You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003327_02100
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003327_02100
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
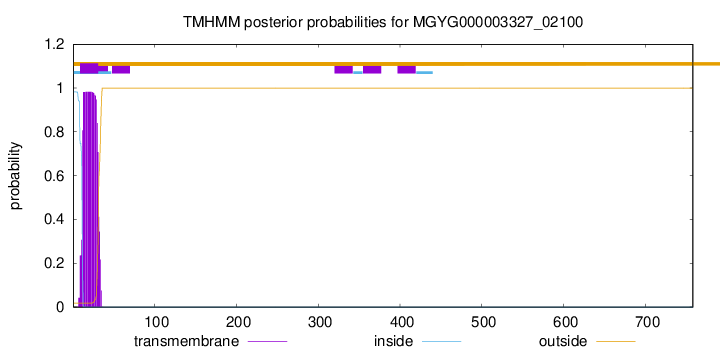
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Lawsonibacter sp900764755 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes_A; Clostridia; Oscillospirales; Oscillospiraceae; Lawsonibacter; Lawsonibacter sp900764755 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003327_02100 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM50 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 32983; End: 35259 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd06242 | M14-like | 8.22e-73 | 252 | 459 | 1 | 220 | Peptidase M14-like domain; uncharacterized subgroup. Peptidase M14-like domain of a functionally uncharacterized subgroup of the M14 family of metallocarboxypeptidases (MCPs). The M14 family are zinc-binding carboxypeptidases (CPs) which hydrolyze single, C-terminal amino acids from polypeptide chains, and have a recognition site for the free C-terminal carboxyl group, which is a key determinant of specificity. Two major subfamilies of the M14 family, defined based on sequence and structural homology, are the A/B and N/E subfamilies. Enzymes belonging to the A/B subfamily are normally synthesized as inactive precursors containing preceding signal peptide, followed by an N-terminal pro-region linked to the enzyme; these proenzymes are called procarboxypeptidases. The A/B enzymes can be further divided based on their substrate specificity; Carboxypeptidase A-like (CPA-like) enzymes favor hydrophobic residues while carboxypeptidase B-like (CPB-like) enzymes only cleave the basic residues lysine or arginine. The A forms have slightly different specificities, with Carboxypeptidase A1 (CPA1) preferring aliphatic and small aromatic residues, and CPA2 preferring the bulky aromatic side chains. Enzymes belonging to the N/E subfamily enzymes are not produced as inactive precursors and instead rely on their substrate specificity and subcellular compartmentalization to prevent inappropriate cleavages. They contain an extra C-terminal transthyretin-like domain, thought to be involved in folding or formation of oligomers. MCPs can also be classified based on their involvement in specific physiological processes; the pancreatic MCPs participate only in alimentary digestion and include carboxypeptidase A and B (A/B subfamily), while others, namely regulatory MCPs or the N/E subfamily, are involved in more selective reactions, mainly in non-digestive tissues and fluids, acting on blood coagulation/fibrinolysis, inflammation and local anaphylaxis, pro-hormone and neuropeptide processing, cellular response and others. Another MCP subfamily, is that of succinylglutamate desuccinylase /aspartoacylase, which hydrolyzes N-acetyl-L-aspartate (NAA), and deficiency in which is the established cause of Canavan disease. Another subfamily (referred to as subfamily C) includes an exceptional type of activity in the MCP family, that of dipeptidyl-peptidase activity of gamma-glutamyl-(L)-meso-diaminopimelate peptidase I which is involved in bacterial cell wall metabolism. |
| cd03857 | M14-like | 1.34e-29 | 254 | 446 | 1 | 202 | Peptidase M14-like domain; uncharacterized subfamily. Peptidase M14-like domain of a functionally uncharacterized subgroup of the M14 family of metallocarboxypeptidases (MCPs). The M14 family are zinc-binding carboxypeptidases (CPs) which hydrolyze single, C-terminal amino acids from polypeptide chains, and have a recognition site for the free C-terminal carboxyl group, which is a key determinant of specificity. Two major subfamilies of the M14 family, defined based on sequence and structural homology, are the A/B and N/E subfamilies. Enzymes belonging to the A/B subfamily are normally synthesized as inactive precursors containing preceding signal peptide, followed by an N-terminal pro-region linked to the enzyme; these proenzymes are called procarboxypeptidases. The A/B enzymes can be further divided based on their substrate specificity; Carboxypeptidase A-like (CPA-like) enzymes favor hydrophobic residues while carboxypeptidase B-like (CPB-like) enzymes only cleave the basic residues lysine or arginine. The A forms have slightly different specificities, with Carboxypeptidase A1 (CPA1) preferring aliphatic and small aromatic residues, and CPA2 preferring the bulky aromatic side chains. Enzymes belonging to the N/E subfamily enzymes are not produced as inactive precursors and instead rely on their substrate specificity and subcellular compartmentalization to prevent inappropriate cleavage. They contain an extra C-terminal transthyretin-like domain, thought to be involved in folding or formation of oligomers. MCPs can also be classified based on their involvement in specific physiological processes; the pancreatic MCPs participate only in alimentary digestion and include carboxypeptidase A and B (A/B subfamily), while others, namely regulatory MCPs or the N/E subfamily, are involved in more selective reactions, mainly in non-digestive tissues and fluids, acting on blood coagulation/fibrinolysis, inflammation and local anaphylaxis, pro-hormone and neuropeptide processing, cellular response and others. Another MCP subfamily, is that of succinylglutamate desuccinylase /aspartoacylase, which hydrolyzes N-acetyl-L-aspartate (NAA), and deficiency in which is the established cause of Canavan disease. Another subfamily (referred to as subfamily C) includes an exceptional type of activity in the MCP family, that of dipeptidyl-peptidase activity of gamma-glutamyl-(L)-meso-diaminopimelate peptidase I which is involved in bacterial cell wall metabolism. |
