You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002737_01889
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002737_01889
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Prevotella sp900553465 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; Prevotella; Prevotella sp900553465 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002737_01889 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH43 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 972; End: 2507 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH43 | 28 | 305 | 2.4e-116 | 0.99644128113879 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd08999 | GH43_ABN-like | 4.66e-100 | 28 | 306 | 1 | 284 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as endo-alpha-L-arabinanase. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes mostly enzymes with alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (ABF; EC 3.2.1.55) and endo-alpha-L-arabinanase (ABN; EC 3.2.1.99) activities. These are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. The GH43 ABN enzymes hydrolyze alpha-1,5-L-arabinofuranoside linkages while the ABF enzymes cleave arabinose side chains so that the combined actions of these two enzymes reduce arabinan to L-arabinose and/or arabinooligosaccharides. These arabinan-degrading enzymes are important in the food industry for efficient production of L-arabinose from agricultural waste; L-arabinose is often used as a bioactive sweetener. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| pfam04616 | Glyco_hydro_43 | 1.77e-83 | 26 | 304 | 1 | 280 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 43. The glycosyl hydrolase family 43 contains members that are arabinanases. Arabinanases hydrolyze the alpha-1,5-linked L-arabinofuranoside backbone of plant cell wall arabinans. The structure of arabinanase Arb43A from Cellvibrio japonicus reveals a five-bladed beta-propeller fold. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd08991 | GH43_HoAraf43-like | 2.99e-70 | 36 | 279 | 1 | 253 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as Halothermothrix orenii H 168 alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (HoAraf43;Hore_20580). This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes Halothermothrix orenii H 168 alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55) (HoAraf43;Hore_20580). It belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) which includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62) families. This GH43_ HoAraf43-like subgroup includes enzymes that have been annotated as having xylan-digesting beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37) and xylanase (endo-alpha-L-arabinanase, EC 3.2.1.8) activities. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd18616 | GH43_ABN-like | 9.64e-62 | 28 | 294 | 1 | 285 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 such as arabinan endo-1 5-alpha-L-arabinosidase. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes mostly enzymes with endo-alpha-L-arabinanase (ABN; EC 3.2.1.99) activity. These are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. The GH43 ABN enzymes hydrolyze alpha-1,5-L-arabinofuranoside linkages. These arabinan-degrading enzymes are important in the food industry for efficient production of L-arabinose from agricultural waste; L-arabinose is often used as a bioactive sweetener. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd08989 | GH43_XYL-like | 4.76e-49 | 28 | 297 | 1 | 269 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43, beta-D-xylosidases and arabinofuranosidases. