You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003137_04716
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003137_04716
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
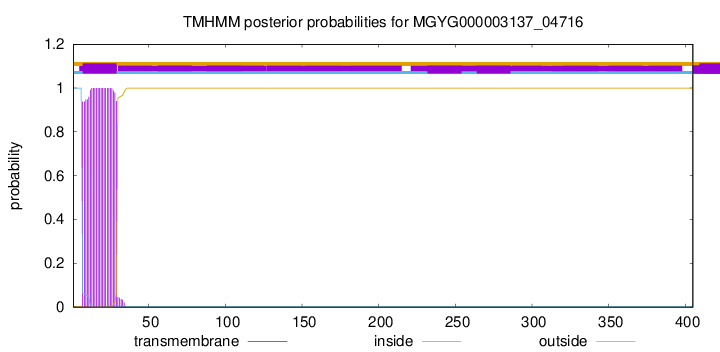
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Bradyrhizobium sp000015165 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Alphaproteobacteria; Rhizobiales; Xanthobacteraceae; Bradyrhizobium; Bradyrhizobium sp000015165 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003137_04716 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM50 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 77480; End: 78697 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRK11198 | PRK11198 | 3.86e-13 | 346 | 403 | 90 | 147 | LysM domain/BON superfamily protein; Provisional |
| cd00118 | LysM | 9.06e-09 | 352 | 398 | 1 | 42 | Lysin Motif is a small domain involved in binding peptidoglycan. LysM, a small globular domain with approximately 40 amino acids, is a widespread protein module involved in binding peptidoglycan in bacteria and chitin in eukaryotes. The domain was originally identified in enzymes that degrade bacterial cell walls, but proteins involved in many other biological functions also contain this domain. It has been reported that the LysM domain functions as a signal for specific plant-bacteria recognition in bacterial pathogenesis. Many of these enzymes are modular and are composed of catalytic units linked to one or several repeats of LysM domains. LysM domains are found in bacteria and eukaryotes. |
| COG1652 | XkdP | 1.58e-07 | 353 | 404 | 212 | 264 | Nucleoid-associated protein YgaU, contains BON and LysM domains [Function unknown]. |
| pfam01476 | LysM | 1.41e-06 | 354 | 402 | 1 | 43 | LysM domain. The LysM (lysin motif) domain is about 40 residues long. It is found in a variety of enzymes involved in bacterial cell wall degradation. This domain may have a general peptidoglycan binding function. The structure of this domain is known. |
| NF033163 | lipo_LipL71 | 3.40e-06 | 360 | 405 | 416 | 463 | lipoprotein LipL71. Members of this family are lipoprotein LipL71, also known as LruA, as described in Leptospira interrogans but found broadly in the genus Leptospira. Close homologs that are not lipoproteins by sequence are likely defective in their reported coding region. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABQ36024.1 | 7.06e-272 | 1 | 405 | 1 | 405 |
| SMX58743.1 | 7.40e-175 | 1 | 404 | 1 | 409 |
| BAM89674.1 | 2.05e-140 | 72 | 405 | 70 | 400 |
| SMX58749.1 | 1.42e-135 | 77 | 405 | 87 | 410 |
| SHI17277.1 | 7.80e-112 | 17 | 404 | 14 | 389 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5FIM_A | 2.63e-07 | 355 | 404 | 100 | 149 | Thestructure of Kbp.K from E. coli [Escherichia coli],7PVC_A Chain A, Potassium binding protein Kbp [Escherichia coli K-12] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0ADE6 | 1.25e-06 | 355 | 404 | 100 | 149 | Potassium binding protein Kbp OS=Escherichia coli (strain K12) OX=83333 GN=kbp PE=1 SV=2 |
| P0ADE7 | 1.25e-06 | 355 | 404 | 100 | 149 | Potassium binding protein Kbp OS=Escherichia coli O6:H1 (strain CFT073 / ATCC 700928 / UPEC) OX=199310 GN=kbp PE=3 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.999990 | 0.000032 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000001 |