| PRK11198 | PRK11198 | 2.41e-13 | 696 | 757 | 86 | 147 | LysM domain/BON superfamily protein; Provisional |
| cd00118 | LysM | 4.58e-13 | 707 | 755 | 2 | 45 | Lysin Motif is a small domain involved in binding peptidoglycan. LysM, a small globular domain with approximately 40 amino acids, is a widespread protein module involved in binding peptidoglycan in bacteria and chitin in eukaryotes. The domain was originally identified in enzymes that degrade bacterial cell walls, but proteins involved in many other biological functions also contain this domain. It has been reported that the LysM domain functions as a signal for specific plant-bacteria recognition in bacterial pathogenesis. Many of these enzymes are modular and are composed of catalytic units linked to one or several repeats of LysM domains. LysM domains are found in bacteria and eukaryotes. |
| cd00596 | Peptidase_M14_like | 2.35e-12 | 255 | 440 | 1 | 202 | M14 family of metallocarboxypeptidases and related proteins. The M14 family of metallocarboxypeptidases (MCPs), also known as funnelins, are zinc-binding carboxypeptidases (CPs) which hydrolyze single, C-terminal amino acids from polypeptide chains, and have a recognition site for the free C-terminal carboxyl group, which is a key determinant of specificity. Two major subfamilies of the M14 family, defined based on sequence and structural homology, are the A/B and N/E subfamilies. Enzymes belonging to the A/B subfamily are normally synthesized as inactive precursors containing preceding signal peptide, followed by an N-terminal pro-region linked to the enzyme; these proenzymes are called procarboxypeptidases. The A/B enzymes can be further divided based on their substrate specificity; Carboxypeptidase A-like (CPA-like) enzymes favor hydrophobic residues while carboxypeptidase B-like (CPB-like) enzymes only cleave the basic residues lysine or arginine. The A forms have slightly different specificities, with Carboxypeptidase A1 (CPA1) preferring aliphatic and small aromatic residues, and CPA2 preferring the bulky aromatic side chains. Enzymes belonging to the N/E subfamily enzymes are not produced as inactive precursors and instead rely on their substrate specificity and subcellular compartmentalization to prevent inappropriate cleavage. They contain an extra C-terminal transthyretin-like domain, thought to be involved in folding or formation of oligomers. MCPs can also be classified based on their involvement in specific physiological processes; the pancreatic MCPs participate only in alimentary digestion and include carboxypeptidase A and B (A/B subfamily), while others, namely regulatory MCPs or the N/E subfamily, are involved in more selective reactions, mainly in non-digestive tissues and fluids, acting on blood coagulation/fibrinolysis, inflammation and local anaphylaxis, pro-hormone and neuropeptide processing, cellular response and others. Another MCP subfamily, is that of succinylglutamate desuccinylase /aspartoacylase, which hydrolyzes N-acetyl-L-aspartate (NAA), and deficiency in which is the established cause of Canavan disease. Another subfamily (referred to as subfamily C) includes an exceptional type of activity in the MCP family, that of dipeptidyl-peptidase activity of gamma-glutamyl-(L)-meso-diaminopimelate peptidase I which is involved in bacterial cell wall metabolism. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QQL05891.1 | 1.34e-13 | 707 | 758 | 43 | 94 |
| BAL01252.1 | 1.67e-13 | 706 | 758 | 623 | 675 |
| QEY33737.1 | 4.45e-10 | 705 | 756 | 168 | 219 |
| BCQ23212.1 | 6.82e-10 | 708 | 758 | 111 | 161 |
| ALP92894.1 | 7.47e-10 | 705 | 756 | 162 | 214 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B6V866 | 8.69e-28 | 196 | 661 | 92 | 538 | Carboxypeptidase 2 OS=Trichophyton tonsurans OX=34387 GN=MCPB PE=3 SV=1 |
| B8XGR2 | 1.16e-27 | 196 | 659 | 92 | 536 | Carboxypeptidase 2 OS=Trichophyton equinum OX=63418 GN=MCPB PE=3 SV=1 |
| A6XHF7 | 3.73e-26 | 252 | 659 | 126 | 536 | Carboxypeptidase 2 OS=Trichophyton rubrum OX=5551 GN=MCPB PE=2 SV=1 |
| C5FYJ7 | 2.82e-25 | 239 | 659 | 118 | 537 | Carboxypeptidase 2 OS=Arthroderma otae (strain ATCC MYA-4605 / CBS 113480) OX=554155 GN=MCPB PE=3 SV=1 |
| D4D4Z1 | 7.62e-25 | 252 | 610 | 126 | 470 | Probable carboxypeptidase 2 OS=Trichophyton verrucosum (strain HKI 0517) OX=663202 GN=MCPB PE=3 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000484 | 0.998655 | 0.000221 | 0.000246 | 0.000187 | 0.000160 |