You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003489_01508
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003489_01508
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Prevotellamassilia sp900768625 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; Prevotellamassilia; Prevotellamassilia sp900768625 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003489_01508 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH85 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 4562; End: 7606 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH85 | 126 | 432 | 3e-42 | 0.946031746031746 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COG4724 | COG4724 | 6.56e-31 | 126 | 599 | 98 | 552 | Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase D [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| cd06547 | GH85_ENGase | 8.61e-26 | 117 | 463 | 5 | 339 | Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase (ENGase) hydrolyzes the N-N'-diacetylchitobiosyl core of N-glycosylproteins. The beta-1,4-glycosyl bond located between two N-acetylglucosamine residues is hydrolyzed such that N-acetylglucosamine 1 remains with the protein and N-acetylglucosamine 2 forms the reducing end of the released glycan. ENGase is a key enzyme in the processing of free oligosaccharides in the cytosol of eukaryotes. Oligosaccharides formed in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum are transported into the cytosol where they are catabolized by cytosolic ENGases and other enzymes, possibly to maximize the reutilization of the component sugars. ENGases have an eight-stranded alpha/beta barrel topology and are classified as a family 85 glycosyl hydrolase (GH85) domain. The GH85 ENGases are sequence-similar to the family 18 glycosyl hydrolases, also known as GH18 chitinases. An ENGase-like protein is also found in bacteria and is included in this alignment model. |
| pfam03644 | Glyco_hydro_85 | 2.65e-12 | 126 | 429 | 4 | 291 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 85. Family of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases. These enzymes work on a broad spectrum of substrates. |
| TIGR04183 | Por_Secre_tail | 2.35e-04 | 970 | 1014 | 25 | 72 | Por secretion system C-terminal sorting domain. Species that include Porphyromonas gingivalis, Fibrobacter succinogenes, Flavobacterium johnsoniae, Cytophaga hutchinsonii, Gramella forsetii, Prevotella intermedia, and Salinibacter ruber average twenty or more copies of a C-terminal domain, represented by this model, associated with sorting to the outer membrane and covalent modification. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCI64641.1 | 0.0 | 2 | 1012 | 3 | 1005 |
| AGB28382.1 | 0.0 | 19 | 1014 | 189 | 1190 |
| QUT74553.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 1011 | 1 | 1017 |
| QUB47476.1 | 0.0 | 2 | 1014 | 3 | 1006 |
| EFC71166.1 | 0.0 | 2 | 1014 | 3 | 1006 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
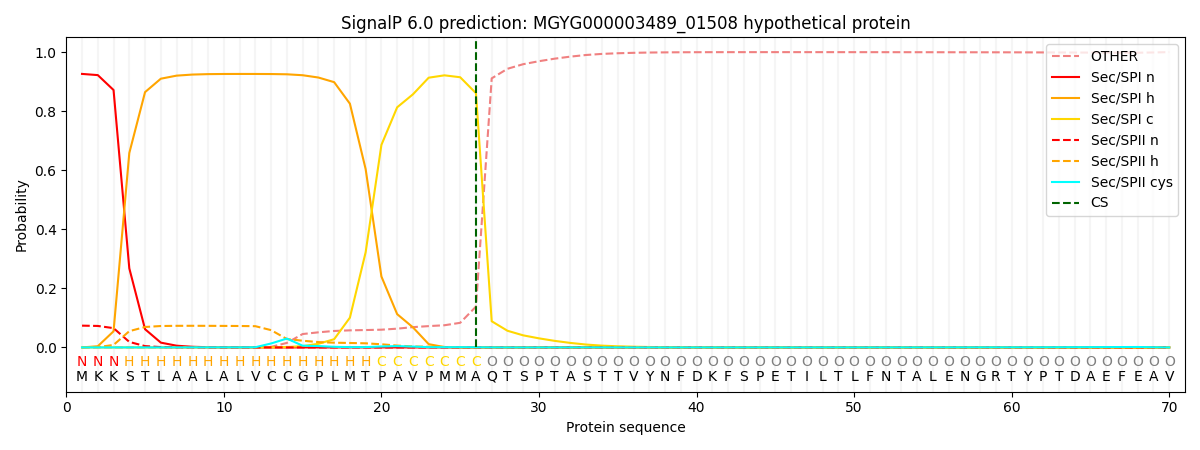
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000863 | 0.915319 | 0.082729 | 0.000466 | 0.000318 | 0.000260 |
