You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003087_01807
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003087_01807
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
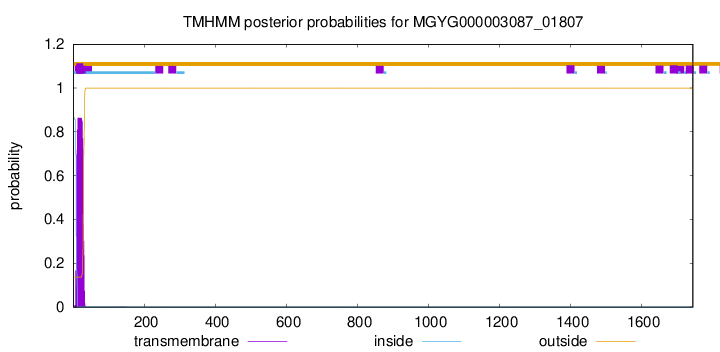
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Merdibacter sp900543035 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Erysipelotrichales; Erysipelotrichaceae; Merdibacter; Merdibacter sp900543035 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003087_01807 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM6 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 10698; End: 15935 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBM6 | 979 | 1094 | 4.9e-16 | 0.7681159420289855 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd04084 | CBM6_xylanase-like | 2.67e-18 | 973 | 1093 | 10 | 123 | Carbohydrate Binding Module 6 (CBM6); many are appended to glycoside hydrolase (GH) family 11 and GH43 xylanase domains. This family includes carbohydrate binding module 6 (CBM6) domains that are appended mainly to glycoside hydrolase (GH) family domains, including GH3, GH11, and GH43 domains. These CBM6s are non-catalytic carbohydrate binding domains that facilitate the strong binding of the GH catalytic modules with their dedicated, insoluble substrates. Examples of proteins having CMB6s belonging to this family are Microbispora bispora GghA, a 1,4-beta-D-glucan glucohydrolase (GH3); Clostridium thermocellum xylanase U (GH11), and Penicillium purpurogenum ABF3, a bifunctional alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase/xylobiohydrolase (GH43). GH3 comprises enzymes with activities including beta-glucosidase (hydrolyzes beta-galactosidase) and beta-xylosidase (hydrolyzes 1,4-beta-D-xylosidase). GH11 family comprises enzymes with xylanase (endo-1,4-beta-xylanase) activity which catalyze the hydrolysis of beta-1,4 bonds of xylan, the major component of hemicelluloses, to generate xylooligosaccharides and xylose. GH43 includes beta-xylosidases and beta-xylanases, using aryl-glycosides as substrates. CBM6 is an unusual CBM as it represents a chimera of two distinct binding sites with different modes of binding: binding site I within the loop regions and binding site II on the concave face of the beta-sandwich fold. |
| pfam03422 | CBM_6 | 2.81e-14 | 968 | 1094 | 4 | 124 | Carbohydrate binding module (family 6). |
| smart00606 | CBD_IV | 1.46e-11 | 970 | 1093 | 14 | 129 | Cellulose Binding Domain Type IV. |
| cd04080 | CBM6_cellulase-like | 1.25e-09 | 986 | 1094 | 47 | 144 | Carbohydrate Binding Module 6 (CBM6); appended to glycoside hydrolase (GH) domains, including GH5 (cellulase). This family includes carbohydrate binding module 6 (CBM6) domains that are appended to several glycoside hydrolase (GH) domains, including GH5 (cellulase) and GH16, as well as to coagulation factor 5/8 carbohydrate-binding domains. CBM6s are non-catalytic carbohydrate binding domains that facilitate the strong binding of the GH catalytic modules with their dedicated, insoluble substrates. The CBM6s are appended to GHs that display a diversity of substrate specificities. For some members of this family information is available about the specific substrates of the appended GH domains. It includes the CBM domains of various enzymes involved in cell wall degradation including, an extracellular