sulfatases catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters from wide range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. The biological roles of sulfatase includes the cycling of sulfur in the environment, in the degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids in the lysosome, and in remodeling sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular space. The sulfatases are essential for human metabolism. At least eight human monogenic diseases are caused by the deficiency of individual sulfatases. |
| cd16158 | ARSA | 2.13e-129 | 33 | 413 | 1 | 422 | Arylsulfatase A or cerebroside-sulfatase. Arylsulfatase A breaks down sulfatides, namely cerebroside 3-sulfate into cerebroside and sulfate. It is a member of the sulfatase family. The arylsulfatase A was located in lysosome-like structures and transported to dense lysosomes in a mannose 6-phosphate receptor-dependent manner. Deficiency of arylsulfatase A leads to the accumulation of cerebroside sulfate, which causes a lethal progressive demyelination. Arylsulfatase A requires the posttranslational oxidation of the -CH2SH group of a conserved cysteine to an aldehyde, yielding a formylglycine to be in an active form. |
| cd16143 | ARS_like | 5.99e-123 | 34 | 414 | 1 | 395 | uncharacterized arylsulfatase subfamily. Sulfatases catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters from wide range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. The biological roles of sulfatase includes the cycling of sulfur in the environment, in the degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids in the lysosome, and in remodeling sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular space. The sulfatases are essential for human metabolism. At least eight human monogenic diseases are caused by the deficiency of individual sulfatases. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QDH57428.1 | 2.34e-113 | 32 | 431 | 21 | 456 |
| QNN23223.1 | 1.28e-108 | 10 | 441 | 13 | 437 |
| VTR91273.1 | 1.63e-100 | 31 | 437 | 21 | 455 |
| QDT95903.1 | 7.53e-96 | 19 | 438 | 23 | 466 |
| QDU36023.1 | 7.02e-95 | 24 | 437 | 30 | 478 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1E1Z_P | 4.31e-92 | 32 | 430 | 1 | 440 | Crystalstructure of an Arylsulfatase A mutant C69S [Homo sapiens] |
| 1E3C_P | 4.31e-92 | 32 | 430 | 1 | 440 | Crystalstructure of an Arylsulfatase A mutant C69S soaked in synthetic substrate [Homo sapiens] |
| 1E2S_P | 1.21e-91 | 32 | 430 | 1 | 440 | Crystalstructure of an Arylsulfatase A mutant C69A [Homo sapiens] |
| 1E33_P | 2.39e-91 | 32 | 430 | 1 | 440 | Crystalstructure of an Arylsulfatase A mutant P426L [Homo sapiens] |
| 1AUK_A | 2.39e-91 | 32 | 430 | 1 | 440 | HumanArylsulfatase A [Homo sapiens],1N2K_A Crystal structure of a covalent intermediate of endogenous human arylsulfatase A [Homo sapiens],1N2L_A Crystal structure of a covalent intermediate of endogenous human arylsulfatase A [Homo sapiens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P15289 | 1.53e-90 | 31 | 430 | 18 | 458 | Arylsulfatase A OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=ARSA PE=1 SV=3 |
| P50428 | 1.19e-85 | 16 | 429 | 3 | 456 | Arylsulfatase A OS=Mus musculus OX=10090 GN=Arsa PE=1 SV=2 |
| Q08DD1 | 3.42e-85 | 31 | 430 | 18 | 458 | Arylsulfatase A OS=Bos taurus OX=9913 GN=ARSA PE=2 SV=1 |
| Q32KH5 | 3.47e-77 | 32 | 432 | 28 | 469 | N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase OS=Canis lupus familiaris OX=9615 GN=GALNS PE=2 SV=1 |
| Q8WNQ7 | 1.35e-76 | 15 | 413 | 15 | 454 | N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase OS=Sus scrofa OX=9823 GN=GALNS PE=2 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
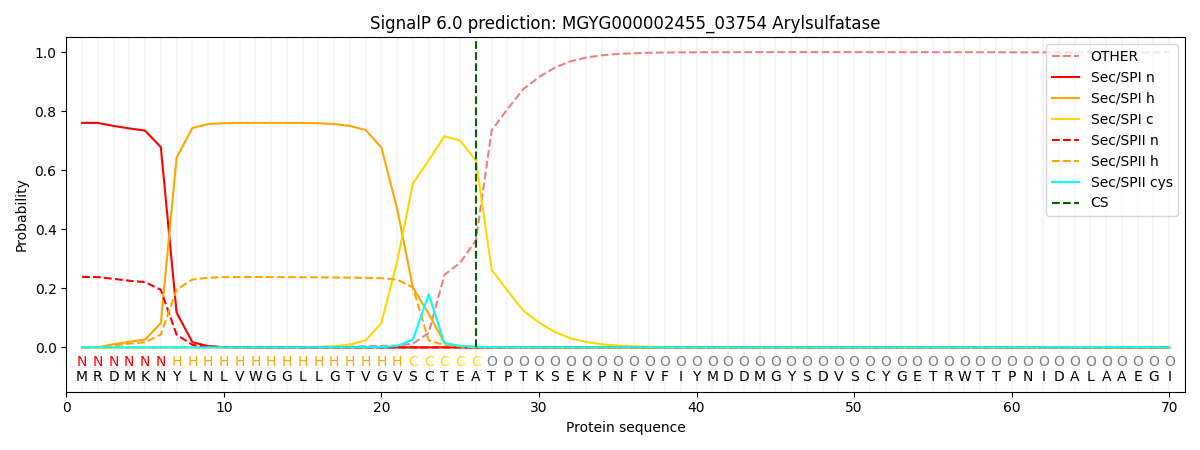
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.002026 | 0.752848 | 0.244040 | 0.000528 | 0.000276 | 0.000242 |
