You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003424_00525
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003424_00525
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | SFTJ01 sp004557385 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Muribaculaceae; SFTJ01; SFTJ01 sp004557385 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003424_00525 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH117 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 9979; End: 12504 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH117 | 601 | 718 | 7.9e-18 | 0.4834123222748815 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd16144 | ARS_like | 4.14e-179 | 32 | 490 | 1 | 421 | uncharacterized arylsulfatase subfamily. Sulfatases catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters from wide range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. The biological roles of sulfatase includes the cycling of sulfur in the environment, in the degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids in the lysosome, and in remodeling sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular space. The sulfatases are essential for human metabolism. At least eight human monogenic diseases are caused by the deficiency of individual sulfatases. |
| cd08994 | GH43_62_32_68_117_130-like | 4.29e-101 | 529 | 825 | 1 | 294 | Glycosyl hydrolase families: GH43, GH62, GH32, GH68, GH117, CH130. Members of the glycosyl hydrolase families 32, 43, 62, 68, 117 and 130 (GH32, GH43, GH62, GH68, GH117, GH130) all possess 5-bladed beta-propeller domains and comprise clans F and J, as classified by the carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY). Clan F consists of families GH43 and GH62. GH43 includes beta-xylosidases (EC 3.2.1.37), beta-xylanases (EC 3.2.1.8), alpha-L-arabinases (EC 3.2.1.99), and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidases (EC 3.2.1.55), using aryl-glycosides as substrates, while family GH62 contains alpha-L-arabinofuranosidases (EC 3.2.1.55) that specifically cleave either alpha-1,2 or alpha-1,3-L-arabinofuranose sidechains from xylans. These are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Clan J consists of families GH32 and GH68. GH32 comprises sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolases, invertases (EC 3.2.1.26), inulinases (EC 3.2.1.7), levanases (EC 3.2.1.65), eukaryotic fructosyltransferases, and bacterial fructanotransferases while GH68 consists of frucosyltransferases (FTFs) that include levansucrase (EC 2.4.1.10); beta-fructofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.26); inulosucrase (EC 2.4.1.9), while GH68 consists of frucosyltransferases (FTFs) that include levansucrase (EC 2.4.1.10); beta-fructofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.26); inulosucrase (EC 2.4.1.9), all of which use sucrose as their preferential donor substrate. Members of this clan are retaining enzymes (i.e. they retain the configuration at anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that catalyze hydrolysis in two steps involving a covalent glycosyl enzyme intermediate: an aspartate located close to the N-terminus acts as the catalytic nucleophile and a glutamate acts as the general acid/base; a conserved aspartate residue in the Arg-Asp-Pro (RDP) motif stabilizes the transition state. Structures of all families in the two clans manifest a funnel-shaped active site that comprises two subsites with a single route for access by ligands. Also included in this superfamily are GH117 enzymes that have exo-alpha-1,3-(3,6-anhydro)-l-galactosidase activity, removing terminal non-reducing alpha-1,3-linked 3,6-anhydro-l-galactose residues from their neoagarose substrate, and GH130 that are phosphorylases and hydrolases for beta-mannosides, involved in the bacterial utilization of mannans or N-linked glycans. |
| cd16146 | ARS_like | 8.27e-99 | 32 | 494 | 1 | 408 | uncharacterized arylsulfatase. Sulfatases catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters from wide range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. The biological roles of sulfatase includes the cycling of sulfur in the environment, in the degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids in the lysosome, and in remodeling sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular space. The sulfatases are essential for human metabolism. At least eight human monogenic diseases are caused by the deficiency of individual sulfatases. |