beta-1,3-glucanase from Lysobacter enzymogenes encoded by the gluC gene (its catalytic domain belongs to the GH16 family), the tandem CBM domains of Pseudomonas sp. PE2 beta-1,3(4)-glucanase A (its catalytic domain also belongs to GH16), and a family 6 CBM from Cellvibrio mixtus Endoglucanase 5A (CmCBM6) which binds to the beta1,4-beta1,3-mixed linked glucans lichenan, and barley beta-glucan, cello-oligosaccharides, insoluble forms of cellulose, the beta1,3-glucan laminarin, and xylooligosaccharides, and the CBM6 of Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 XynD xylanase, appended to a GH10 domain, and Cellvibrio japonicas Cel5G appended to a GH5 (cellulase) domain. GH5 (cellulase) family includes enzymes with several known activities such as endoglucanase, beta-mannanase, and xylanase, which are involved in the degradation of cellulose and xylans. GH16 family includes enzymes with lichenase, xyloglucan endotransglycosylase (XET), and beta-agarase activities. CBM6 is an unusual CBM as it represents a chimera of two distinct binding sites with different modes of binding: binding site I within the loop regions and binding site II on the concave face of the beta-sandwich fold. For CmCBM6 it has been shown that these two binding sites have different ligand specificities. |
| cd02795 | CBM6-CBM35-CBM36_like | 7.94e-07 | 968 | 1093 | 6 | 124 | Carbohydrate Binding Module 6 (CBM6) and CBM35_like superfamily. Carbohydrate binding module family 6 (CBM6, family 6 CBM), also known as cellulose binding domain family VI (CBD VI), and related CBMs (CBM35 and CBM36). These are non-catalytic carbohydrate binding domains found in a range of enzymes that display activities against a diverse range of carbohydrate targets, including mannan, xylan, beta-glucans, cellulose, agarose, and arabinans. These domains facilitate the strong binding of the appended catalytic modules to their dedicated, insoluble substrates. Many of these CBMs are associated with glycoside hydrolase (GH) domains. CBM6 is an unusual CBM as it represents a chimera of two distinct binding sites with different modes of binding: binding site I within the loop regions and binding site II on the concave face of the beta-sandwich fold. CBM36s are calcium-dependent xylan binding domains. CBM35s display conserved specificity through extensive sequence similarity, but divergent function through their appended catalytic modules. This alignment model also contains the C-terminal domains of bacterial insecticidal toxins, where they may be involved in determining insect specificity through carbohydrate binding functionality. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBW21394.1 | 3.93e-219 | 6 | 953 | 2 | 1069 |
| AKA50869.1 | 3.93e-219 | 6 | 953 | 2 | 1069 |
| BAD47589.1 | 1.08e-218 | 6 | 953 | 2 | 1069 |
| ANQ59507.1 | 2.96e-218 | 6 | 953 | 2 | 1069 |
| CAH06509.1 | 5.79e-218 | 6 | 953 | 2 | 1069 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2V4V_A | 7.42e-09 | 973 | 1094 | 14 | 128 | CrystalStructure of a Family 6 Carbohydrate-Binding Module from Clostridium cellulolyticum in complex with xylose [Ruminiclostridium cellulolyticum] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
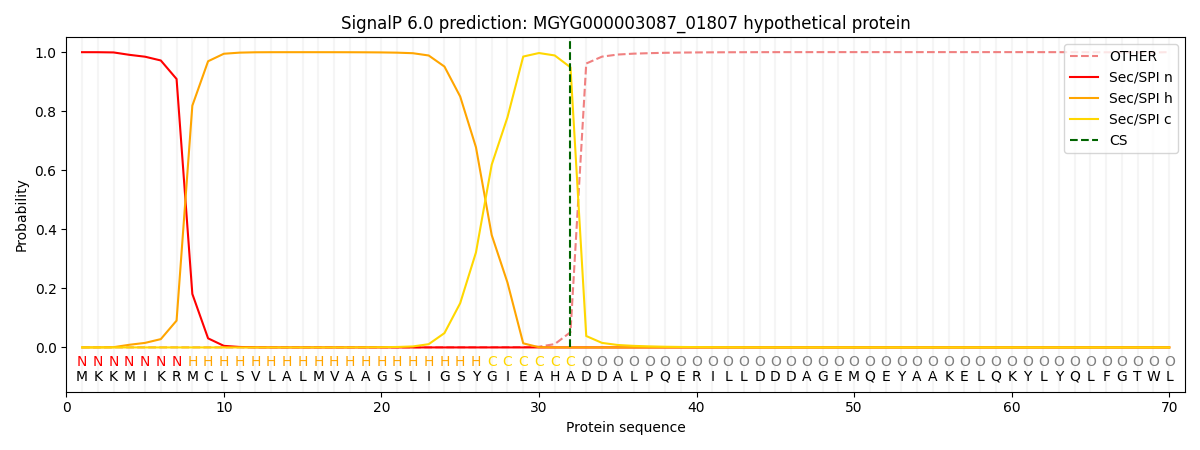
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.002875 | 0.995402 | 0.000364 | 0.000563 | 0.000399 | 0.000347 |