You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003445_01439
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003445_01439
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | RC9 sp900767375 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; UBA932; RC9; RC9 sp900767375 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003445_01439 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH43 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 7393; End: 10206 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH43 | 24 | 361 | 3.3e-109 | 0.9965986394557823 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd18620 | GH43_XylA-like | 2.34e-70 | 34 | 364 | 1 | 269 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43-like protein such as Clostridium stercorarium alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase XylA. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup belongs to the GH43_AXH-like subgroup which includes enzymes that have been characterized with beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37), alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55), alpha-1,2-L-arabinofuranosidase 43A (arabinan-specific; EC 3.2.1.-), endo-alpha-L-arabinanase as well as arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (AXH) activities. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. The GH43_XylA-like subgroup includes Clostridium stercorarium alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase XylA, and enzymes that have been annotated as having beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37), alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55), endo-alpha-L-arabinanase (EC 3.2.1.-) as well as arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (AXH) activities. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. AXHs specifically hydrolyze the glycosidic bond between arabinofuranosyl substituents and xylopyranosyl backbone residues of arabinoxylan. |
| cd07712 | MBLAC2-like_MBL-fold | 4.56e-42 | 708 | 867 | 10 | 182 | uncharacterized human metallo-beta-lactamase domain-containing protein 2 and related proteins; MBL-fold metallo hydrolase domain. Includes the MBL-fold metallo hydrolase domain of uncharacterized human MBLAC2 and related proteins. Members of this subgroup belong to the MBL-fold metallo-hydrolase superfamily which is comprised mainly of hydrolytic enzymes which carry out a variety of biological functions. |
| cd08990 | GH43_AXH_like | 2.14e-29 | 35 | 364 | 2 | 264 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein, includes arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase, beta-xylosidase, endo-1,4-beta-xylanase, and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase. This subgroup includes Bacillus subtilis arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (XynD;BsAXH-m23;BSU18160), Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (Xsa43E;bpr_I2319), Clostridium stercorarium alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase XylA, and metagenomic beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37) / alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55) CoXyl43. It belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) which includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62) families. The GH43_AXH-like subgroup includes enzymes that have been characterized with beta-xylosidase, alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase, endo-alpha-L-arabinanase as well as arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (AXH) activities. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. AXHs specifically hydrolyze the glycosidic bond between arabinofuranosyl substituents and xylopyranosyl backbone residues of arabinoxylan. Metagenomic beta-xylosidase/alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase CoXyl43 shows synergy with Trichoderma reesei cellulases and promotes plant biomass saccharification by degrading xylo-oligosaccharides, such as xylobiose and xylotriose, into the monosaccharide xylose. Studies show that the hydrolytic activity of CoXyl43 is stimulated in the presence of calcium. Several of these enzymes also contain carbohydrate binding modules (CBMs) that bind cellulose or xylan. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd06262 | metallo-hydrolase-like_MBL-fold | 1.32e-25 | 710 | 867 | 13 | 188 | mainly hydrolytic enzymes and related proteins which carry out various biological functions; MBL-fold metallohydrolase domain. Members of the MBL-fold metallohydrolase superfamily are mainly hydrolytic enzymes which carry out a variety of biological functions. The class B metal beta-lactamases (MBLs) for which this fold was named perform only a small fraction of the activities included in this superfamily. Activities carried out by superfamily members include class B beta-lactamases which can catalyze the hydrolysis of a wide range of beta-lactam antibiotics, hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolases (also called glyoxalase II) which hydrolyze S-d-lactoylglutathione to d-lactate in the second step of the glycoxlase system, AHL lactonases which catalyze the hydrolysis and opening of the homoserine lactone rings of acyl homoserine lactones (AHLs), persulfide dioxygenase which catalyze the oxidation of glutathione persulfide to glutathione and persulfite in the mitochondria, flavodiiron proteins which catalyze the reduction of oxygen and/or nitric oxide to water or nitrous oxide respectively, cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factors such as the Int9 and Int11 subunits of Integrator, Sdsa1-like and AtsA-like arylsulfatases, 5'-exonucleases human SNM1A and yeast Pso2p, ribonuclease J which has both 5'-3' exoribonucleolytic and endonucleolytic activity and ribonuclease Z which catalyzes the endonucleolytic removal of the 3' extension of the majority of tRNA precursors, cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases which decompose cyclic adenosine and guanosine 3', 5'-monophosphate (cAMP and cGMP) respectively, insecticide hydrolases, and proteins required for natural transformation competence. The diversity of biological roles is reflected in variations in the active site metallo-chemistry, for example classical members of the superfamily are di-, or less commonly mono-, zinc-ion-dependent hydrolases, human persulfide dioxygenase ETHE1 is a mono-iron binding member of the superfamily; Arabidopsis thaliana hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolases incorporates iron, manganese, and zinc in its dinuclear metal binding site, and flavodiiron proteins contains a diiron site. |
| smart00849 | Lactamase_B | 3.59e-25 | 710 | 867 | 3 | 177 | Metallo-beta-lactamase superfamily. Apart from the beta-lactamases a number of other proteins contain this domain. These proteins include thiolesterases, members of the glyoxalase II family, that catalyse the hydrolysis of S-D-lactoyl-glutathione to form glutathione and D-lactic acid and a competence protein that is essential for natural transformation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae and could be a transporter involved in DNA uptake. Except for the competence protein these proteins bind two zinc ions per molecule as cofactor. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QNL41333.1 | 0.0 | 24 | 667 | 36 | 681 |
| QCD37057.1 | 0.0 | 24 | 667 | 30 | 675 |
| QRQ49698.1 | 3.51e-316 | 24 | 674 | 41 | 692 |
| QUT44391.1 | 1.22e-315 | 24 | 674 | 56 | 707 |
| ALJ60075.1 | 1.53e-315 | 24 | 667 | 42 | 688 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4NOV_A | 2.11e-13 | 35 | 365 | 56 | 328 | Xsa43E,a GH43 family enzyme from Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus [Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus B316] |
| 4AD9_A | 4.54e-06 | 710 | 867 | 35 | 200 | Crystalstructure of human LACTB2. [Homo sapiens],4AD9_B Crystal structure of human LACTB2. [Homo sapiens],4AD9_C Crystal structure of human LACTB2. [Homo sapiens],4AD9_D Crystal structure of human LACTB2. [Homo sapiens],4AD9_E Crystal structure of human LACTB2. [Homo sapiens],4AD9_F Crystal structure of human LACTB2. [Homo sapiens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P48790 | 4.23e-31 | 24 | 469 | 7 | 404 | Xylosidase/arabinosidase OS=Thermoclostridium stercorarium OX=1510 GN=xylA PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q5F336 | 3.33e-11 | 699 | 879 | 13 | 240 | Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase MBLAC2 OS=Gallus gallus OX=9031 GN=MBLAC2 PE=2 SV=1 |
| Q68D91 | 2.11e-09 | 699 | 879 | 13 | 243 | Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase MBLAC2 OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=MBLAC2 PE=1 SV=3 |
| Q8BL86 | 2.11e-09 | 719 | 879 | 62 | 243 | Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase MBLAC2 OS=Mus musculus OX=10090 GN=Mblac2 PE=1 SV=2 |
| A5PJT0 | 3.80e-09 | 699 | 879 | 13 | 243 | Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase MBLAC2 OS=Bos taurus OX=9913 GN=MBLAC2 PE=2 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
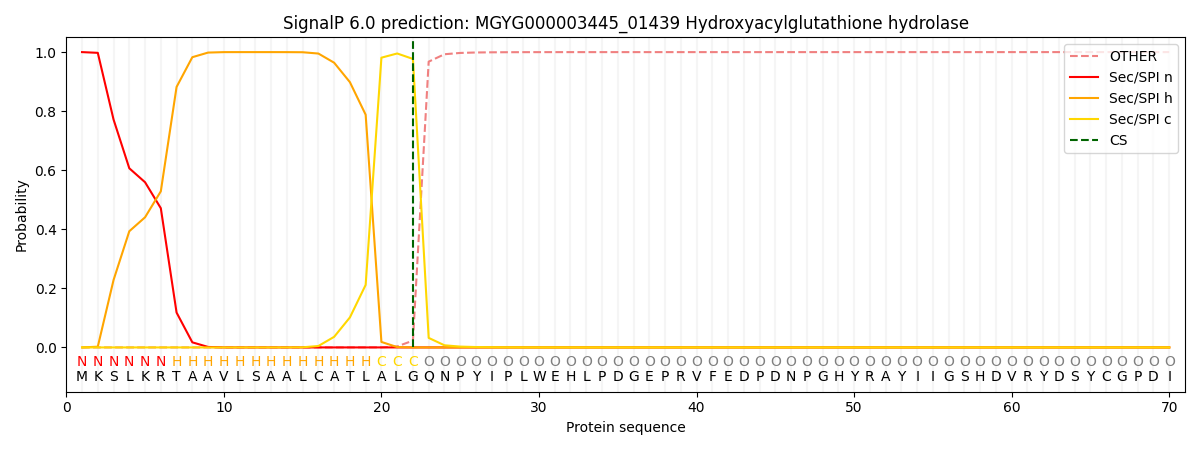
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000290 | 0.998986 | 0.000224 | 0.000168 | 0.000153 | 0.000142 |