| cd16145 | ARS_like | 4.57e-87 | 32 | 477 | 1 | 415 | uncharacterized arylsulfatase subfamily. Sulfatases catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters from wide range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. The biological roles of sulfatase includes the cycling of sulfur in the environment, in the degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids in the lysosome, and in remodeling sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular space. The sulfatases are essential for human metabolism. At least eight human monogenic diseases are caused by the deficiency of individual sulfatases. |
| cd16026 | GALNS_like | 6.24e-85 | 32 | 473 | 2 | 399 | galactosamine-6-sulfatase; also known as N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase (GALNS). Lysosomal galactosamine-6-sulfatase removes sulfate groups from a terminal N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate (or galactose-6-sulfate) in mucopolysaccharides such as keratan sulfate and chondroitin-6-sulfate. Defects in GALNS lead to accumulation of substrates, resulting in the development of the lysosomal storage disease mucopolysaccharidosis IV A. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EAR02039.1 | 5.84e-222 | 29 | 628 | 26 | 626 |
| QUT89376.1 | 4.22e-178 | 16 | 512 | 7 | 498 |
| ALJ59588.1 | 4.69e-177 | 26 | 512 | 18 | 498 |
| QRO24268.1 | 6.94e-138 | 516 | 813 | 70 | 369 |
| AKP49980.1 | 4.92e-115 | 515 | 841 | 23 | 351 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6USS_A | 6.67e-235 | 13 | 514 | 15 | 517 | ChainA, Sulfatase [Bacteroides fragilis CAG:558],6USS_B Chain B, Sulfatase [Bacteroides fragilis CAG:558] |
| 6UST_A | 7.79e-69 | 32 | 499 | 5 | 461 | ChainA, N-acetylgalactosamine 6-sulfate sulfatase [Hungatella hathewayi],6UST_B Chain B, N-acetylgalactosamine 6-sulfate sulfatase [Hungatella hathewayi],6UST_C Chain C, N-acetylgalactosamine 6-sulfate sulfatase [Hungatella hathewayi],6UST_D Chain D, N-acetylgalactosamine 6-sulfate sulfatase [Hungatella hathewayi] |
| 7STT_A | 2.61e-58 | 32 | 499 | 7 | 441 | ChainA, N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase [Pedobacter yulinensis],7STU_A Chain A, N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase [Pedobacter yulinensis],7STV_A Chain A, N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase [Pedobacter yulinensis] |
| 7ANA_AAA | 1.75e-48 | 25 | 479 | 22 | 486 | ChainAAA, N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482],7ANA_BBB Chain BBB, N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482],7ANB_AAA Chain AAA, N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482],7ANB_BBB Chain BBB, N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482] |
| 6PSM_A | 4.33e-46 | 32 | 478 | 25 | 424 | Crystalstructure of PsS1_19B C77S in complex with kappa-neocarrabiose [Pseudoalteromonas fuliginea],6PSM_B Crystal structure of PsS1_19B C77S in complex with kappa-neocarrabiose [Pseudoalteromonas fuliginea],6PSM_C Crystal structure of PsS1_19B C77S in complex with kappa-neocarrabiose [Pseudoalteromonas fuliginea],6PSM_D Crystal structure of PsS1_19B C77S in complex with kappa-neocarrabiose [Pseudoalteromonas fuliginea],6PSM_E Crystal structure of PsS1_19B C77S in complex with kappa-neocarrabiose [Pseudoalteromonas fuliginea],6PSM_F Crystal structure of PsS1_19B C77S in complex with kappa-neocarrabiose [Pseudoalteromonas fuliginea],6PSO_A Crystal structure of PsS1_19B C77S in complex with iota-neocarratetraose [Pseudoalteromonas fuliginea],6PSO_B Crystal structure of PsS1_19B C77S in complex with iota-neocarratetraose [Pseudoalteromonas fuliginea] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2KPJ9 | 2.01e-48 | 17 | 511 | 16 | 543 | Sulfatase OS=Formosa agariphila (strain DSM 15362 / KCTC 12365 / LMG 23005 / KMM 3901 / M-2Alg 35-1) OX=1347342 GN=BN863_22020 PE=3 SV=1 |
| P77318 | 1.12e-34 | 24 | 493 | 50 | 536 | Uncharacterized sulfatase YdeN OS=Escherichia coli (strain K12) OX=83333 GN=ydeN PE=3 SV=2 |
| P34059 | 2.29e-34 | 25 | 485 | 24 | 467 | N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=GALNS PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q571E4 | 5.42e-34 | 17 | 422 | 14 | 382 | N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase OS=Mus musculus OX=10090 GN=Galns PE=1 SV=2 |
| Q32KJ6 | 3.34e-33 | 17 | 469 | 18 | 453 | N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase OS=Rattus norvegicus OX=10116 GN=Galns PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
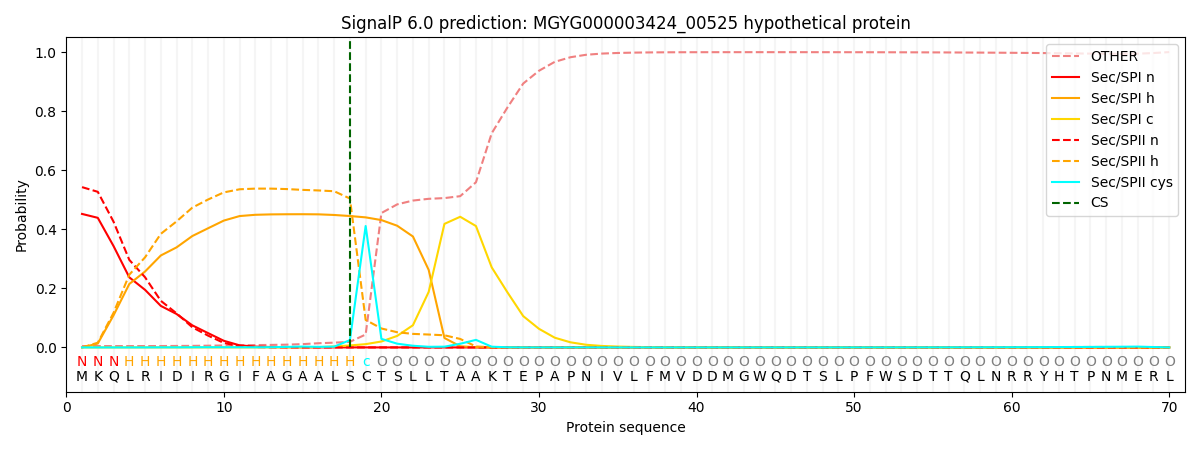
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.007670 | 0.435524 | 0.554579 | 0.001001 | 0.000724 | 0.000480 |