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes mostly enzymes that have been annotated as having beta-1,4-xylosidase (beta-D-xylosidase;xylan 1,4-beta-xylosidase; EC 3.2.1.37) activity, including Selenomonas ruminantium beta-D-xylosidase SXA. These are part of an array of hemicellulases that are involved in the final breakdown of plant cell-wall whereby they degrade xylan. They hydrolyze beta-1,4 glycosidic bonds between two xylose units in short xylooligosaccharides. It also includes various GH43 family GH43 arabinofuranosidases (EC 3.2.1.55) including Humicola insolens alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase AXHd3, Bacteroides ovatus alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (BoGH43, XynB), and the bifunctional Phanerochaete chrysosporium xylosidase/arabinofuranosidase (Xyl;PcXyl). GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QUT41950.1 | 4.68e-169 | 11 | 508 | 10 | 508 |
| BCA48631.1 | 4.68e-169 | 11 | 508 | 10 | 508 |
| QUT69775.1 | 6.64e-169 | 11 | 508 | 10 | 508 |
| AAO79200.1 | 1.89e-168 | 15 | 508 | 14 | 508 |
| ALJ43657.1 | 1.89e-168 | 15 | 508 | 14 | 508 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6MS3_A | 1.32e-32 | 19 | 481 | 23 | 498 | Crystalstructure of the GH43 protein BlXynB mutant (K247S) from Bacillus licheniformis [Bacillus licheniformis DSM 13 = ATCC 14580],6MS3_B Crystal structure of the GH43 protein BlXynB mutant (K247S) from Bacillus licheniformis [Bacillus licheniformis DSM 13 = ATCC 14580] |
| 6MS2_A | 2.44e-32 | 19 | 481 | 23 | 498 | Crystalstructure of the GH43 BlXynB protein from Bacillus licheniformis [Bacillus licheniformis DSM 13 = ATCC 14580] |
| 1YRZ_A | 7.26e-30 | 28 | 344 | 7 | 336 | ChainA, xylan beta-1,4-xylosidase [Halalkalibacterium halodurans C-125],1YRZ_B Chain B, xylan beta-1,4-xylosidase [Halalkalibacterium halodurans C-125] |
| 4QQS_A | 5.01e-28 | 25 | 308 | 4 | 302 | Crystalstructure of a thermostable family-43 glycoside hydrolase [Halothermothrix orenii H 168],4QQS_B Crystal structure of a thermostable family-43 glycoside hydrolase [Halothermothrix orenii H 168] |
| 1GYD_B | 1.75e-27 | 34 | 306 | 3 | 300 | Structureof Cellvibrio cellulosa alpha-L-arabinanase [Cellvibrio japonicus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P95470 | 2.94e-28 | 15 | 306 | 19 | 332 | Extracellular exo-alpha-(1->5)-L-arabinofuranosidase ArbA OS=Cellvibrio japonicus (strain Ueda107) OX=498211 GN=arbA PE=1 SV=1 |
| A9ZND1 | 2.10e-27 | 25 | 472 | 4 | 487 | Xylan 1,3-beta-xylosidase OS=Vibrio sp. OX=678 GN=xloA PE=1 SV=1 |
| A7LXT8 | 2.91e-26 | 12 | 355 | 8 | 344 | Non-reducing end alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase BoGH43A OS=Bacteroides ovatus (strain ATCC 8483 / DSM 1896 / JCM 5824 / BCRC 10623 / CCUG 4943 / NCTC 11153) OX=411476 GN=BACOVA_02654 PE=1 SV=1 |
| P94522 | 1.90e-23 | 2 | 259 | 8 | 275 | Extracellular endo-alpha-(1->5)-L-arabinanase 1 OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=abnA PE=1 SV=3 |
| A7LXU0 | 3.57e-23 | 22 | 347 | 23 | 348 | Non-reducing end alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase BoGH43B OS=Bacteroides ovatus (strain ATCC 8483 / DSM 1896 / JCM 5824 / BCRC 10623 / CCUG 4943 / NCTC 11153) OX=411476 GN=BACOVA_02656 PE=1 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
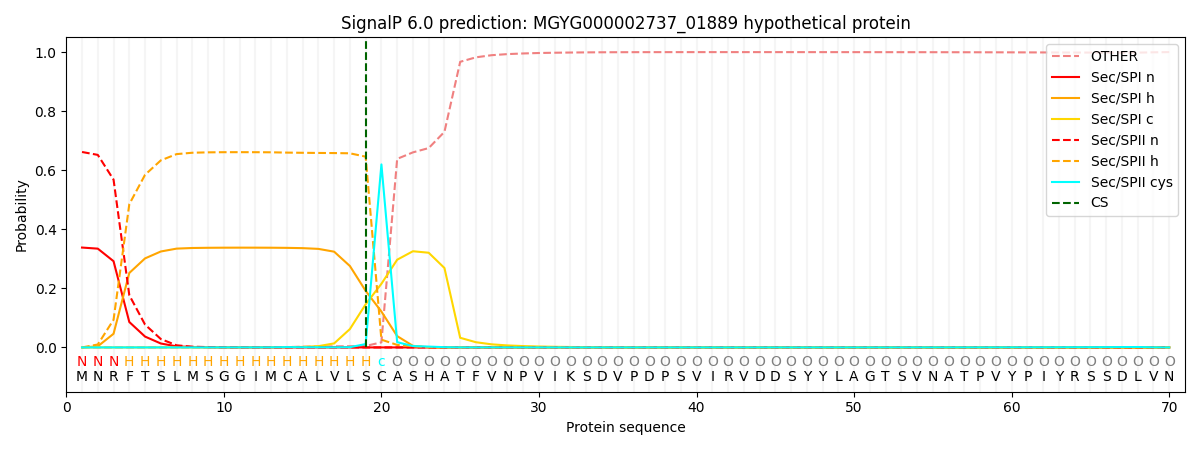
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000445 | 0.331253 | 0.667783 | 0.000178 | 0.000184 | 0.000149 |
